Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Repeated Low High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Nationwide Population- Based Study in Korea
- Jinyoung Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):303-311. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1332

- 4,627 View
- 153 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) plays an important role in the reverse cholesterol transport pathway and prevents atherosclerosis-mediated disease. It has also been suggested that HDL-C may be a protective factor against cancer. However, an inverse correlation between HDL-C and cancer has not been established, and few studies have explored thyroid cancer.
Methods
The study participants received health checkups provided by the Korean National Health Insurance Service from 2009 to 2013 and were followed until 2019. Considering the variability of serum HDL-C level, low HDL-C level was analyzed by grouping based on four consecutive health checkups. The data analysis was performed using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models.
Results
A total of 3,134,278 total study participants, thyroid cancer occurred in 16,129. In the crude model, the hazard ratios for the association between repeatedly measured low HDL-C levels and thyroid cancer were 1.243, 1.404, 1.486, and 1.680 (P for trend <0.01), respectively, which were significant even after adjusting for age, sex, lifestyle factors, and metabolic diseases. The subgroup analysis revealed that low HDL-C levels likely had a greater impact on the group of patients with central obesity (P for interaction= 0.062), high blood pressure (P for interaction=0.057), impaired fasting glucose (P for interaction=0.051), and hyperlipidemia (P for interaction=0.126).
Conclusion
Repeatedly measured low HDL-C levels can be considered a risk factor for cancer as well as vascular disease. Low HDL-C levels were associated with the risk of thyroid cancer, and this correlation was stronger in a metabolically unhealthy population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between total cholesterol levels and all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed patients with cancer
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between organophosphate flame retardant exposure and lipid metabolism: data from the 2013–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Fu-Jen Cheng, Kai-Fan Tsai, Kuo-Chen Huang, Chia-Te Kung, Wan-Ting Huang, Huey-Ling You, Shau-Hsuan Li, Chin-Chou Wang, Wen-Chin Lee, Hsiu-Yung Pan
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low serum total cholesterol levels predict inferior prognosis of patients with POEMS syndrome
Jue Zhang, Ting Zhang, Ye Yao, Xuxing Shen, Yuanyuan Jin, Run Zhang, Lijuan Chen
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipoprotein alterations in endocrine disorders - a review of the recent developments in the field
Michal Olejarz, Ewelina Szczepanek-Parulska, Marek Ruchala
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Carbohydrate, Lipid, and Apolipoprotein Biomarkers in Blood and Risk of Thyroid Cancer: Findings from the AMORIS Cohort
Xue Xiao, Yi Huang, Fetemeh Sadeghi, Maria Feychting, Niklas Hammar, Fang Fang, Zhe Zhang, Qianwei Liu
Cancers.2023; 15(2): 520. CrossRef - Altered serum lipid levels are associated with prognosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma and influenced by utility of rituximab
Fei Wang, Luo Lu, HuiJuan Chen, Yanhua Yue, Yanting Sun, Feng Yan, Bai He, Rongrong Lin, Weiying Gu
Annals of Hematology.2023; 102(2): 393. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and carcinogenesis
Meijuan Tan, Shijie Yang, Xiequn Xu
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 34(5): 303. CrossRef - Low Serum Cholesterol Level Is a Significant Prognostic Factor That Improves CLL-IPI in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
Rui Gao, Kaixin Du, Jinhua Liang, Yi Xia, Jiazhu Wu, Yue Li, Bihui Pan, Li Wang, Jianyong Li, Wei Xu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(8): 7396. CrossRef - Do metabolic factors increase the risk of thyroid cancer? a Mendelian randomization study
Weiwei Liang, FangFang Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of causal association between differentiated thyroid cancer and disordered serum lipid profile: a Mendelian randomization study
Qiang Ma, Yu Li, Lijuan An, Liang Guo, Xiaokang Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors and diagnostic prediction models for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xiaowen Zhang, Yuyang Ze, Jianfeng Sang, Xianbiao Shi, Yan Bi, Shanmei Shen, Xinlin Zhang, Dalong Zhu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exposure to multiple trace elements and thyroid cancer risk in Chinese adults: A case-control study
Jia-liu He, Hua-bing Wu, Wen-lei Hu, Jian-jun Liu, Qian Zhang, Wei Xiao, Ming-jun Hu, Ming Wu, Fen Huang
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2022; 246: 114049. CrossRef
- Association between total cholesterol levels and all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed patients with cancer

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Lower High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Concentration Is Independently Associated with Greater Future Accumulation of Intra-Abdominal Fat
- Sun Ok Song, You-Cheol Hwang, Han Uk Ryu, Steven E. Kahn, Donna L. Leonetti, Wilfred Y. Fujimoto, Edward J. Boyko
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):835-844. Published online August 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1130
- 4,363 View
- 119 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
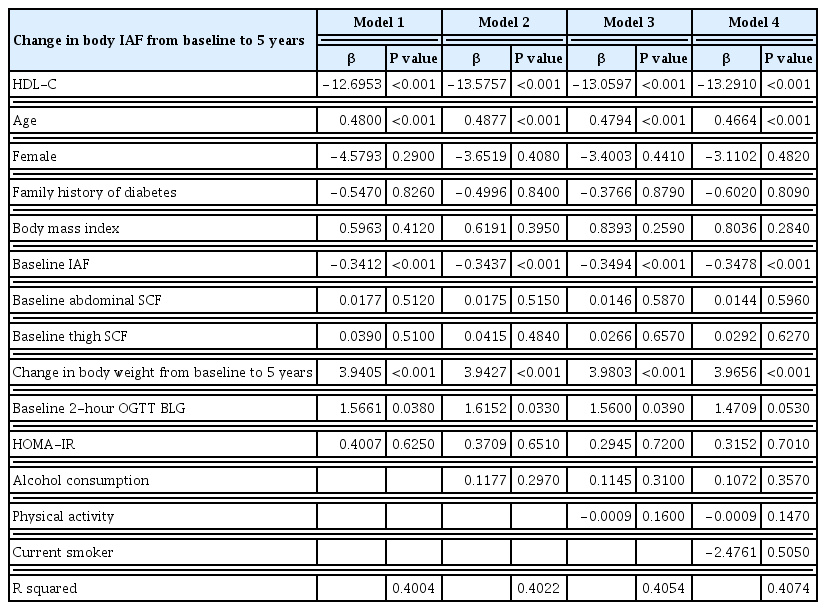
Both intra-abdominal fat (IAF) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) are known to be associated with cardiometabolic health. We evaluated whether the accumulation of computed tomography (CT)-measured IAF over 5 years was related to baseline HDL-C concentration in a prospective cohort study.
Methods
All participants were Japanese-Americans between the ages of 34 and 74 years. Plasma HDL-C concentration and CT measurements of IAF, abdominal subcutaneous fat (SCF), and thigh SCF cross-sectional areas were assessed at baseline and at 5-year follow-up visits.
Results
A total of 397 subjects without diabetes were included. The mean±standard deviation HDL-C concentration was 51.6±13.0 mg/dL in men and 66.0±17.0 mg/dL in women, and the IAF was 91.9±48.4 cm2 in men and 63.1±39.5 cm2 in women. The baseline plasma concentration of HDL-C was inversely associated with the change in IAF over 5 years using multivariable regression analysis with adjustment for age, sex, family history of diabetes, weight change over 5 years, and baseline measurements of body mass index, IAF, abdominal SCF, abdominal circumference, thigh SCF, and homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance.
Conclusion
These results demonstrate that HDL-C concentration significantly predicts future accumulation of IAF over 5 years independent of age, sex, insulin sensitivity, and body composition in Japanese-American men and women without diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - The associations between lipid profiles and visceral obesity among gastrointestinal cancer patients: a cross-sectional study
Bo Gao, Xiangrui Li, Wenqing Chen, Shu’an Wang, Jian He, Yu Liu, Chao Ding, Xiaotian Chen
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels

- Obesity and Metabolism
- High-Density Lipoprotein, Lecithin: Cholesterol Acyltransferase, and Atherosclerosis
- Alice Ossoli, Chiara Pavanello, Laura Calabresi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):223-229. Published online June 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.223
- 5,534 View
- 77 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 32 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Epidemiological data clearly show the existence of a strong inverse correlation between plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) concentrations and the incidence of coronary heart disease. This relation is explained by a number of atheroprotective properties of HDL, first of all the ability to promote macrophage cholesterol transport. HDL are highly heterogeneous and are continuously remodeled in plasma thanks to the action of a number of proteins and enzymes. Among them, lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) plays a crucial role, being the only enzyme able to esterify cholesterol within lipoproteins. LCAT is synthetized by the liver and it has been thought to play a major role in reverse cholesterol transport and in atheroprotection. However, data from animal studies, as well as human studies, have shown contradictory results. Increased LCAT concentrations are associated with increased HDL-C levels but not necessarily with atheroprotection. On the other side, decreased LCAT concentration and activity are associated with decreased HDL-C levels but not with increased atherosclerosis. These contradictory results confirm that HDL-C levels
per se do not represent the functionality of the HDL system.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection, high‑density lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular health (Review)
Tao Shen, Yanfang Li, Tingting Liu, Yunzhi Lian, Luke Kong
Biomedical Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Link between Magnesium Supplements and Statin Medication in Dyslipidemic Patients
Roxana Nartea, Brindusa Ilinca Mitoiu, Ioana Ghiorghiu
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2023; 45(4): 3146. CrossRef - Mannose-Coated Reconstituted Lipoprotein Nanoparticles for the Targeting of Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Optimization, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation of Effectiveness
Akpedje S. Dossou, Morgan E. Mantsch, Ammar Kapic, William L. Burnett, Nirupama Sabnis, Jeffery L. Coffer, Rance E. Berg, Rafal Fudala, Andras G. Lacko
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(6): 1685. CrossRef - Abdominal obesity negatively influences key metrics of reverse cholesterol transport
Jennifer Härdfeldt, Marica Cariello, Sara Simonelli, Alice Ossoli, Natasha Scialpi, Marilidia Piglionica, Emanuela Pasculli, Alessia Noia, Elsa Berardi, Patrizia Suppressa, Giuseppina Piazzolla, Carlo Sabbà, Laura Calabresi, Antonio Moschetta
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids.2022; 1867(2): 159087. CrossRef - Effects of Lactobacillus paracasei N1115 on dyslipidaemia: A randomized controlled study
Hua Jiang, Shengjie Tan, Ke Ning, Hao Li, Wenzhi Zhao, Ai Zhao, Hong Zhu, Shijie Wang, Peiyu Wang, Yumei Zhang
Journal of Functional Foods.2022; 89: 104956. CrossRef - LCAT- targeted therapies: Progress, failures and future
Kaixu Yang, Junmin Wang, Hongjiao Xiang, Peilun Ding, Tao Wu, Guang Ji
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 147: 112677. CrossRef - Cyclodextrin boostered-high density lipoprotein for antiatherosclerosis by regulating cholesterol efflux and efferocytosis
Yanyan Wang, Hai Gao, Xinya Huang, Zhaoan Chen, Pengyu Kang, Yunyi Zhou, Danhua Qin, Wenli Zhang, Jianping Liu
Carbohydrate Polymers.2022; 292: 119632. CrossRef - Lipidomic Approaches to Study HDL Metabolism in Patients with Central Obesity Diagnosed with Metabolic Syndrome
Gabriele Mocciaro, Simona D’Amore, Benjamin Jenkins, Richard Kay, Antonio Murgia, Luis Vicente Herrera-Marcos, Stefanie Neun, Alice P. Sowton, Zoe Hall, Susana Alejandra Palma-Duran, Giuseppe Palasciano, Frank Reimann, Andrew Murray, Patrizia Suppressa, C
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(12): 6786. CrossRef - rHDL modeling and the anchoring mechanism of LCAT activation
Tommaso Laurenzi, Chiara Parravicini, Luca Palazzolo, Uliano Guerrini, Elisabetta Gianazza, Laura Calabresi, Ivano Eberini
Journal of Lipid Research.2021; 62: 100006. CrossRef - Vasculoprotective properties of plasma lipoproteins from brown bears (Ursus arctos)
Matteo Pedrelli, Paolo Parini, Jonas Kindberg, Jon M. Arnemo, Ingemar Bjorkhem, Ulrika Aasa, Maria Westerståhl, Anna Walentinsson, Chiara Pavanello, Marta Turri, Laura Calabresi, Katariina Öörni, Gérman Camejo, Ole Fröbert, Eva Hurt-Camejo
Journal of Lipid Research.2021; 62: 100065. CrossRef - The Fate of Dietary Cholesterol in the Kissing Bug Rhodnius prolixus
Petter F. Entringer, David Majerowicz, Katia C. Gondim
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Excesive consumption of unsaturated fatty acids leads to oxidative and inflammatory instability in Wistar rats
Jelica D. Grujić-Milanović, Zoran Z. Miloradović, Nevena D. Mihailović-Stanojević, Vojislav V. Banjac, Strahinja Vidosavljević, Milan S. Ivanov, Danijela J. Karanović, Una-Jovana V. Vajić, Djurdjica M. Jovović
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 139: 111691. CrossRef - Cholesterol Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer and Its Pharmacological Modulation as Therapeutic Strategy
Isabella Giacomini, Federico Gianfanti, Maria Andrea Desbats, Genny Orso, Massimiliano Berretta, Tommaso Prayer-Galetti, Eugenio Ragazzi, Veronica Cocetta
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Serum Concentrations of Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) and Alzheimer’s Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marco Zuin, Carlo Cervellati, Alessandro Trentini, Angelina Passaro, Valentina Rosta, Francesca Zimetti, Giovanni Zuliani
Diagnostics.2021; 11(6): 984. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin reduces thrombin generation and platelet activation: implications for cardiovascular risk reduction in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Christina Kohlmorgen, Stephen Gerfer, Kathrin Feldmann, Sören Twarock, Sonja Hartwig, Stefan Lehr, Meike Klier, Irena Krüger, Carolin Helten, Petra Keul, Sabine Kahl, Amin Polzin, Margitta Elvers, Ulrich Flögel, Malte Kelm, Bodo Levkau, Michael Roden, Jen
Diabetologia.2021; 64(8): 1834. CrossRef - Impact of Dietary Lipids on the Reverse Cholesterol Transport: What We Learned from Animal Studies
Bianca Papotti, Joan Carles Escolà-Gil, Josep Julve, Francesco Potì, Ilaria Zanotti
Nutrients.2021; 13(8): 2643. CrossRef - Supramolecular copolymer modified statin-loaded discoidal rHDLs for atherosclerotic anti-inflammatory therapy by cholesterol efflux and M2 macrophage polarization
Qiqi Zhang, Jianhua He, Fengfei Xu, Xinya Huang, Yanyan Wang, Wenli Zhang, Jianping Liu
Biomaterials Science.2021; 9(18): 6153. CrossRef - Association between Small Dense Low-Density Lipoproteins and High-Density Phospolipid Content in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease with or without Diabetes
Hanene Aoua, Ymène Nkaies, Ali Ben Khalfallah, Mohsen Sakly, Ezzedine Aouani, Nebil Attia
Laboratory Medicine.2020; 51(3): 271. CrossRef - Biomechanical and biochemical investigation of erythrocytes in late stage human leptospirosis
J.A.X. Silva, A.V.P. Albertini, C.S.M. Fonseca, D.C.N. Silva, V.C.O. Carvalho, V.L.M. Lima, A. Fontes, E.V.L. Costa, R.A. Nogueira
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardioprotective Properties of HDL: Structural and Functional Considerations
Eleni Pappa, Moses S. Elisaf, Christina Kostara, Eleni Bairaktari, Vasilis K. Tsimihodimos
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2020; 27(18): 2964. CrossRef - Relationship between non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol/apolipoprotein A-I and monocyte/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and coronary heart disease
Ya Li, Shu Li, Yulin Ma, Jialing Li, Mingying Lin, Jing Wan
Coronary Artery Disease.2020; 31(7): 623. CrossRef - Lipid transfer to high‐density lipoproteins in coronary artery disease patients with and without previous cerebrovascular ischemic events
Carlos J.D.G. Barbosa, Raul C. Maranhão, Renata S. Barreiros, Fatima R. Freitas, André Franci, Célia M.C. Strunz, Flávia B.B. Arantes, Thauany M. Tavoni, José A.F. Ramires, Roberto Kalil Filho, José C. Nicolau
Clinical Cardiology.2019; 42(11): 1100. CrossRef - Antibodies Against the C-Terminus of ApoA-1 Are Inversely Associated with Cholesterol Efflux Capacity and HDL Metabolism in Subjects with and without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Robin Dullaart, Sabrina Pagano, Frank Perton, Nicolas Vuilleumier
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(3): 732. CrossRef - The effect of chronic kidney disease on lipid metabolism
Neris Dincer, Tuncay Dagel, Baris Afsar, Adrian Covic, Alberto Ortiz, Mehmet Kanbay
International Urology and Nephrology.2019; 51(2): 265. CrossRef - Biological Consequences of Dysfunctional HDL
Angela Pirillo, Alberico Luigi Catapano, Giuseppe Danilo Norata
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2019; 26(9): 1644. CrossRef - Plasma lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and phospholipid transfer protein activity independently associate with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Karlijn J. Nass, Eline H. van den Berg, Eke G. Gruppen, Robin P. F. Dullaart
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - An integrated metabolomic strategy for the characterization of the effects of Chinese yam and its three active components on septic cardiomyopathy
Ning Zhou, Meng-Nan Zeng, Kai Li, Yan-Yun Yang, Zhi-Yao Bai, Xiao-Ke Zheng, Wei-Sheng Feng
Food & Function.2018; 9(9): 4989. CrossRef - Effect of Rosuvastatin on Cholesterol Efflux Capacity and Endothelial Function in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia
Kyong Yeun Jung, Kyoung Min Kim, Sun Kyoung Han, Han Mi Yun, Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
Circulation Journal.2018; 82(5): 1387. CrossRef - Association Between Serum LDL-C and ApoB and SYNTAX Score in Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease
Taiwu Lin, Luzhao Wang, Jingbin Guo, Peng Liu, Liheng Chen, Mengqiu Wei, Gongxin Li
Angiology.2018; 69(8): 724. CrossRef - Influence of i.v. lipid emulsion on lipoprotein subclass in preterm infants
Hiroki Suganuma, Naho Ikeda, Natsuki Ohkawa, Hiromichi Shoji, Toshiaki Shimizu
Pediatrics International.2018; 60(9): 839. CrossRef - The HDL cholesterol/apolipoprotein A-I ratio: an indicator of cardiovascular disease
Eun-Jung Rhee, Christopher D. Byrne, Ki-Chul Sung
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2017; 24(2): 148. CrossRef - Moringa Leaves Prevent Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in Guinea Pigs by Reducing the Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Metabolism
Manal Almatrafi, Marcela Vergara-Jimenez, Ana Murillo, Gregory Norris, Christopher Blesso, Maria Fernandez
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(7): 1330. CrossRef
- Association between Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection, high‑density lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular health (Review)

- Obesity and Metabolism
- High Density Lipoprotein: A Therapeutic Target in Type 2 Diabetes
- Philip J. Barter
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(3):169-177. Published online September 13, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.3.169
- 3,725 View
- 32 Download
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader High density lipoproteins (HDLs) have a number of properties that have the potential to inhibit the development of atherosclerosis and thus reduce the risk of having a cardiovascular event. These protective effects of HDLs may be reduced in patients with type 2 diabetes, a condition in which the concentration of HDL cholesterol is frequently low. In addition to their potential cardioprotective properties, HDLs also increase the uptake of glucose by skeletal muscle and stimulate the synthesis and secretion of insulin from pancreatic β cells and may thus have a beneficial effect on glycemic control. This raises the possibility that a low HDL concentration in type 2 diabetes may contribute to a worsening of diabetic control. Thus, there is a double case for targeting HDLs in patients with type 2 diabetes: to reduce cardiovascular risk and also to improve glycemic control. Approaches to raising HDL levels include lifestyle factors such as weight reduction, increased physical activity and stopping smoking. There is an ongoing search for HDL-raising drugs as agents to use in patients with type 2 diabetes in whom the HDL level remains low despite lifestyle interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and type 2 diabetes mellitus: dual evidence from NHANES database and Mendelian randomization analysis
Zhaoqi Yan, Yifeng Xu, Keke Li, Liangji Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of serum HDL level with HRV indices using multiple linear regression analysis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Fareedabanu A. Balikai, Shivalingappa B. Javali, Varsha M. Shindhe, Neeta Deshpande, Jyoti M. Benni, Darshit P. Shetty, Nitin Kapoor, Kamaruddin Jaalam
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 190: 109988. CrossRef - High Vaccenic Acid Content in Beef Fat Attenuates High Fat and High Carbohydrate Western Diet Induced Changes in Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Pigs
Vijay P. Singh, Melanie A. Fontaine, Rabban Mangat, Janelle M. Fouhse, Abdoulaye Diane, Benjamin P. Willing, Spencer D. Proctor
Microorganisms.2021; 9(12): 2517. CrossRef - Inverse Association between High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Adverse Outcomes among Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Guoliang Hu, Yuesong Pan, Mengxing Wang, Xia Meng, Yong Jiang, Zixiao Li, Hao Li, Yongjun Wang, Yilong Wang
Biomedicines.2021; 9(12): 1947. CrossRef - High Incidence of Diabetes in People with Extremely High High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol: Results of the Kanagawa Investigation of Total Checkup Data from the National Database-1 (KITCHEN-1)
Kei Nakajima, Ryoko Higuchi, Taizo Iwane, Michi Shibata, Kento Takada, Michiko Sugiyama, Masafumi Matsuda, Teiji Nakamura
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(3): 381. CrossRef - Total adiponectin in overweight and obese subjects and its response to visceral fat loss
Salah Gariballa, Juma Alkaabi, Javed Yasin, Awad Al Essa
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Impaired Glucose Metabolism in People with Extremely Elevated High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Low Alcohol Consumption: Results of the Kanagawa Investigation of Total Checkup Data from the National Database-3 (KITCHEN-3)
Kei Nakajima, Ryoko Higuchi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(11): 1825. CrossRef - Phenotyping of Korean patients with better-than-expected efficacy of moderate-intensity statins using tensor factorization
Jingyun Choi, Yejin Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, In Young Choi, Hwanjo Yu, Katriina Aalto-Setala
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0197518. CrossRef - Serum Levels of Apolipoproteins and Incident Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study
Adela Brahimaj, Symen Ligthart, M. Arfan Ikram, Albert Hofman, Oscar H. Franco, Eric J.G. Sijbrands, Maryam Kavousi, Abbas Dehghan
Diabetes Care.2017; 40(3): 346. CrossRef - Psoriasis and metabolic syndrome in children: current data
A. Pietrzak, E. Grywalska, M. Walankiewicz, T. Lotti, J. Roliński, W. Myśliński, P. Chabros, D. Piekarska-Myślińska, K. Reich
Clinical and Experimental Dermatology.2017; 42(2): 131. CrossRef - A Shift in ApoM/S1P Between HDL-Particles in Women With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Is Associated With Impaired Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the ApoM/S1P Complex
Cecilia Frej, Armando J. Mendez, Mario Ruiz, Melanie Castillo, Thomas A. Hughes, Björn Dahlbäck, Ronald B. Goldberg
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2017; 37(6): 1194. CrossRef - Improvement in Biochemical Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes After Twenty-Four Sessions of Aerobic Exercise: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Soulmaz Rahbar, Sedigheh Sadat Naimi, Asghar Reza Soltani, Abbas Rahimi, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Vahid Rashedi, Hossein Moein Tavakkoli
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The therapeutic efficacy of intensive medical therapy in ameliorating high-density lipoprotein dysfunction in subjects with type two diabetes
Sangeeta Kashyap, Karim Kheniser, Ling Li, James Bena, Takhar Kasumov
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in high-density lipoprotein physiology: surprises, overturns, and promises
Caterina Constantinou, Eleni A. Karavia, Eva Xepapadaki, Peristera-Ioanna Petropoulou, Eugenia Papakosta, Marilena Karavyraki, Evangelia Zvintzou, Vassilis Theodoropoulos, Serafoula Filou, Aikaterini Hatziri, Christina Kalogeropoulou, George Panayiotakopo
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 310(1): E1. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids for hypertriglyceridaemia management in Korea
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, Y. J. Jeong, S. J. Yang, S. J. Baik, H. Lee, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, I.-Y. Choi, H. W. Yim, K.-H. Yoon
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(5): 508. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of statin prescription patterns and outcomes according to clinical department
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, H. Lee, B. Park, S. Park, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, H. Song, J. H. Kim, K.-H. Yoon, I. Y. Choi
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(1): 70. CrossRef - Statin‐related aminotransferase elevation according to baseline aminotransferases level in real practice in Korea
H.‐S. Kim, S. H. Lee, H. Kim, S.‐H. Lee, J. H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, S.‐H. Kim, I.‐Y. Choi, K.‐H. Yoon, J. H. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(3): 266. CrossRef - Diabetes Associated to Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Patients of Family Health Unity
Polyane Medeiros Alves, Raiane dos Santos Pereira, Ariel Gustavo Letti, Álvaro Luís Müller da Fonseca
Open Journal of Preventive Medicine.2015; 05(04): 177. CrossRef - Cis-9, trans-11 and trans-10, cis-12 CLA Mixture does not Change Body Composition, Induces Insulin Resistance and Increases Serum HDL Cholesterol Level in Rats
Mariana Macedo de Almeida, Yamara Oliveira de Souza, Sheila Cristina Potente Dutra Luquetti, Céphora Maria Sabarense, José Otávio do Amaral Corrêa, Ellen Paula Santos da Conceição, Patrícia Cristina Lisboa, Egberto Gaspar de Moura, Sara Malaguti Andrade S
Journal of Oleo Science.2015; 64(5): 539. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Not All Smokers Die Young: A Model for Hidden Heterogeneity within the Human Population
Morgan Levine, Eileen Crimmins, Hong Wei Chu
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(2): e87403. CrossRef - Oxidative Damage and Inflammation in Obese Diabetic Emirati Subjects
Salah Gariballa, Melita Kosanovic, Javed Yasin, Awad Essa
Nutrients.2014; 6(11): 4872. CrossRef - Low HDL cholesterol is correlated to the acute ischemic stroke with diabetes mellitus
Yun Luo, Jingwei Li, Junfeng Zhang, Yun Xu
Lipids in Health and Disease.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Butter naturally enriched in cis-9, trans-11 CLA prevents hyperinsulinemia and increases both serum HDL cholesterol and triacylglycerol levels in rats
Mariana Macedo de Almeida, Sheila Cristina Potente Dutra Luquetti, Céphora Maria Sabarense, José Otávio do Amaral Corrêa, Larissa Gomes dos Reis, Ellen Paula Santos da Conceição, Patrícia Cristina Lisboa, Egberto Gaspar de Moura, Jacy Gameiro, Marco Antôn
Lipids in Health and Disease.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Conference report
Andrew J. Krentz
Cardiovascular Endocrinology.2014; 3(Supplement): S5. CrossRef
- Association between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and type 2 diabetes mellitus: dual evidence from NHANES database and Mendelian randomization analysis

- APOA5 Polymorphism Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Postmenopausal Women.
- Doh Hee Kim, Seung Hee Lee, Kyung Hoon Han, Chae Bong Kim, Kwan Young Song, Sook Cho, Kye Heui Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(4):276-281. Published online December 20, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.4.276
- 4,642 View
- 23 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Menopause is an independent risk factor in metabolic syndrome which induced an alteration of the lipid metabolism by hormonal changes. Apolipoprotein A5 gene (APOA5) was related to the regulation of triglyceride and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) level with biosynthesis and decomposition. This study was conducted to investigate the relationship between APOA5 polymorphism and metabolic syndrome in Korean postmenopausal women. METHODS: This study included 307 postmenopausal women with anthropometric and biochemical measurement in 2010-2011. The polymorphism of APOA5 was analyzed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism method with MseI restriction enzyme. RESULTS: The metabolic syndrome prevalence with TT genotype was significantly lower than the frequency in those with TC/CC (27.09%, 38.46%, and 45.71% for TT, TC, and CC, respectively; P < 0.05). Multiple regression analysis of metabolic syndrome risk factors indicated that postmenopausal women with CC genotype had a higher risk with 3 times than that in TT genotype (P < 0.05). APOA5 C carriers showed an increased risk of triglyceride level (odd ratio, 2.93 and 1.85 for CC and TC+CC, respectively; P < 0.05). Interestingly, HDL-C was related to triglyceride directly in comparison to APOA5. CONCLUSION: The results of this study indicate that APOA5 has an influence on serum triglyceride and HDL-C, which contribute to metabolic syndrome in Korean postmenopausal women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a 3-year dietary intervention on age-related changes in triglyceride and apolipoprotein A-V levels in patients with impaired fasting glucose or new-onset type 2 diabetes as a function of the APOA5 -1131 T > C polymorphism
Minjoo Kim, Jey Sook Chae, Miri Kim, Sang-Hyun Lee, Jong Ho Lee
Nutrition Journal.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - APOA5Polymorphism Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Postmenopausal Women
Mi Hae Seo, Won Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2012; 27(4): 274. CrossRef
- Effects of a 3-year dietary intervention on age-related changes in triglyceride and apolipoprotein A-V levels in patients with impaired fasting glucose or new-onset type 2 diabetes as a function of the APOA5 -1131 T > C polymorphism

- Lipid Profile Changes in Postmenopausal Korean Women Treated with Alendronate (10 mg) for 2 Years: Comparing with Control Group.
- Il Woo Joo, Han Jin Oh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(1):19-25. Published online February 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.1.19
- 1,776 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Bisphosphonate, which has been used for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis with the mechanism of inhibiting bone resorption, also has an association with the cholesterol synthethic process. This suggests that bisphosphonate might have benefit to improve the lipid profile in humans through a process that blocks the mevalonate-squalene pathway. However, few reports have revealed the relationship between the action of bisphosphonate and lipid metabolism in postmenopausal Korean women. We planned this study to determine the effect of alendronate (10 mg) on the serum lipid level in postmenopausal Korean women. Subjects and METHODS: We retrospectively evaluated the postmenopausal Korean women (aged over 50) who visited the Osteoporosis clinic in the Health Care Center in Seoul from March of 2003 to October of 2005. The changes of the serum lipid levels, including total cholesterol, triglyceride, and HDL cholesterol, after 2-years of alendronate 10 mg administration were evaluated and comparing to a control group. RESULTS: After 2-years alendronate (10 mg) administration, the total cholesterol was decreased by 11.8 +/- 3.7 mg/dL, and the HDL cholesterol was increased by 5.2 +/-1.4 mg/dL as compared to the baseline lipid level. Both of these results showed statistical significance. Changes of the triglyceride and fasting blood glucose also showed a decline by 15.4 +/-9.8 mg/dL and 6.0 +/-1.4 mg/dL, respectively, but this was not statistically significant. However, in the control group, the total cholesterol was increased by 9.4 +/-8.8 mg/dL, and the triglyceride was increased by 10.5 +/-7.2 mg/dL as compared to the baseline lipid level. Both of the results showed statistical significance. CONCLUSION: Alendronate might have a beneficial effect on lipid metabolism to decrease cholesterol and increase HDL. Taking into consideration about the postmenopausal increase in the cholesterol level, alendronate is recommended for the prevention of hyperlipidemia in postmenopausal women, in addition to preventing and treating osteoporosi -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of alendronate on lipid profile of postmenopausal women with osteopenia and prediabetes: A randomized triple-blind clinical trial
Maryam Karimifard, Ashraf Aminorroaya, Massoud Amini, Ali Kachuie, Awat Feizi, SimaAminorroaya Yamini, MolukHadi Alijanvand
Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2021; 26(1): 52. CrossRef
- The effect of alendronate on lipid profile of postmenopausal women with osteopenia and prediabetes: A randomized triple-blind clinical trial

- Relationship between Adiponectin, Leptin and Body Fat in Men with Hypogonadism Before and After Testosterone Treatment.
- Sang Wan Kim, Joon Ku Kang, Do Joon Park, Chan Soo Shin, Kyung Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(5):473-484. Published online October 1, 2004
- 1,101 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Testosterone replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism improves sexual function, decreases body fat, and increases the mass and function of lean muscle. These beneficial effects of testosterone replacement therapy are accompanied by slight lowering of the high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, increase in the hematocrit/hemoglobin ratio and size of the prostate gland. It is presently unknown whether the effect of testosterone on body fat could also reduce the risk of atherosclerotic disease associated with obesity. We investigated the relationship between body fat and blood leptin and adiponectin levels to elucidate the effect of testosterone on body fat metabolism, as well as the effect of testosterone on lipid and bone metabolism. METHODS: We selected 28 men, who were hypogonadal (mean serum testosterone+/-SD, 22.3+/-35.3 ng/dL) due to an organic disease, and them with oral testosterone (testosterone undecanoate) for 12 months. We measured the body composition, serum leptin, plasma adiponectin, biochemical bone markers, bone mineral density, prostate-specific antigen, and serum lipids before and 3, 6 and 12 months after treatment. We analyzed the relationship between body fat and blood leptin and adiponectin levels. RESULTS: The mean serum testosterone concentration reached the subnormal range after 6 months of treatment, which remained for the duration of treatment. The fat mass decreased and muscle mass increased, not within the first 6 months, but principally within 12 months (p<0.05). Although the decrease in the serum leptin level was not statistically significant, there were positive correlations between the leptin level and fat mass before and after 6 months of treatment (p<0.05). The plasma adiponectin did not increase or correlate with body fat parameters. The bone mineral densities of the lumbar spine (L2-L4) and femoral neck did not increased, but the serum osteocalcin and urine N-telopeptide were significantly decreased (p<0.05 and <0.01, respectively). The HDL-cholesterol decreased, principally within the first 6 months (p<0.01), but the total and LDL cholesterols, and the triglycerides remained unchanged during the course of treatment. There was also no change in prostate-specific antigen. CONCLUSION: Twelve months of oral testosterone replacement in men with hypogonadism improved body composition and bone metabolism, but demonstrated subnormal serum testosterone levels, had no effect on the leptin and adiponectin levels and decrease in HDL-cholesterol levels. It will be necessary to examine the long-term effects of testosterone replacement on the incidence of cardiovascular events as well as cardiovascular risk factors in men with hypogonadism

- Serum Lipoprotein (a) and Lipid Concentrations in Patients with Subelinical Hypothyroidism.
- Kyoung Ah Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Yeun Sun Kim, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Eun Mi Koh, Young Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Jong Hun Lee, Kwang Won Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(1):11-17. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,136 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Overt hypothyroidism is well-known cause of secondary hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. However, there have been dissenting reports of abnormalities in serum lipid concentrations in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism (SH). Recently, it has been reported that serum Lp (a) concentration, an independent risk factor of atherosclerosis, was increased in patients with SH. Therefore, we analyzed serum Lp (a) and other lipid concentrations to investigate whether they are increased in patients with SH and the correlation between serum Lp (a) and TSH concentrations. METHODS: We undertook this study in 53 patients with SH (TSH > 6 uiU/ml) and 197 age-and sex-matched healthy control subjects, They had no abnormalities in liver function, BUN, creatinine, fasting blood glucose, urinalysis, and past medical histories. Serum T3, T4, and TSH concentrations were measured by RIA using commercial kits. Serum concentrations of Lp (a), total cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), and HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) were measured by rate nephelometry and enzyme assay, respectively. RESULTS: There were no significant differences of serum Lp (a), total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, TG, and HDL-C concentrations in 53 patients with SH and 197 control subjects (25.6+-3.8mg/dL vs. 25.4+-1.5mg/dL ; 204.0+-4.2mg/dL vs. 204.0+-2.4mg/dL ; 127.0+-3.9mg/dL vs. 125.0+-2.3 mg/dL ; 133.0+-8.5mg/dL vs. 130.0+-6.0mg/dL ; 50.0+-1.5mg/dL vs. 53.0+-0.9mg/dL). There was no correlation between Lp (a) and TSH concentrations in SH (r=0.12, p>0.05). CONCLUSION: Serum Lp (a) concentration as well as total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and TG was not increased in patients with SH. There was no correlation between serum Lp (a) and TSH levels in subclinical hypothyroidism.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



