Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Miscellaneous
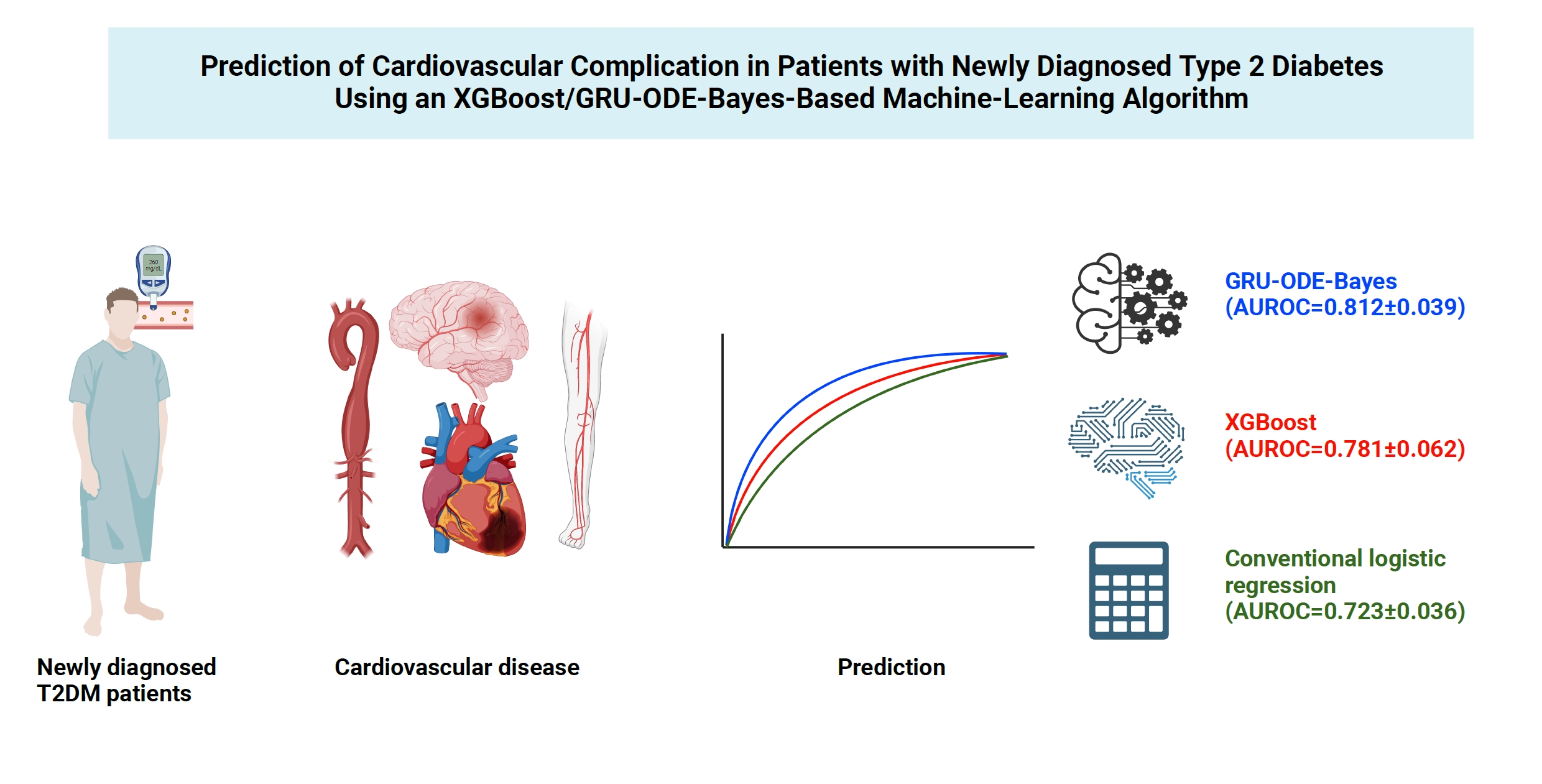
- Prediction of Cardiovascular Complication in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Using an XGBoost/GRU-ODE-Bayes-Based Machine-Learning Algorithm
- Joonyub Lee, Yera Choi, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Juyoung Shin, Hun-Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):176-185. Published online November 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1739
- 1,191 View
- 58 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Cardiovascular disease is life-threatening yet preventable for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Because each patient with T2DM has a different risk of developing cardiovascular complications, the accurate stratification of cardiovascular risk is critical. In this study, we proposed cardiovascular risk engines based on machine-learning algorithms for newly diagnosed T2DM patients in Korea.
Methods
To develop the machine-learning-based cardiovascular disease engines, we retrospectively analyzed 26,166 newly diagnosed T2DM patients who visited Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital between July 2009 and April 2019. To accurately measure diabetes-related cardiovascular events, we designed a buffer (1 year), an observation (1 year), and an outcome period (5 years). The entire dataset was split into training and testing sets in an 8:2 ratio, and this procedure was repeated 100 times. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was calculated by 10-fold cross-validation on the training dataset.
Results
The machine-learning-based risk engines (AUROC XGBoost=0.781±0.014 and AUROC gated recurrent unit [GRU]-ordinary differential equation [ODE]-Bayes=0.812±0.016) outperformed the conventional regression-based model (AUROC=0.723± 0.036).
Conclusion
GRU-ODE-Bayes-based cardiovascular risk engine is highly accurate, easily applicable, and can provide valuable information for the individualized treatment of Korean patients with newly diagnosed T2DM.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):770-781. Published online November 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1726

- 1,098 View
- 47 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Elevated γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GTP) levels are associated with metabolic syndrome. We investigated the association of cumulative exposure to high γ-GTP with the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in a large-scale population.
Methods
Using nationally representative data from the Korean National Health Insurance system, 1,640,127 people with 4 years of consecutive γ-GTP measurements from 2009 to 2012 were included and followed up until the end of 2019. For each year of the study period, participants were grouped by the number of exposures to the highest γ-GTP quartile (0–4), and the sum of quartiles (0–12) was defined as cumulative γ-GTP exposure. The hazard ratio for CVD was evaluated using the Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
During the 6.4 years of follow-up, there were 15,980 cases (0.97%) of myocardial infarction (MI), 14,563 (0.89%) of stroke, 29,717 (1.81%) of CVD, and 25,916 (1.58%) of death. Persistent exposure to high γ-GTP levels was associated with higher risks of MI, stroke, CVD, and death than those without such exposure. The risks of MI, stroke, CVD, and mortality increased in a dose-dependent manner according to total cumulative γ-GTP (all P for trend <0.0001). Subjects younger than 65 years, with a body mass index <25 kg/m2, and without hypertension or fatty liver showed a stronger relationship between cumulative γ-GTP and the incidence of MI, CVD, and death.
Conclusion
Cumulative γ-GTP elevation is associated with CVD. γ-GTP could be more widely used as an early marker of CVD risk, especially in individuals without traditional CVD risk factors.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
- Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):568-577. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1770

- 1,507 View
- 112 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) has become an important tool for evaluating cardiovascular disease (CVD). This study evaluated the significance of CACS for future CVD through more than 10 years of follow-up in asymptomatic Korean populations with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) known to have a relatively low CACS burden.
Methods
We enrolled 981 asymptomatic T2DM patients without CVD at baseline who underwent CACS evaluation using multidetector computed tomography between January 2008 and December 2014. They were grouped into five predefined CACS categories based on Agatston scores and followed up by August 2020. The primary endpoint was incident CVD events, including coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial disease.
Results
The relative risk of CVD was significantly higher in patients with CACS ≥10, and the significance persisted after adjustment for known confounders. A higher CACS category indicated a higher incidence of future CVD: hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) 4.09 (1.79 to 9.36), 12.00 (5.61 to 25.69), and 38.79 (16.43 to 91.59) for 10≤ CACS <100, 100≤ CACS <400, and CACS ≥400, respectively. During the 12-year follow-up period, the difference in event-free survival more than doubled as the category increased. Patients with CACS below 10 had very low CVD incidence throughout the follow-up. The receiver operating characteristic analysis showed better area under curve when the CACS cutoff was 10 than 100.
Conclusion
CACS can be a sensitive marker of CVD risk. Specifically, CACS above 10 is an indicator of CVD high-risk requiring more intensive medical treatment in Koreans with T2DM.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Future Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A 16-Year Follow-up in a Prospective, Community-Dwelling Cohort Study
- Joon Ho Moon, Yongkang Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H. Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):406-417. Published online August 3, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1703

- 2,636 View
- 165 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
While the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is a measure of insulin resistance, its association with cardiovascular disease (CVD) has not been well elucidated. We evaluated the TyG index for prediction of CVDs in a prospective large communitybased cohort.
Methods
Individuals 40 to 70 years old were prospectively followed for a median 15.6 years. The TyG index was calculated as the Ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL)×fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2]. CVDs included any acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular disease. We used a Cox proportional hazards model to estimate CVD risks according to quartiles of the TyG index and plotted the receiver operating characteristics curve for the incident CVD.
Results
Among 8,511 subjects (age 51.9±8.8 years; 47.5% males), 931 (10.9%) had incident CVDs during the follow-up. After adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, total cholesterol, smoking, alcohol, exercise, and C-reactive protein, subjects in the highest TyG quartile had 36% increased risk of incident CVD compared with the lowest TyG quartile (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% confidence interval, 1.10 to 1.68). Carotid plaque, assessed by ultrasonography was more frequent in subjects in the higher quartile of TyG index (P for trend=0.049 in men and P for trend <0.001 in women). The TyG index had a higher predictive power for CVDs than the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (area under the curve, 0.578 for TyG and 0.543 for HOMA-IR). Adding TyG index on diabetes or hypertension alone gave sounder predictability for CVDs.
Conclusion
The TyG index is independently associated with future CVDs in 16 years of follow-up in large, prospective Korean cohort. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kaisheng Yuan, Bing Wu, Ruiqi Zeng, Fuqing Zhou, Ruixiang Hu, Cunchuan Wang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 169. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride glucose index and chronic total coronary occlusion: A cross-sectional study from southwest China
Kaiyong Xiao, Huili Cao, Bin Yang, Zhe Xv, Lian Xiao, Jianping Wang, Shuiqing Ni, Hui Feng, Zhongwei He, Lei Xv, Juan Li, Dongmei Xv
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(4): 850. CrossRef - The association between TyG and all-cause/non-cardiovascular mortality in general patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is modified by age: results from the cohort study of NHANES 1999–2018
Younan Yao, Bo Wang, Tian Geng, Jiyan Chen, Wan Chen, Liwen Li
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Evaluation of the novel three lipid indices for predicting five- and ten-year incidence of cardiovascular disease: findings from Kerman coronary artery disease risk factors study (KERCADRS)
Alireza Jafari, Hamid Najafipour, Mitra Shadkam, Sina Aminizadeh
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Impact of Post-Transplant Diabetes Mellitus on Survival and Cardiovascular Events in Kidney Transplant Recipients
- Ja Young Jeon, Shin Han-Bit, Bum Hee Park, Nami Lee, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan-Woo Lee, Seung Jin Han
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):139-145. Published online February 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1594

- 1,640 View
- 119 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM) is a risk factor for poor outcomes after kidney transplantation (KT). However, the outcomes of KT have improved recently. Therefore, we investigated whether PTDM is still a risk factor for mortality, major atherosclerotic cardiovascular events (MACEs), and graft failure in KT recipients.
Methods
We studied a retrospective cohort of KT recipients (between 1994 and 2017) at a single tertiary center, and compared the rates of death, MACEs, overall graft failure, and death-censored graft failure after KT between patients with and without PTDM using Kaplan-Meier analysis and a Cox proportional hazard model.
Results
Of 571 KT recipients, 153 (26.8%) were diagnosed with PTDM. The mean follow-up duration was 9.6 years. In the Kaplan- Meier analysis, the PTDM group did not have a significantly increased risk of death or four-point MACE compared with the non-diabetes mellitus group (log-rank test, P=0.957 and P=0.079, respectively). Multivariate Cox proportional hazard models showed that PTDM did not have a negative impact on death or four-point MACE (P=0.137 and P=0.181, respectively). In addition, PTDM was not significantly associated with overall or death-censored graft failure. However, patients with a long duration of PTDM had a higher incidence of four-point MACE.
Conclusion
Patient survival and MACEs were comparable between groups with and without PTDM. However, PTDM patients with long duration diabetes were at higher risk of cardiovascular disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of post-transplant diabetes mellitus on cardiovascular events and mortality: a single‐center retrospective cohort study
Uğur Ünlütürk, Tolga Yıldırım, Merve Savaş, Seda Hanife Oğuz, Büşra Fırlatan, Deniz Yüce, Nesrin Damla Karakaplan, Cemile Selimova, Rahmi Yılmaz, Yunus Erdem, Miyase Bayraktar
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Qiufeng Du, Tao Li, Xiaodong Yi, Shuang Song, Jing Kang, Yunlan Jiang
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Safety and efficacy of semaglutide in post kidney transplant patients with type 2 diabetes or Post-Transplant diabetes
Moeber Mohammed Mahzari, Omar Buraykan Alluhayyan, Mahdi Hamad Almutairi, Mohammed Abdullah Bayounis, Yazeed Hasan Alrayani, Amir A. Omair, Awad Saad Alshahrani
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology.2024; 36: 100343. CrossRef
- Effect of post-transplant diabetes mellitus on cardiovascular events and mortality: a single‐center retrospective cohort study

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
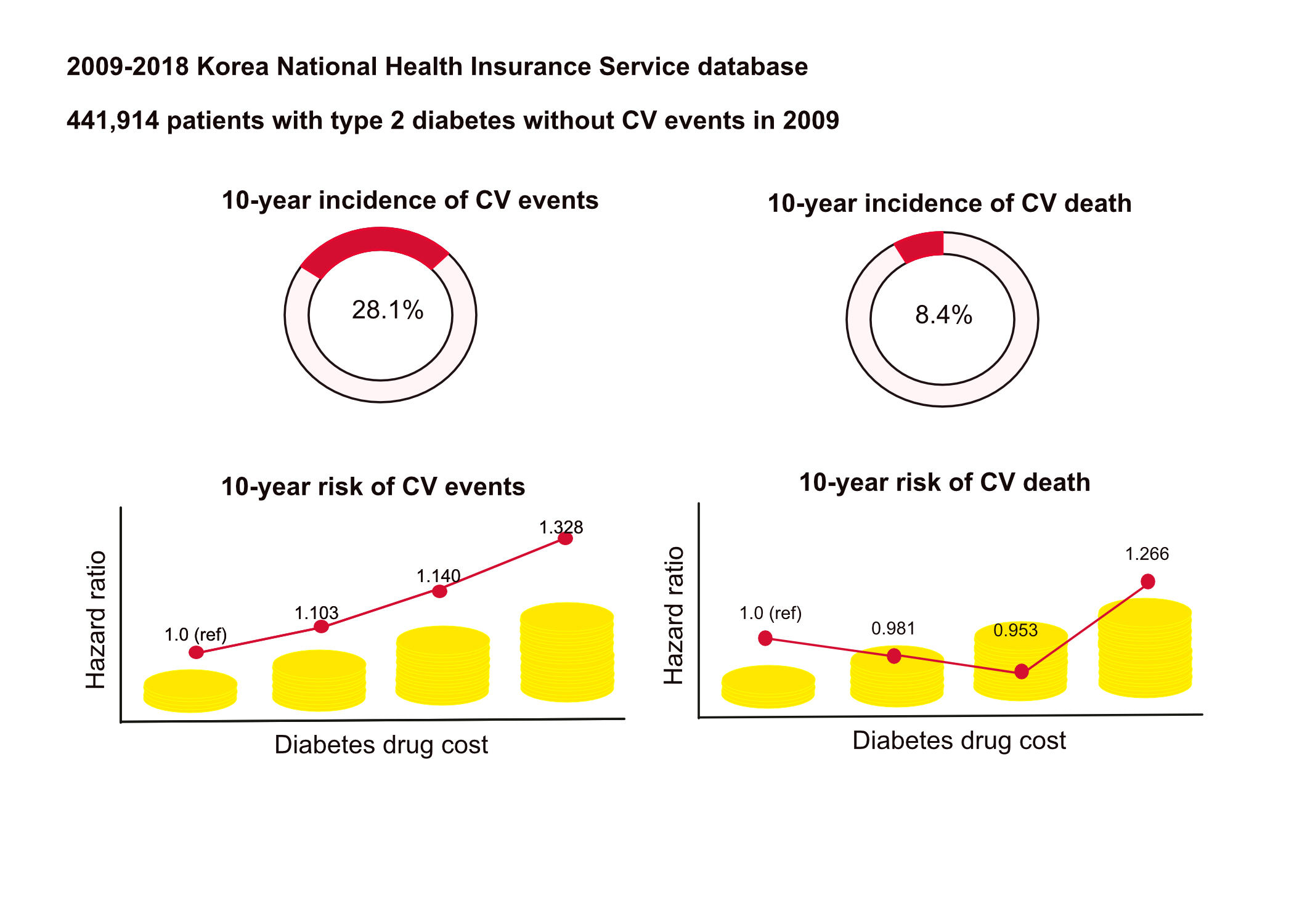
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
- Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):759-769. Published online October 5, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1515
- 3,159 View
- 191 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the long-term effects of diabetes drug costs on cardiovascular (CV) events and death.
Methods
This retrospective observational study used data from 2009 to 2018 from the National Health Insurance in Korea. Among the patients with type 2 diabetes, those taking antidiabetic drugs and who did not have CV events until 2009 were included. Patients were divided into quartiles (Q1 [lowest]–4 [highest]) according to the 2009 diabetes drug cost. In addition, the 10-year incidences of CV events (non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, hospitalization for heart failure, and coronary revascularization) and CV death (death due to CV events) were analyzed.
Results
A total of 441,914 participants were enrolled (median age, 60 years; men, 57%). CV events and death occurred in 28.1% and 8.36% of the patients, respectively. The 10-year incidences of CV events and deaths increased from Q1 to 4. After adjusting for sex, age, income, type of diabetes drugs, comorbidities, and smoking and drinking status, the risk of CV events significantly increased according to the sequential order of the cost quartiles. In contrast, the risk of CV death showed a U-shaped pattern, which was the lowest in Q3 (hazard ratio [HR], 0.953; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.913 to 0.995) and the highest in Q4 (HR, 1.266; 95% CI, 1.213 to 1.321).
Conclusion
Diabetes drug expenditure affects 10-year CV events and mortality. Therefore, affording an appropriate diabetes drug cost at a similar risk of CV is an independent protective factor against CV death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study

Review Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
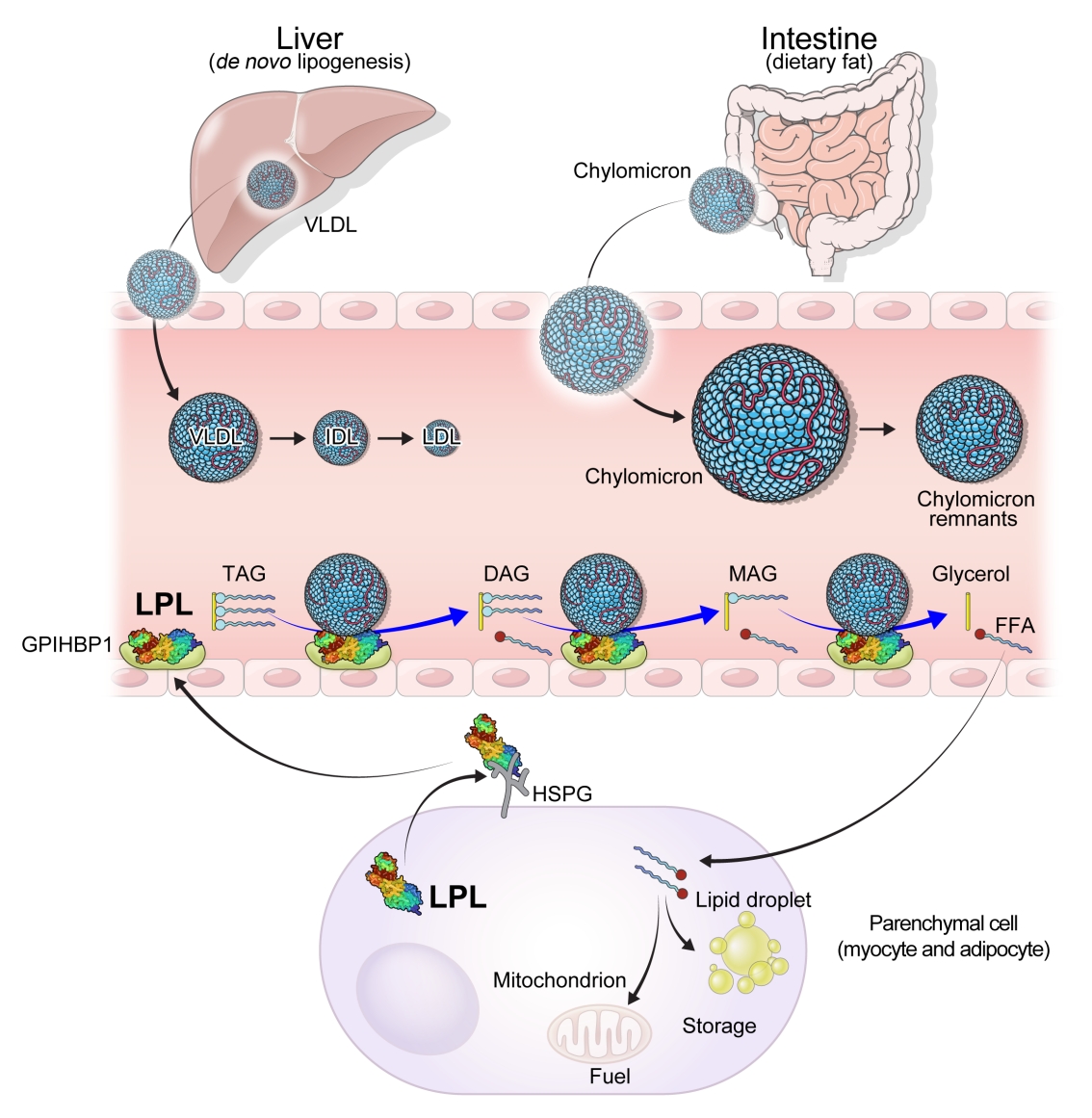
- Lipoprotein Lipase: Is It a Magic Target for the Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia
- Joon Ho Moon, Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):575-586. Published online August 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.402
- 7,769 View
- 437 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - High levels of triglycerides (TG) and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TGRLs) confer a residual risk of cardiovascular disease after optimal low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)–lowering therapy. Consensus has been made that LDL-C is a non-arguable primary target for lipid lowering treatment, but the optimization of TGRL for reducing the remnant risk of cardiovascular diseases is urged. Omega-3 fatty acids and fibrates are used to reduce TG levels, but many patients still have high TG and TGRL levels combined with low high-density lipoprotein concentration that need to be ideally treated. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) is a key regulator for TGs that hydrolyzes TGs to glycerol and free fatty acids in lipoprotein particles for lipid storage and consumption in peripheral organs. A deeper understanding of human genetics has enabled the identification of proteins regulating the LPL activity, which include the apolipoproteins and angiopoietin-like families. Novel therapeutic approach such as antisense oligonucleotides and monoclonal antibodies that regulate TGs have been developed in recent decades. In this article, we focus on the biology of LPL and its modulators and review recent clinical application, including genetic studies and clinical trials of novel therapeutics. Optimization of LPL activity to lower TG levels could eventually reduce incident atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in conjunction with successful LDL-C reduction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The chylomicron saga: time to focus on postprandial metabolism
Alejandro Gugliucci
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sanghuangporus vaninii extract ameliorates hyperlipidemia in rats by mechanisms identified with transcriptome analysis
Ning Gao, Yuanzhen Liu, Guangjie Liu, Bo Liu, Yupeng Cheng
Food Science & Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting host-specific metabolic pathways—opportunities and challenges for anti-infective therapy
Monika I. Konaklieva, Balbina J. Plotkin
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity, dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular disease: A joint expert review from the obesity medicine association and the National Lipid Association 2024
Harold Edward Bays, Carol Kirkpatrick, Kevin C. Maki, Peter P. Toth, Ryan T. Morgan, Justin Tondt, Sandra Michelle Christensen, Dave Dixon, Terry A. Jacobson
Obesity Pillars.2024; : 100108. CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Xanthohumol, a prenylated chalcone, regulates lipid metabolism by modulating the LXRα/RXR-ANGPTL3-LPL axis in hepatic cell lines and high-fat diet-fed zebrafish models
Wan-Yun Gao, Pei-Yi Chen, Hao-Jen Hsu, Je-Wen Liou, Chia-Ling Wu, Ming-Jiuan Wu, Jui-Hung Yen
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 174: 116598. CrossRef - High producer variant of lipoprotein lipase may protect from hepatocellular carcinoma in alcohol-associated cirrhosis
Franziska Schmalz, Janett Fischer, Hamish Innes, Stephan Buch, Christine Möller, Madlen Matz-Soja, Witigo von Schönfels, Benjamin Krämer, Bettina Langhans, Alexandra Klüners, Michael Soyka, Felix Stickel, Jacob Nattermann, Christian P. Strassburg, Thomas
JHEP Reports.2023; 5(4): 100684. CrossRef - Measurement of Serum Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Triglyceride-Rich Remnant Cholesterol as Independent Predictors of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Possibilities and Limitations
Dieter Lütjohann, Hans-Ulrich Klör, Frans Stellaard
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2202. CrossRef - Influence of antipsychotic medications on hyperlipidemia risk in patients with schizophrenia: evidence from a population-based cohort study and in vitro hepatic lipid homeostasis gene expression
Tien-Yuan Wu, Ni Tien, Cheng-Li Lin, Yu-Cun Cheah, Chung Y. Hsu, Fuu-Jen Tsai, Yi-Jen Fang, Yun-Ping Lim
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Metabolism: Key Regulators of Their Flux
Alejandro Gugliucci
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4399. CrossRef - Sugar and Dyslipidemia: A Double-Hit, Perfect Storm
Alejandro Gugliucci
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(17): 5660. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Updated Overview
Sang Heon Suh, Soo Wan Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 612. CrossRef - Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α in Lipoprotein Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Elena Valeria Fuior, Evangelia Zvintzou, Theodosios Filippatos, Katerina Giannatou, Victoria Mparnia, Maya Simionescu, Anca Violeta Gafencu, Kyriakos E. Kypreos
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2696. CrossRef - Developing a model to predict the early risk of hypertriglyceridemia based on inhibiting lipoprotein lipase (LPL): a translational study
Julia Hernandez-Baixauli, Gertruda Chomiciute, Juan María Alcaide-Hidalgo, Anna Crescenti, Laura Baselga-Escudero, Hector Palacios-Jordan, Elisabet Foguet-Romero, Anna Pedret, Rosa M. Valls, Rosa Solà, Miquel Mulero, Josep M. Del Bas
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The chylomicron saga: time to focus on postprandial metabolism

Original Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
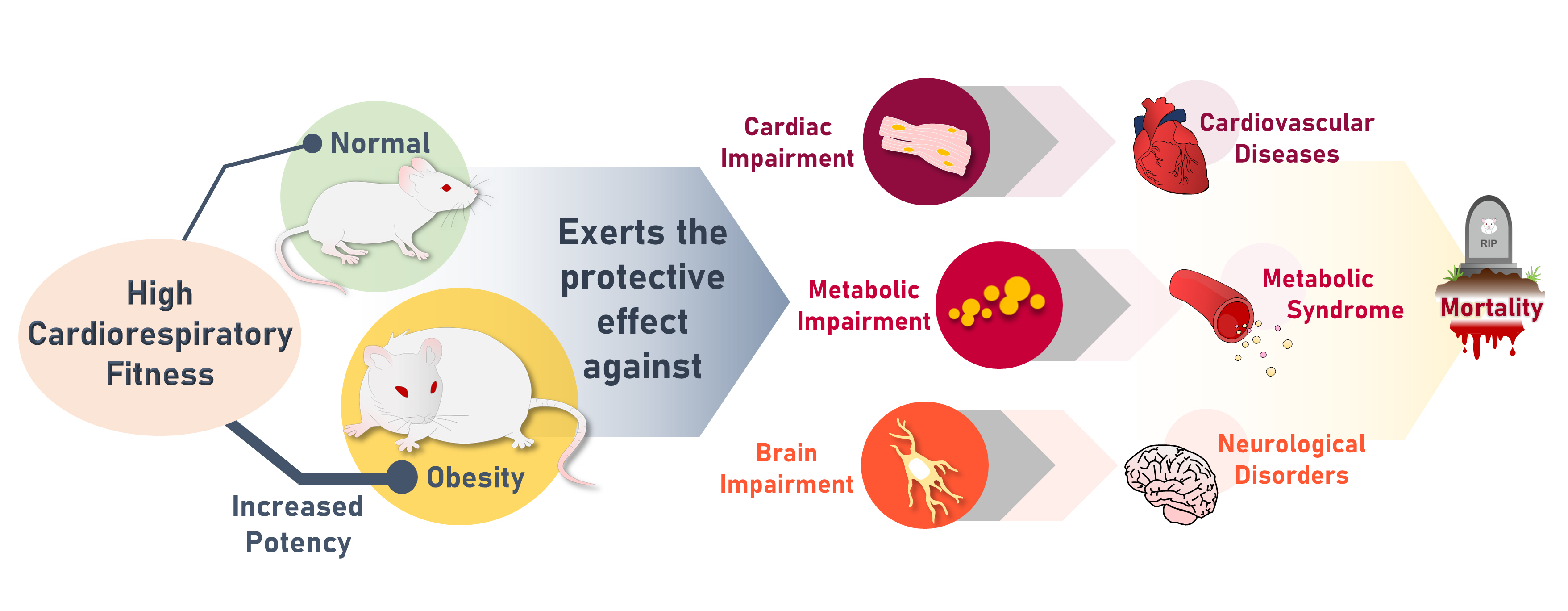
- High Cardiorespiratory Fitness Protects against Molecular Impairments of Metabolism, Heart, and Brain with Higher Efficacy in Obesity-Induced Premature Aging
- Patcharapong Pantiya, Chanisa Thonusin, Natticha Sumneang, Benjamin Ongnok, Titikorn Chunchai, Sasiwan Kerdphoo, Thidarat Jaiwongkam, Busarin Arunsak, Natthaphat Siri-Angkul, Sirawit Sriwichaiin, Nipon Chattipakorn, Siriporn C. Chattipakorn
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):630-640. Published online August 5, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1430
- 4,007 View
- 121 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
High cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) protects against age-related diseases. However, the mechanisms mediating the protective effect of high intrinsic CRF against metabolic, cardiac, and brain impairments in non-obese versus obese conditions remain incompletely understood. We aimed to identify the mechanisms through which high intrinsic CRF protects against metabolic, cardiac, and brain impairments in non-obese versus obese untrained rats.
Methods
Seven-week-old male Wistar rats were divided into two groups (n=8 per group) to receive either a normal diet or a highfat diet (HFD). At weeks 12 and 28, CRF, carbohydrate and fatty acid oxidation, cardiac function, and metabolic parameters were evaluated. At week 28, behavior tests were performed. At the end of week 28, rats were euthanized to collect heart and brain samples for molecular studies.
Results
The obese rats exhibited higher values for aging-related parameters than the non-obese rats, indicating that they experienced obesity-induced premature aging. High baseline CRF levels were positively correlated with several favorable metabolic, cardiac, and brain parameters at follow-up. Specifically, the protective effects of high CRF against metabolic, cardiac, and brain impairments were mediated by the modulation of body weight and composition, the lipid profile, substrate oxidation, mitochondrial function, insulin signaling, autophagy, apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, cardiac function, neurogenesis, blood-brain barrier, synaptic function, accumulation of Alzheimer’s disease-related proteins, and cognition. Interestingly, this effect was more obvious in HFD-fed rats.
Conclusion
The protective effect of high CRF is mediated by the modulation of several mechanisms. These effects exhibit greater efficacy under conditions of obesity-induced premature aging. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations that Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Mass Index Loss Have with Deficit Accumulation Frailty
KAYLONI OLSON, DENISE K. HOUSTON, JOHNATHAN ROSS, RENA R. WING, FELICIA R. SIMPSON, AMBARISH PANDEY, MICHAEL P. WALKUP, MIA YANG, MARK A. ESPELAND
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.2024; 56(4): 717. CrossRef - Interplay between obesity and aging on myocardial geometry and function: Role of leptin-STAT3-stress signaling
Wei Jin, Fei Tu, Feng Dong, Qinqin Deng, Miyesaier Abudureyimu, Wei Yu, Guo-jun Cai, Jian-ming Pei, Zhaohui Pei, Jun Ren
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects.2023; 1867(2): 130281. CrossRef - Epidemiological, mechanistic, and practical bases for assessment of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle status in adults in healthcare settings
Jaime A. Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 123(5): 945. CrossRef
- Associations that Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Mass Index Loss Have with Deficit Accumulation Frailty

Review Articles
- Adrenal Gland
- Long-Term Outcomes of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- Anna Nordenström, Svetlana Lajic, Henrik Falhammar
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):587-598. Published online July 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1528
- 30,201 View
- 275 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - A plethora of negative long-term outcomes have been associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH). The causes are multiple and involve supra-physiological gluco- and mineralocorticoid replacement, excess adrenal androgens both intrauterine and postnatal, elevated steroid precursor and adrenocorticotropic hormone levels, living with a congenital condition as well as the proximity of the cytochrome P450 family 21 subfamily A member 2 (CYP21A2) gene to other genes. This review aims to discuss the different long-term outcomes of CAH.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased Prevalence of Accidents and Injuries in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: A Population-based Cohort Study
Henrik Falhammar, Angelica Lindén Hirschberg, Agneta Nordenskjöld, Henrik Larsson, Anna Nordenström
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1175. CrossRef - International Newborn Screening Practices for the Early Detection of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Tracey A. Conlon, Colin P. Hawkes, Jennifer J. Brady, J. Gerard Loeber, Nuala Murphy
Hormone Research in Paediatrics.2024; 97(2): 113. CrossRef - Low renin forms of monogenic hypertension: review of the evidence
Ugochi Chinenye Okorafor, Uchechi Chioma Okorafor
Journal of Clinical Medicine of Kazakhstan.2024; 21(1): 14. CrossRef - Increased risk of nephrolithiasis: an emerging issue in children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Mariangela Chiarito, Crescenza Lattanzio, Vito D’Ascanio, Donatella Capalbo, Paolo Cavarzere, Anna Grandone, Francesca Aiello, Giorgia Pepe, Malgorzata Wasniewska, Thomas Zoller, Mariacarolina Salerno, Maria Felicia Faienza
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: New biomarkers and adult treatments
Bleuenn Dreves, Yves Reznik, Antoine Tabarin
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2023; 84(4): 472. CrossRef - Interpretation of Steroid Biomarkers in 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency and Their Use in Disease Management
Kyriakie Sarafoglou, Deborah P Merke, Nicole Reisch, Hedi Claahsen-van der Grinten, Henrik Falhammar, Richard J Auchus
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(9): 2154. CrossRef - Impact of Newborn Screening on Adult Height in Patients With Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
Heike Hoyer-Kuhn, Alexander J Eckert, Gerhard Binder, Walter Bonfig, Angelika Dübbers, Stefan Riedl, Joachim Woelfle, Helmuth G Dörr, Reinhard W Holl
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(11): e1199. CrossRef - Specialty grand challenge in adrenal endocrinology
Henrik Falhammar
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Contexts of care for people with differences of sex development
Alexandra E. Kulle, Martina Jürgensen, Ulla Döhnert, Lisa Malich, Louise Marshall, Olaf Hiort
Medizinische Genetik.2023; 35(3): 181. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risk in Cuban adolescents and young adults with congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Tania M. Espinosa Reyes, Alba Katherine Pesántez Velepucha, Julio Oscar Cabrera Rego, Wendy Valdés Gómez, Emma Domínguez Alonso, Henrik Falhammar
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Landscape of Adrenal Tumours in Patients with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Mara Carsote, Ana-Maria Gheorghe, Claudiu Nistor, Alexandra-Ioana Trandafir, Oana-Claudia Sima, Anca-Pati Cucu, Adrian Ciuche, Eugenia Petrova, Adina Ghemigian
Biomedicines.2023; 11(11): 3081. CrossRef - Editorial: Recent advances in diagnosis and treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Semra Çaglar Çetinkaya
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Approach of Heterogeneous Spectrum Involving 3beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase 2 Deficiency
Andreea Gabriela Nicola, Mara Carsote, Ana-Maria Gheorghe, Eugenia Petrova, Alexandru Dan Popescu, Adela Nicoleta Staicu, Mihaela Jana Țuculină, Cristian Petcu, Ionela Teodora Dascălu, Tiberiu Tircă
Diagnostics.2022; 12(9): 2168. CrossRef - Effetti di Crinecerfont sulla secrezione di ACTH nell’iperplasia surrenalica congenita: uno studio di fase 2
Marianna Rita Stancampiano, Silvia Laura Carla Meroni, Giovanna Weber, Gianni Russo
L'Endocrinologo.2022; 23(6): 662. CrossRef
- Increased Prevalence of Accidents and Injuries in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: A Population-based Cohort Study

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Extra-Glycemic Effects of Anti-Diabetic Medications: Two Birds with One Stone?
- Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):415-429. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.304

- 4,478 View
- 261 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The world is suffering from a rapid increase in the number of people with diabetes due to the increased prevalence of obesity and lengthened life span. Since the development of insulin thanks to the efforts of Prof. Banting and Dr. Best in 1922, for which they won the Nobel Prize, remarkable developments in anti-diabetic medications have dramatically lengthened the lifespan of patients with diabetes. However, the control rate of hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes remains unsatisfactory, since glycemic control requires both medication and lifestyle modifications to slow the deterioration of pancreatic beta-cell function and prevent diabetic complications. From the initial “triumvirate” to the “ominous octet,” and now the “egregious eleven,” the number of organs recognized as being involved in hyperglycemia and diabetes has increased with the development of anti-diabetic medications. Recent unexpected results from outcome trials of anti-diabetic medications have enabled anti-diabetic medications to be indicated for the prevention of chronic kidney disease and heart failure, even in patients without diabetes. In this review, I would like to summarize the extra-glycemic effects of anti-diabetic medications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung‐Do Han, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 671. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide Receptor Agonist Inhibits Angiotensin II-Induced Proliferation and Migration in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Ameliorates Phosphate-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Calcification
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 83. CrossRef - To do one and to get more: Part I. Diabetes and bone
Wen-Ling Lee, Peng-Hui Wang, Szu-Ting Yang, Chia-Hao Liu, Wen-Hsun Chang, Fa-Kung Lee
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2022; 85(10): 965. CrossRef
- Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients

Original Articles
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
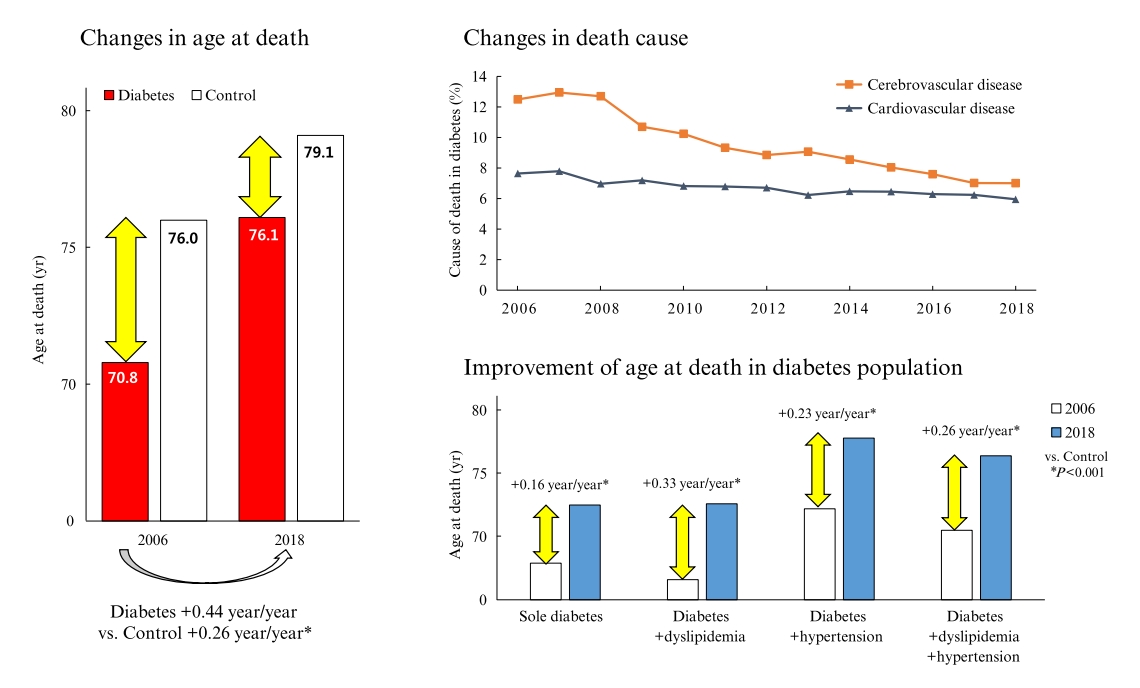
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
- Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):466-474. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1440
- 3,878 View
- 137 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetes is a leading cause of death that is responsible for 1.6 million annual deaths worldwide. However, the life expectancy and age at death of people with diabetes have been a matter of debate.
Methods
The National Health Insurance Service claims database, merged with death records from the National Statistical Information Service in Korea from 2006 to 2018, was analyzed.
Results
In total, 1,432,567 deaths were collected. The overall age at death increased by 0.44 and 0.26 year/year in the diabetes and control populations, respectively. The disparity in the mean age at death between the diabetes and control populations narrowed from 5.2 years in 2006 to 3.0 years in 2018 (p<0.001). In a subgroup analysis according to the presence of comorbid diseases, the number and proportion of deaths remained steady in the group with diabetes only, but steadily increased in the groups with diabetes combined with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension. Compared to the control population, the increase in the mean death age was higher in the population with diabetes. This trend was more prominent in the groups with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension than in the diabetes only group. Deaths from vascular disease and diabetes decreased, whereas deaths from cancer and pneumonia increased. The decline in the proportion of deaths from vascular disease was greater in the diabetes groups with hypertension and/or dyslipidemia than in the control population.
Conclusion
The age at death in the population with diabetes increased more steeply and reached a comparable level to those without diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Cause-of-Death Mortality in Children and Young Adults with Diabetes: A Nationwide 10-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study
Iee-Ho Choi, Sang-Woo Yeom, Sun-Young Kim, Jihye You, Jong-Seung Kim, Minsun Kim
Children.2023; 10(2): 358. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef
- Analysis of Cause-of-Death Mortality in Children and Young Adults with Diabetes: A Nationwide 10-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
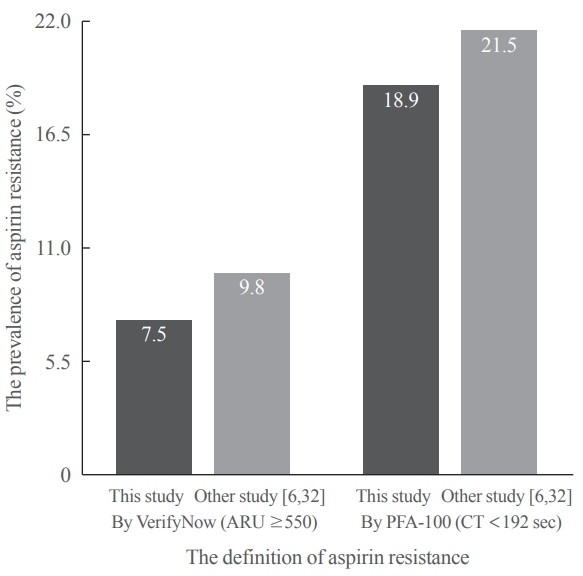
- Comparative Study of Ex Vivo Antiplatelet Activity of Aspirin and Cilostazol in Patients with Diabetes and High Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
- Sangmo Hong, Woo Je Lee, Cheol-Young Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):233-242. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1353
- 3,797 View
- 165 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The role of aspirin in primary cardiovascular disease prevention in patients with diabetes remains controversial. However, some studies have suggested beneficial effects of cilostazol on cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. We prospectively investigated the antiplatelet effects of cilostazol compared with aspirin in patients with diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods
We randomly assigned 116 patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors but no evident cardiovascular disease to receive aspirin at a dose of 100 mg or cilostazol at a dose of 200 mg daily for 14 days. The primary efficacy outcome was antiplatelet effects of aspirin and cilostazol assessed with the VerifyNow system (aspirin response units [ARU]) and PFA-100 (closure time [CT]). Secondary outcomes were changes of clinical laboratory data (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02933788).
Results
After 14 days, there was greater decrease in ARU in aspirin (–28.9%±9.9%) compared cilostazol (–0.4%±7.1%, P<0.001) and was greater increase in CT in aspirin (99.6%±63.5%) compared cilostazol (25.7%±54.1%, P<0.001). The prevalence of aspirin resistance was 7.5% according to VerifyNow (defined by ARU ≥550) and 18.9% according to PFA-100 (CT <192 seconds). Compared with aspirin, cilostazol treatment was associated with increased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (7.1%±12.7% vs. 4.2%±18.0%, P=0.006) and decreased triglycerides (–9.4%±33.7% vs. 4.4%±17.57%, P=0.016). However, there were no significant changes in total and low density lipoprotein cholesterol, C-reactive protein level, and cluster of differentiation 40 ligand between cilostazol and aspirin groups.
Conclusion
Aspirin showed better antiplatelet effects assessed with VerifyNow and PFA-100 compared with cilostazol. However, there were favorable changes in atherogenic dyslipidemia only in the cilostazol.

Namgok Lecture 2021
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
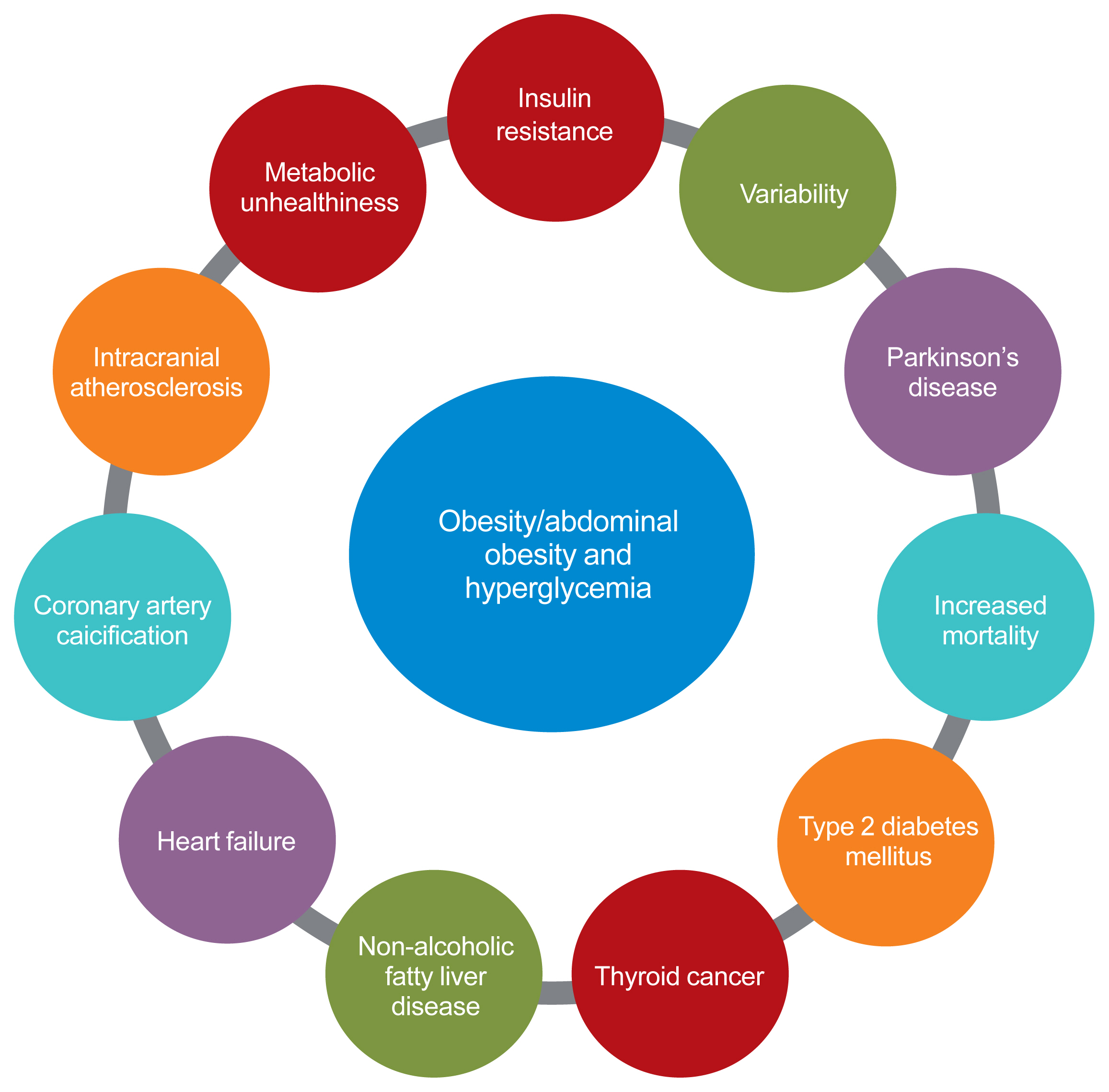
- The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health
- Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):1-8. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.101
- 6,952 View
- 298 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The prevalence of obesity is rapidly increasing worldwide. Obesity should not be understood only as the accumulation of fat in the body, but instead as a phenomenon that exerts different effects on our health according to the place of fat deposition and its stability. Obesity is the starting point of most metabolic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, sleep apnea, and eventually cardiovascular disease. There are different kinds of obesity, ranging from simple obesity to sarcopenic obesity. The main purpose of intervening to address obesity is to decrease the ultimate consequence of obesity—namely, cardiovascular disease. The main mechanism through which obesity, especially abdominal obesity, increases cardiovascular risk is the obesity-induced derangement of metabolic health, leading to the development of metabolic diseases such as diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and metabolic syndrome, which are the main initiators of vascular damage. In this review, I discuss the influence of various types of obesity on the risk of metabolic diseases, and how these diseases increase cardiovascular disease risk.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - Severity of abdominal obesity and cardiometabolic diseases in US adults
S. Wang, S. Shi, Y. Huang, H. Huang, V.W. Zhong
Public Health.2024; 227: 154. CrossRef - Anti-obesity effects of fucoidan from
Sargassum thunbergii in adipocytes and high fat diet induced obese mice through inhibiting adipogenic specific transcription factor
Hyo-Geun Lee, H.H.A.C.K. Jayawardhana, Fengqi Yang, D.P. Nagahawaththa, N.M. Liyanage, Kyung-Mo Song, Yun-Sang Choi, Seung-Hong Lee, You-Jin Jeon, Min-Cheol Kang
Food Science and Human Wellness.2024; 13(3): 1608. CrossRef - Association of a High Healthy Eating Index Diet with Long-Term Visceral Fat Loss in a Large Longitudinal Study
Sunmin Park
Nutrients.2024; 16(4): 534. CrossRef - Ancistrocladus tectorius Extract Inhibits Obesity by Promoting Thermogenesis and Mitochondrial Dynamics in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice
Minju Kim, Jin Hyub Paik, Hwa Lee, Min Ji Kim, Sang Mi Eum, Soo Yong Kim, Sangho Choi, Ho-Yong Park, Hye Gwang Jeong, Tae-Sook Jeong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3743. CrossRef - Biological Activity Evaluation of Olive, Grape, and Fig at Various Mixing Ratios
Chan-Hwi Lee, So-Young Lee, Ae-Jung Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2024; 22(1): 91. CrossRef - Investigation and Comparison of Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index Coupled with Gestational Weight Gain on Maternal–Fetal Complications Based on US and Chinese Guidelines: A Retrospective Study
Wan-Ju Kung, Hsin-Yi Kuo, Ching-Feng Chang, Yeong-Hwa Zen, Ching-Chiang Lin
Reproductive Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanistic insights into dietary (poly)phenols and vascular dysfunction-related diseases using multi-omics and integrative approaches: Machine learning as a next challenge in nutrition research
Dragan Milenkovic, Tatjana Ruskovska
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2023; 89: 101101. CrossRef - Pharmacological Support for the Treatment of Obesity—Present and Future
Marcin Kosmalski, Kacper Deska, Bartłomiej Bąk, Monika Różycka-Kosmalska, Tadeusz Pietras
Healthcare.2023; 11(3): 433. CrossRef - Prioritizing obesity treatment: expanding the role of cardiologists to improve cardiovascular health and outcomes
Donna H. Ryan, John E. Deanfield, Stephan Jacob
Cardiovascular Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 12(1): e0279. CrossRef - Adipopenia is associated with osteoporosis in community-dwelling non-underweight adults independent of sarcopenia
Seunghyun Lee, Kyoungmyoung Ko, Sungjae Shin, Hye Sun Park, Namki Hong, Yumie Rhee
Archives of Osteoporosis.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Design, synthesis and evaluation of 2-pyrimidinylindole derivatives as anti-obesity agents by regulating lipid metabolism
Shi-Yao Guo, Li-Yuan Wei, Bing-Bing Song, Yu-Tao Hu, Zhi Jiang, Dan-Dan Zhao, Yao-Hao Xu, Yu-Wei Lin, Shu-Min Xu, Shuo-Bin Chen, Zhi-Shu Huang
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 260: 115729. CrossRef - Short-Term L-Citrulline Supplementation Does Not Affect Blood Pressure, Pulse Wave Reflection, or Arterial Stiffness at Rest and during Isometric Exercise in Older Males
Andrea Tryfonos, Filippos Christodoulou, George M. Pamboris, Stephanos Christodoulides, Anastasios A. Theodorou
Sports.2023; 11(9): 177. CrossRef - Skinfold Thickness as a Cardiometabolic Risk Predictor in Sedentary and Active Adult Populations
Sughey González-Torres, Luis Miguel Anaya-Esparza, Gabriel Fermín Trigueros del Valle, Edgar Alfonso Rivera-León, Zuamí Villagrán, Sergio Sánchez-Enríquez
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(9): 1326. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Fenofibrate enhances lipid deposition via modulating PPARγ, SREBP-1c, and gut microbiota in ob/ob mice fed a high-fat diet
Ying Zhang, Xiu-Bin Jia, Yun-Chao Liu, Wen-Qian Yu, Yan-Hong Si, Shou-Dong Guo
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive Roles of Basal Metabolic Rate and Body Water Distribution in Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: The link to Carbohydrates
Lizheng Guan, Tiantian Li, Xuan Wang, Kang Yu, Rong Xiao, Yuandi Xi
Nutrients.2022; 14(19): 3911. CrossRef - Metabolic risk factors in patients with comorbidity in Ufa primary health care
O.V. Molchanova, A.V. Mamaeva, A.R. Dunayeva, Z.A. Lust, E.M. Faskhetdinova, R.N. Shepel, D.O. Orlov, L.M. Zhamalov, G.F. Andreeva, O.M. Drapkina
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2022; 25(9): 39. CrossRef - Assessment of Vitamin D Levels in Relation to Statin Therapy in Elderly Hypertensive Patients with Comorbidities
Kinga-Ilona Nyulas, Zsuzsánna Simon-Szabó, Zoltán Preg, Sándor Pál, Arundhati Sharma, Tünde Pál, Márta Germán-Salló, Enikő Nemes-Nagy
Journal of Interdisciplinary Medicine.2022; 7(4): 88. CrossRef
- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study

Original Articles
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Frequency of Exposure to Impaired Fasting Glucose and Risk of Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes
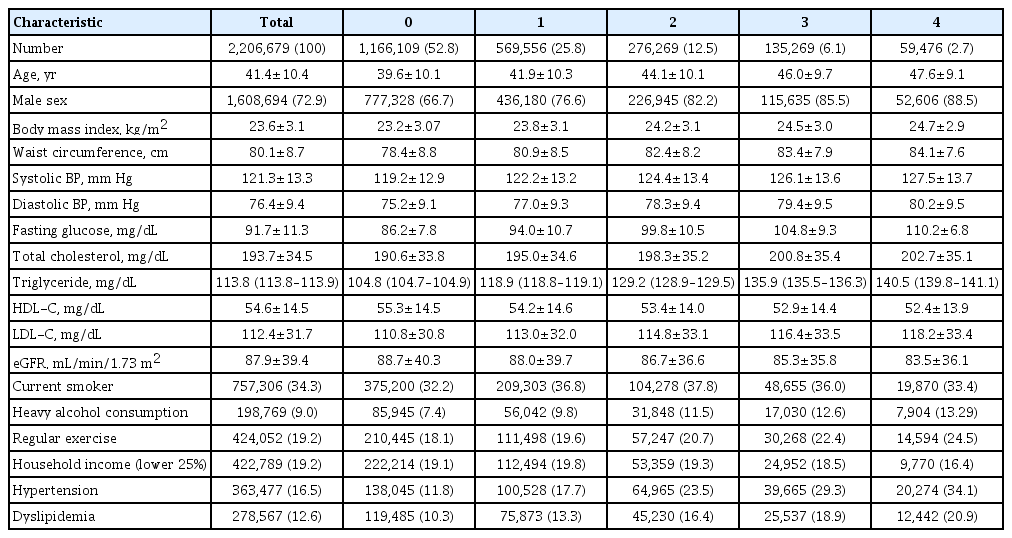
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Mee Kyoung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1007-1015. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1218
- 3,814 View
- 126 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Metabolic abnormalities, such as impaired fasting glucose (IFG), are dynamic phenomena; however, it is unclear whether the timing of IFG exposure and cumulative exposure to IFG are related to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality risk.
Methods
Data were extracted from a nationwide population-based cohort in South Korea for adults (n=2,206,679) who were free of diabetes and had 4 years of consecutive health examination data. Fasting blood glucose levels of 100 to 125 mg/dL were defined as IFG, and the number of IFG diagnoses for each adult in the 4-year period was tabulated as the IFG exposure score (range, 0 to 4). Adults with persistent IFG for the 4-year period received a score of 4.
Results
The median follow-up was 8.2 years. There were 24,820 deaths, 13,502 cases of stroke, and 13,057 cases of myocardial infarction (MI). IFG exposure scores of 1, 2, 3, and 4 were associated with all-cause mortality (multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08 to 1.15; aHR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.20; aHR, 1.20; 95% CI, 1.15 to 1.25; aHR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.11 to 1.25, respectively) compared with an IFG exposure score of 0. Adjusting for hypertension and dyslipidemia attenuated the slightly increased risk of MI or stroke associated with high IFG exposure scores, but significant associations for allcause mortality remained.
Conclusion
The intensity of IFG exposure was associated with an elevated risk of all-cause mortality, independent of cardiovascular risk factors. The association between IFG exposure and CVD risk was largely mediated by the coexistence of dyslipidemia and hypertension. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease
Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
npj Parkinson's Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes severity is strongly associated with the risk of active tuberculosis in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study with a 6-year follow-up
Ji Young Kang, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and Validation of a Model for Predicting Impaired Fasting Glucose Based on More Than 4000 General Population
Cuicui Wang, Xu Zhang, Chenwei Li, Na Li, Xueni Jia, Hui Zhao
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 1415. CrossRef - Factors Affecting High Body Weight Variability
Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 163. CrossRef - Exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of stroke in adults: a meta-analysis
Min Cheol Chang, Seung Min Chung, Sang Gyu Kwak
Reviews on Environmental Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Longitudinal Retrospective Observational Study on Obesity Indicators and the Risk of Impaired Fasting Glucose in Pre- and Postmenopausal Women
Myung Ji Nam, Hyunjin Kim, Yeon Joo Choi, Kyung-Hwan Cho, Seon Mee Kim, Yong-Kyun Roh, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Yong-Gyu Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Do-Hoon Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(10): 2795. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Lipid cutoffs for increased cardiovascular disease risk in non-diabetic young people
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 29(14): 1866. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef - Additive interaction of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in cancer patient mortality risk
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Cardiovascular Outcomes of Obesity According to Menopausal Status: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Bo Kyung Koo, Sang-Hyun Park, Kyungdo Han, Min Kyong Moon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1029-1041. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1197
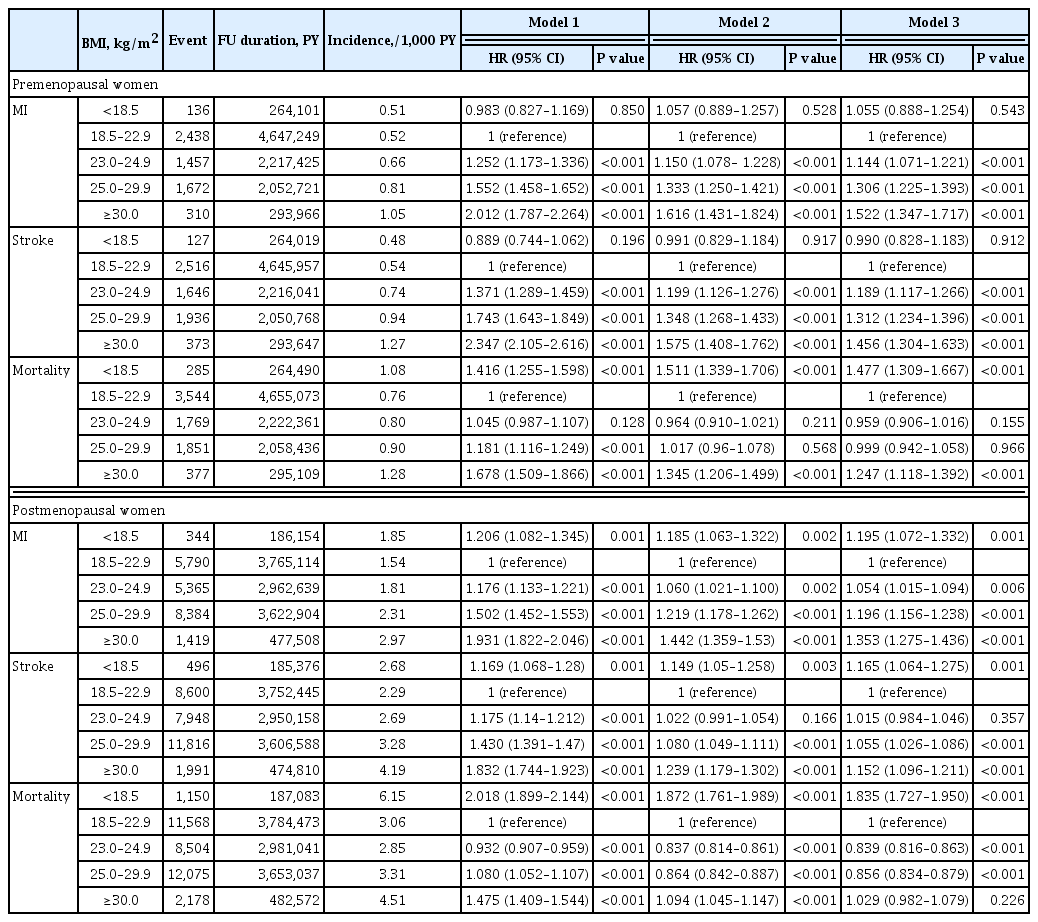
- 3,664 View
- 117 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We estimated the effect of obesity on the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality in women according to menopausal status.
Methods
Women aged 40 to 69 years under routine health check-ups provided by the National Health Insurance Service in 2009 were followed up till 2018 (n=2,208,559).
Results
In premenopausal women, a significant increment of mortality rate was found in underweight and obesity class II (hazard ratio [HR], 1.48; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31 to 1.67; and HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.39) compared to normal body mass index (BMI); overweight and obesity class I did not affect mortality rate. In postmenopausal women, obesity as well as overweight status reduced the risk of mortality compared to normal BMI (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.83 to 0.88; and HR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.82 to 0.86). By contrast, there was a linear association between CVD and BMI above the normal range irrespective of menopausal status, which was attenuated in diabetic women.
Conclusion
The current study replicated the J-shaped relationship between BMI and mortality, being more prominent in the postmenopausal group. The risk of CVD was linearly increased as BMI was increased above the normal range irrespective of menopausal status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biosocial predictors and blood pressure goal attainment among postmenopausal women with hypertension
Geetha Kandasamy, Thangamani Subramani, Gigi Sam, Mona Almanasef, Tahani Almeleebia, Eman Shorog, Asma M. Alshahrani, Amjad Hmlan, Atheer Y. Al Suhaym, Kousalya Prabahar, Vinoth Prabhu Veeramani, Palanisamy Amirthalingam
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease
Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
npj Parkinson's Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Outcomes according to Comorbidities and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 45. CrossRef - The effect of menopause on cardiovascular risk factors according to body mass index in middle-aged Korean women
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Aysha Almas
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283393. CrossRef - Low‐quality muscle mass rather than normal‐quality muscle mass determines fibrosis progression in biopsy‐proven NAFLD
Yun Kyu Lee, Bo Kyung Koo, Sae Kyung Joo, Dong Hyeon Lee, Heejoon Jang, Jee Won Chai, Myoung Seok Lee, Si Won Jang, Young Ho So, Jeong Hwan Park, Mee Soo Chang, Won Kim
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2023; 58(3): 322. CrossRef - Diabetes severity is strongly associated with the risk of active tuberculosis in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study with a 6-year follow-up
Ji Young Kang, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of exercise initiation and smoking cessation after new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus on risk of mortality and cardiovascular outcomes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-pharmacologic treatment for obesity
Bo Kyung Koo
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(7): 400. CrossRef
- Biosocial predictors and blood pressure goal attainment among postmenopausal women with hypertension


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



