Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Clinical Study
- Longitudinal Changes of High Molecular Weight Adiponectin are Associated with Postpartum Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Dong-Hwa Lee, Jung Ah Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):114-122. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.831
- 3,902 View
- 102 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The influence of serial changes of adipokines on maternal glucose metabolism from pregnancy to postpartum periods in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus (pGDM) has not been thoroughly explored. We tried to examine the relationship between the serial changes of adipokines and the development of diabetes mellitus (DM) in women with pGDM.
Methods
We longitudinally measured following adipokines: high molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin, retinol-binding protein-4 (RBP-4), lipocalin-2, and chemerin, during pregnancy, and at 2 months and 3 years after delivery. Based on glucose status at postpartum 3 years, we divided into three groups: normal glucose tolerance (GDM-NGT, n=20), impaired glucose tolerance (GDM-IGT, n=23), and GDM-DM (n=22). We analyzed the correlations between adipokines and various metabolic parameters.
Results
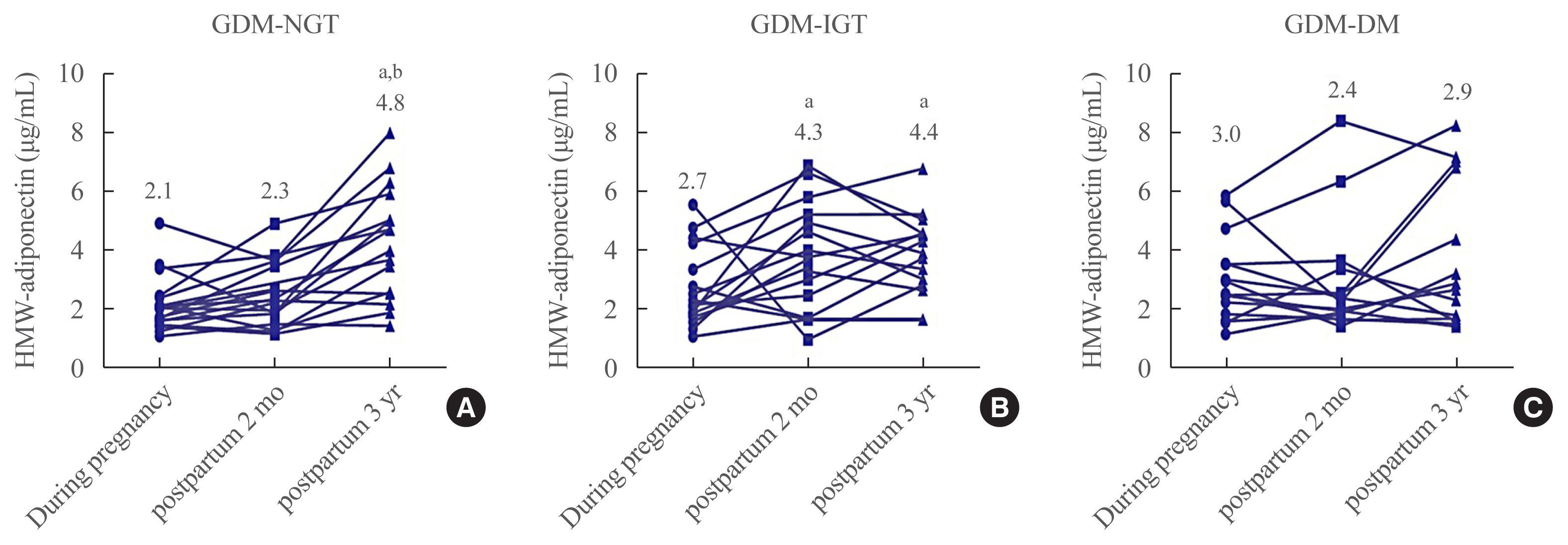
Plasma HMW adiponectin levels were not different among the three groups during pregnancy. However, HMW adiponectin levels increased at 3 years after the delivery in women with GDM-NGT compared with women with GDM-DM. In the GDM-IGT group, HMW adiponectin levels increased at 2 months postpartum compared to pregnancy period. In contrast, HMW adiponectin levels showed no alternation after parturition in women with GDM-DM. HMW adiponectin was negatively correlated with body mass index and a homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance. Other adipokines such as RBP-4, lipocalin-2, and chemerin neither showed any differences among the groups nor any significant correlations with 3 years postpartum status of glucose intolerance.
Conclusion
Serial changes of HMW adiponectin are associated with the maintenance of glucose metabolism in women with pGDM after delivery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reproductive risk factors across the female lifecourse and later metabolic health
Amy R. Nichols, Jorge E. Chavarro, Emily Oken
Cell Metabolism.2024; 36(2): 240. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Colostral Appetite-Regulating Adipokines
Jolanta Lis-Kuberka, Marta Berghausen-Mazur, Magdalena Orczyk-Pawiłowicz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3853. CrossRef - The levels of osteopontin in human milk of Chinese mothers and its associations with maternal body composition
Huijuan Ruan, Qingya Tang, Xuan Zhao, Yajie Zhang, Xuelin Zhao, Yi Xiang, Wei Geng, Yi Feng, Wei Cai
Food Science and Human Wellness.2022; 11(5): 1419. CrossRef - Association of circulatory adiponectin with the parameters of Madras Diabetes Research Foundation-Indian Diabetes Risk Score
MohdD Khan, MohammadK Ahmad, Roshan Alam, Saba Khan, Geeta Jaiswal, MohammadM Khan
Journal of Diabetology.2022; 13(4): 331. CrossRef
- Reproductive risk factors across the female lifecourse and later metabolic health

- Clinical Study
- Serum Adiponectin and Progranulin Level in Patients with Benign Thyroid Nodule or Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Ji-Sup Yun, Cheol-Young Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):396-406. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.396

- 5,609 View
- 107 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity is associated with thyroid cancer risk. Adiponectin has insulin-sensitizing and anti-inflammatory effects, while progranulin is associated with inflammation and tumorigenesis. We investigated serum adiponectin and progranulin levels in patients with benign thyroid nodule (benign group) and papillary thyroid cancer (PTC; PTC group). The associations between these levels and the clinicopathological features of PTC were evaluated.
Methods
We included 157 patients who underwent thyroid surgery (17% of benign and 83% of PTC group). Clinicopathological features including size, lymph node metastasis, extrathyroidal extension (ETE), multifocality, American Thyroid Association risk stratification were evaluated.
Results
The age was 42.0 years, and 69% were female. Serum adiponectin and progranulin levels were 6.3 μg/mL and 101.5 ng/mL in the benign group and 5.4 μg/mL and 106.1 ng/mL in the PTC group, respectively (P=0.6 and P=0.4, respectively). Serum adiponectin levels showed no significant differences according to clinicopathological features of PTC. The proportions of patients with primary tumor size >1 cm were 3%, 5%, 8%, and 8% according to serum progranulin level quartiles, respectively (P=0.03). The proportions of patients with microscopic/gross ETE were 8%/0%, 9%/1%, 11%/1%, and 11%/2% according to serum progranulin level quartiles, respectively. Median serum progranulin level was significantly higher in patients with PTC >1 cm than in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (P=0.04, 115.3 ng/mL and 104.7 ng/mL, respectively).
Conclusion
Serum adiponectin and progranulin levels showed no significant difference between benign and PTC groups. Increased serum progranulin levels were significantly associated with PTC >1 cm and microscopic and gross ETE. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the logic and conducting a comprehensive evaluation of AdipoRon-based adiponectin replacement therapy against hormone-related cancers—a systematic review
Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Andreline Franchi Sosin, Caroline Barbalho Lamas, Ricardo de Alvares Goulart, Jesselina Francisco dos Santos Haber, Claudia Rucco Penteado Detregiachi, Sandra Maria Barbalho
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2024; 397(4): 2067. CrossRef - Adiponectin Inhibits the Progression of Obesity-Associated Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Through Autophagy
Changlin Li, Jiao Zhang, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Nan Liang, Haixia Guan, Hui Sun
Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Progranulin Oncogenic Network in Solid Tumors
Elisa Ventura, Giacomo Ducci, Reyes Benot Dominguez, Valentina Ruggiero, Antonino Belfiore, Elena Sacco, Marco Vanoni, Renato V. Iozzo, Antonio Giordano, Andrea Morrione
Cancers.2023; 15(6): 1706. CrossRef - Obesity and thyroid cancer risk
Lauren C. Burrage, Donald S.A. McLeod, Susan J. Jordan
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2023; 30(5): 244. CrossRef - Progranulin promoted the proliferation, metastasis, and suppressed apoptosis via JAK2-STAT3/4 signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Yanxu Dong, Hao Tan, Lidong Wang, Zhen Liu
Cancer Cell International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Risk: An Update
Fabiana Franchini, Giuseppe Palatucci, Annamaria Colao, Paola Ungaro, Paolo Emidio Macchia, Immacolata Cristina Nettore
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(3): 1116. CrossRef - Obesity and Overweight Are Associated with Minimal Extrathyroidal Extension, Multifocality and Bilaterality of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Krzysztof Kaliszewski, Dorota Diakowska, Marta Rzeszutko, Jerzy Rudnicki
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(5): 970. CrossRef - Adiponectin and Thyroid Cancer: Insight into the Association between Adiponectin and Obesity
Yuanyuan Zhou, Ying Yang, Taicheng Zhou, Bai Li, Zhanjian Wang
Aging and disease.2021; 12(2): 597. CrossRef
- Exploring the logic and conducting a comprehensive evaluation of AdipoRon-based adiponectin replacement therapy against hormone-related cancers—a systematic review

- Clinical Study
- Calpain-10 and Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Ji Sun Nam, Jung Woo Han, Sang Bae Lee, Ji Hong You, Min Jin Kim, Shinae Kang, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):364-371. Published online September 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.3.364
- 3,494 View
- 49 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Genetic variations in calpain-10 and adiponectin gene are known to influence insulin secretion and resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Recently, several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in calpain-10 and adiponectin gene have been reported to be associated with type 2 diabetes and various metabolic derangements. We investigated the associations between specific calpain-10 and adiponectin gene polymorphisms and Korean type 2 diabetes patients.
Methods Overall, 249 type 2 diabetes patients and 131 non-diabetic control subjects were enrolled in this study. All the subjects were genotyped for SNP-43 and -63 of calpain-10 gene and G276T and T45G frequencies of the adiponectin gene. The clinical characteristics and measure of glucose metabolism were compared within these genotypes.
Results Among calpain-10 polymorphisms, SNP-63 T/T were more frequent in diabetes patients, and single SNP-63 increases the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. However, SNP-43 in calpain-10 and T45G and intron G276T in adiponectin gene were not significantly associated with diabetes, insulin resistance, nor insulin secretion.
Conclusion Variations in calpain-10, SNP-63 seems to increase the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in Koreans while SNP-43 and adiponectin SNP-45, -276 are not associated with impaired glucose metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decoding type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk variants in Pakistani Pashtun ethnic population using the nascent whole exome sequencing and MassARRAY genotyping: A case-control association study
Asif Jan, Zakiullah, Sajid Ali, Basir Muhammad, Amina Arshad, Yasar Shah, Haji Bahadur, Hamayun Khan, Fazli Khuda, Rani Akbar, Kiran Ijaz, Giuseppe Novelli
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(1): e0281070. CrossRef - Silencing LncRNA PVT1 Reverses High Glucose-Induced Regulation of the
High Expression of PVT1 in HRMECs by Targeting miR-128-3p
Xuyang Wang, Wangling Chen, Wei Lao, Yunxin Chen
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2022; 54(02): 119. CrossRef - Association of CAPN10 (SNP-19) genetic polymorphism and obesity with T2DM: a study on Bengali Hindu caste population
Pranabesh Sarkar, Diptendu Chatterjee, Arup Ratan Bandyopadhyay
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(1): 37. CrossRef - Association of Candidate Gene Polymorphism with Metabolic Syndrome among Mongolian Subjects: A Case-Control Study
Ariunbold Chuluun-Erdene, Orgil Sengeragchaa, Tsend-Ayush Altangerel, Purevjal Sanjmyatav, Batnaran Dagdan, Solongo Battulga, Lundiamaa Enkhbat, Nyamjav Byambasuren, Munkhzol Malchinkhuu, Munkhtstetseg Janlav
Medical Sciences.2020; 8(3): 38. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of the association between adiponectin SNP 45, SNP 276, and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yuwei Dong, Gongping Huang, Xin Wang, Zhaoming Chu, Jingzhi Miao, Houwen Zhou, Mingqing Xu
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(10): e0241078. CrossRef - Association of three SNPs in adiponectin gene with lipid traits of Tianzhu Black Muscovy (Cairina moschata)
Yuan-Yu Qin, Yi-Yu Zhang, Hua-Lun Luo, Lei Wu
Molecular Biology Reports.2019; 46(1): 325. CrossRef
- Decoding type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk variants in Pakistani Pashtun ethnic population using the nascent whole exome sequencing and MassARRAY genotyping: A case-control association study

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Association of Adipokines with Development and Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Chrysoula Boutari, Nikolaos Perakakis, Christos Socrates Mantzoros
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):33-43. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.33
- 8,623 View
- 141 Download
- 111 Web of Science
- 106 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a chronic liver disease affecting 30% of the general population and 40% to 70% of obese individuals. Adipose tissue plays a crucial role in its pathogenesis, as it produces and secretes pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines called adipokines. Adiponectin and leptin have well-determined actions in terms of NAFLD pathophysiology. Adiponectin deficiency is associated with a pro-inflammatory condition, as it is observed in obesity and other metabolic disorders. On the other hand, increased leptin levels, above the normal levels, act as a pro-inflammatory stimulus. Regarding other adipokines (resistin, visfatin, chemerin, retinol-binding protein 4, irisin), data about their contribution to NAFLD pathogenesis and progression are inconclusive. In addition, pharmacological agents like thiazolidinediones (pioglitazone and rosiglitazone), that are used in the management of NAFLD exert favourable effects on adipokine levels, which in turn may contribute to the improvement of liver function. This review summarizes the current knowledge and developments in the association between adipokines and NAFLD and discusses possible therapeutic implications targeting the modulation of adipokine levels as a potential tool for the treatment of NAFLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proanthocyanidins-Based Synbiotics as a Novel Strategy for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Risk Reduction
Wasitha P. D. W. Thilakarathna, H. P. Vasantha Rupasinghe
Molecules.2024; 29(3): 709. CrossRef - The role of novel adipokines and adipose-derived extracellular vesicles (ADEVs): Connections and interactions in liver diseases
Lijun Xie, Huiying Wang, Jinying Hu, Zhuoying Liu, Fang Hu
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 222: 116104. CrossRef - Mechanisms and clinical relevance of the bidirectional relationship of viral infections with metabolic diseases
Nikolaos Perakakis, Hani Harb, Benjamin G Hale, Zsuzsanna Varga, Charlotte Steenblock, Waldemar Kanczkowski, Vasileia Ismini Alexaki, Barbara Ludwig, Peter Mirtschink, Michele Solimena, Nicole Toepfner, Sebastian Zeissig, Manuel Gado, Irene Alma Abela, Fe
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2023; 11(9): 675. CrossRef - Lipocalin‐2 activates hepatic stellate cells and promotes nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in high‐fat diet–fed Ob/Ob mice
Kyung Eun Kim, Jaewoong Lee, Hyun Joo Shin, Eun Ae Jeong, Hye Min Jang, Yu Jeong Ahn, Hyeong Seok An, Jong Youl Lee, Meong Cheol Shin, Soo Kyoung Kim, Won Gi Yoo, Won Ho Kim, Gu Seob Roh
Hepatology.2023; 77(3): 888. CrossRef - Effect of Dietary Intervention, with or without Cointerventions, on Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Renate L. Hall, Elena S. George, Audrey C. Tierney, Anjana J. Reddy
Advances in Nutrition.2023; 14(3): 475. CrossRef - The Anti-Obesity and Anti-Steatotic Effects of Chrysin in a Rat Model of Obesity Mediated through Modulating the Hepatic AMPK/mTOR/lipogenesis Pathways
Ghaleb Oriquat, Inas M. Masoud, Maher A. Kamel, Hebatallah Mohammed Aboudeya, Marwa B. Bakir, Sara A. Shaker
Molecules.2023; 28(4): 1734. CrossRef - Association between caffeine intake and liver biomarkers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Kübra UÇAR, Evrim KAHRAMANOĞLU, Zeynep GÖKTAŞ
Cukurova Medical Journal.2023; 48(1): 177. CrossRef - Changes in liver enzymes are associated with changes in insulin resistance, inflammatory biomarkers and leptin in prepubertal children with obesity
Rosario Valle-Martos, Luis Jiménez-Reina, Ramón Cañete, Rosario Martos, Miguel Valle, María Dolores Cañete
Italian Journal of Pediatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The key role of inflammation in the pathogenesis and management of obesity and CVD
Chrysoula Boutari, Michael A. Hill, Claudio Procaccini, Giuseppe Matarese, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155627. CrossRef - Obesity and diabetes
Chrysoula Boutari, Antea DeMarsilis, Christos S. Mantzoros
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 202: 110773. CrossRef - Identifying a distinct fibrosis subset of NAFLD via molecular profiling and the involvement of profibrotic macrophages
Weiwei He, Yinxiang Huang, Xiulin Shi, Qingxuan Wang, Menghua Wu, Han Li, Qiuhong Liu, Xiaofang Zhang, Caoxin Huang, Xuejun Li
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The emerging significance of mitochondrial targeted strategies in NAFLD treatment
Tao Zhang, Yingli Nie, Jiliang Wang
Life Sciences.2023; 329: 121943. CrossRef - Association between leptin and NAFLD: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Ziwei Guo, Hongbo Du, Yi Guo, Qian Jin, Ruijia Liu, Zhangjun Yun, Jiaxin Zhang, Xiaoke Li, Yong’an Ye
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Liver fat as risk factor of hepatic and cardiometabolic diseases
Münevver Demir, Stefan R. Bornstein, Christos S. Mantzoros, Nikolaos Perakakis
Obesity Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating hormones in biopsy-proven steatotic liver disease and steatohepatitis: A Multicenter Observational Study
Laura Valenzuela-Vallejo, Pavlina Chrysafi, Matina Kouvari, Valentina Guatibonza-Garcia, Sophia C. Mylonakis, Angeliki Katsarou, Ornella Verrastro, Georgios Markakis, Mohammed Eslam, Georgios Papatheodoridis, Geltrude Mingrone, Jacob George, Christos S. M
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155694. CrossRef - Linalool attenuates lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease via Sirt1/Akt/PPRA-α/AMPK and Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathways
P. Tamilmani, V. V. Sathibabu Uddandrao, P. Chandrasekaran, G. Saravanan, Parim Brahma Naidu, S. Sengottuvelu, S. Vadivukkarasi
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2023; 47(10): 102231. CrossRef - Uncovering the Cardiovascular Threat: A Comprehensive Examination of Liver Fibrosis and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Niketa Sharma, Swarupa Chakole, Bhushan Wandile
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fetal programming by androgen excess impairs liver lipid content and PPARg expression in adult rats
Aimé Florencia Silva, Giselle Adriana Abruzzese, María José Ferrer, María Florencia Heber, Silvana Rocío Ferreira, Gloria Edith Cerrone, Alicia Beatriz Motta
Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease.2022; 13(3): 300. CrossRef - Adipose tissue dysfunction and MAFLD in obesity on the scene of COVID-19
Adryana Cordeiro, Amanda Ribamar, Andrea Ramalho
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2022; 46(3): 101807. CrossRef - Comparison of bioelectrical impedance analysis, mass index, and waist circumference in assessing risk for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Katherine J.P. Schwenger, Alexander Kiu, Maryam AlAli, Amnah Alhanaee, Sandra E. Fischer, Johane P. Allard
Nutrition.2022; 93: 111491. CrossRef - Unveiling the Role of the Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in the Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Juan Moreno-Vedia, Josefa Girona, Daiana Ibarretxe, Lluís Masana, Ricardo Rodríguez-Calvo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(1): 197. CrossRef - Predictive and Diagnostic Value of Serum Adipokines in Pregnant Women with Intrahepatic Cholestasis
Nazan Yurtcu, Canan Soyer Caliskan, Huri Guvey, Samettin Celik, Safak Hatirnaz, Andrea Tinelli
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2254. CrossRef - Symposium review: Adipose tissue endocrinology in the periparturient period of dairy cows
Susanne Häussler, Hassan Sadri, Morteza H. Ghaffari, Helga Sauerwein
Journal of Dairy Science.2022; 105(4): 3648. CrossRef - Rodent models and metabolomics in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: What can we learn?
Maria Martin-Grau, Vannina G Marrachelli, Daniel Monleon
World Journal of Hepatology.2022; 14(2): 304. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in HIV/HBV Patients – a Metabolic Imbalance Aggravated by Antiretroviral Therapy and Perpetuated by the Hepatokine/Adipokine Axis Breakdown
Simona Alexandra Iacob, Diana Gabriela Iacob
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Protective Roles of Shilajit in Modulating Resistin, Adiponectin, and Cytokines in Rats with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Baran Ghezelbash, Nader Shahrokhi, Mohammad Khaksari, Gholamreza Asadikaram, Maryam Shahrokhi, Sara Shirazpour
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine.2022; 28(6): 531. CrossRef - The pathophysiological mechanism between hypopituitarism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Xinhe Zhang, Haoyu Tian, Yiling Li
iLIVER.2022; 1(1): 65. CrossRef - Correlation of Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms rs266729 and rs3774261 With Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yong-Tian Zheng, Tian-Mei Xiao, Chan-Xian Wu, Jin-Yan Cheng, Le-Yu Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - An Overview of the TRP-Oxidative Stress Axis in Metabolic Syndrome: Insights for Novel Therapeutic Approaches
Mizael C. Araújo, Suzany H. S. Soczek, Jaqueline P. Pontes, Leonardo A. C. Marques, Gabriela S. Santos, Gisele Simão, Laryssa R. Bueno, Daniele Maria-Ferreira, Marcelo N. Muscará, Elizabeth S. Fernandes
Cells.2022; 11(8): 1292. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio as a predictor of NAFLD in lean and overweight men and women with effect modification by sex
Yoosun Cho, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Hyun‐Suk Jung, Chan‐won Kim, Hyungseok Oh, Mi Kyung Kim, Won Sohn, Hocheol Shin, Sarah H. Wild, Christopher D. Byrne
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(9): 2238. CrossRef - The Perirenal Fat Thickness Was Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yuxian Yang, Shuting Li, Yuechao Xu, Jing Ke, Dong Zhao
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1505. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development: A multifactorial pathogenic phenomena
Aamir Bashir, Ajay Duseja, Arka De, Manu Mehta, Pramil Tiwari
Liver Research.2022; 6(2): 72. CrossRef - Relationship between Liver Stiffness and Steatosis in Obesity Conditions: In Vivo and In Vitro Studies
Francesca Baldini, Mohamad Khalil, Alice Bartolozzi, Massimo Vassalli, Agostino Di Ciaula, Piero Portincasa, Laura Vergani
Biomolecules.2022; 12(5): 733. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Atherosclerosis: Explaining Their Pathophysiology, Association and the Role of Incretin-Based Drugs
Eleftheria Galatou, Elena Mourelatou, Sophia Hatziantoniou, Ioannis S. Vizirianakis
Antioxidants.2022; 11(6): 1060. CrossRef - The epidemiology of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in the United States between 2010-2020: a population-based study
Osama Hamid, Ahmed Eltelbany, Abdul Mohammed, Khaled Alsabbagh Alchirazi, Sushrut Trakroo, Imad Asaad
Annals of Hepatology.2022; 27(5): 100727. CrossRef - Helicobacter Pylori-Induced Gastric Infections: From Pathogenesis to Novel Therapeutic Approaches Using Silver Nanoparticles
Romelia Pop, Alexandru-Flaviu Tăbăran, Andrei Paul Ungur, Andrada Negoescu, Cornel Cătoi
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(7): 1463. CrossRef - Traumatic brain injury alters the gut-derived serotonergic system and associated peripheral organs
Natosha M. Mercado, Guanglin Zhang, Zhe Ying, Fernando Gómez-Pinilla
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2022; 1868(11): 166491. CrossRef - Detangling the interrelations between MAFLD, insulin resistance, and key hormones
Shreya C. Pal, Mohammed Eslam, Nahum Mendez-Sanchez
Hormones.2022; 21(4): 573. CrossRef - Historical Changes in Weight Classes and the Influence of NAFLD Prevalence: A Population Analysis of 34,486 Individuals
Benjamin Kai Yi Nah, Cheng Han Ng, Kai En Chan, Caitlyn Tan, Manik Aggarwal, Rebecca Wenling Zeng, Jieling Xiao, Yip Han Chin, Eunice X. X. Tan, Yi Ping Ren, Douglas Chee, Jonathan Neo, Nicholas W. S. Chew, Michael Tseng, Mohammad Shadab Siddiqui, Arun J.
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 9935. CrossRef - Adipokines in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Are We on the Road toward New Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets?
Vera Francisco, Maria Jesus Sanz, José T. Real, Patrice Marques, Maurizio Capuozzo, Djedjiga Ait Eldjoudi, Oreste Gualillo
Biology.2022; 11(8): 1237. CrossRef - Fatty Liver/Adipose Tissue Dual‐Targeting Nanoparticles with Heme Oxygenase‐1 Inducer for Amelioration of Obesity, Obesity‐Induced Type 2 Diabetes, and Steatohepatitis
Juhyeong Hong, Yong‐Hee Kim
Advanced Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Genome-wide association and Mendelian randomization study of fibroblast growth factor 21 reveals causal associations with hyperlipidemia and possibly NASH
Susanna C. Larsson, Karl Michaëlsson, Marina Mola-Caminal, Jonas Höijer, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155329. CrossRef - Gender differences in the ideal cutoffs of visceral fat area for predicting MAFLD in China
Pingping Yu, Huachao Yang, Xiaoya Qi, Ruixue Bai, Shouqin Zhang, Jianping Gong, Ying Mei, Peng Hu
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Apelin and chemerin receptors are G protein-coupled receptors involved in metabolic as well as reproductive functions: Potential therapeutic implications?
Anthony Estienne, Alice Bongrani, Pascal Froment, Joëlle Dupont
Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research.2021; 16: 86. CrossRef - Metformin dose increase versus added linagliptin in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: An analysis of the J‐LINK study
Yasuji Komorizono, Kaori Hosoyamada, Naoko Imamura, Shoko Kajiya, Yasuhiro Hashiguchi, Norio Ueyama, Hirohiko Shinmaki, Nobuyuki Koriyama, Masako Tsukasa, Tetsuro Kamada
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(3): 832. CrossRef - Gender Differences in the Relationships among Metabolic Syndrome and Various Obesity-Related Indices with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Taiwanese Population
I-Ting Lin, Mei-Yueh Lee, Chih-Wen Wang, Da-Wei Wu, Szu-Chia Chen
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 857. CrossRef - Leptin in Leanness and Obesity
Nikolaos Perakakis, Olivia M. Farr, Christos S. Mantzoros
Journal of the American College of Cardiology.2021; 77(6): 745. CrossRef - Severe insulin resistance syndromes
Angeliki M. Angelidi, Andreas Filippaios, Christos S. Mantzoros
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Liver Enzymes Correlate With Metabolic Syndrome, Inflammation, and Endothelial Dysfunction in Prepubertal Children With Obesity
Rosario Valle-Martos, Miguel Valle, Rosario Martos, Ramón Cañete, Luis Jiménez-Reina, María Dolores Cañete
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)—New Terminology in Pediatric Patients as a Step in Good Scientific Direction?
Marta Flisiak-Jackiewicz, Anna Bobrus-Chociej, Natalia Wasilewska, Dariusz Marek Lebensztejn
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(5): 924. CrossRef - Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy in the Pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Current Evidence and Perspectives
Christina-Maria Flessa, Ioannis Kyrou, Narjes Nasiri-Ansari, Gregory Kaltsas, Athanasios G. Papavassiliou, Eva Kassi, Harpal S. Randeva
Current Obesity Reports.2021; 10(2): 134. CrossRef - Role of Insulin Resistance in MAFLD
Yoshitaka Sakurai, Naoto Kubota, Toshimasa Yamauchi, Takashi Kadowaki
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(8): 4156. CrossRef - Elafibranor and liraglutide improve differentially liver health and metabolism in a mouse model of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis
Nikolaos Perakakis, Konstantinos Stefanakis, Michael Feigh, Sanne S. Veidal, Christos S. Mantzoros
Liver International.2021; 41(8): 1853. CrossRef - Metabolic Spectrum of Liver Failure in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: From NAFLD to NASH to HCC
Hyunmi Kim, Da Som Lee, Tae Hyeon An, Hyun-Ju Park, Won Kon Kim, Kwang-Hee Bae, Kyoung-Jin Oh
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4495. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Metabolic, Genetic, Epigenetic and Environmental Risk Factors
Oriol Juanola, Sebastián Martínez-López, Rubén Francés, Isabel Gómez-Hurtado
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(10): 5227. CrossRef - Serum Visfatin Levels in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abdulrahman Ismaiel, Daniel-Corneliu Leucuta, Stefan-Lucian Popa, Dan L. Dumitrascu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(14): 3029. CrossRef - Possible Hepatoprotective Effect of Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Vitamin E in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Children and Adolescents
Farah D.R. Al-Baiaty, Aziana Ismail, Zarina Abdul Latiff, Khairul Najmi Muhammad Nawawi, Raja Affendi Raja Ali, Norfilza Mohd Mokhtar
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipokines in Insulin Resistance: Current Updates
Utpal Jagdish Dongre
Biosciences Biotechnology Research Asia.2021; 18(2): 357. CrossRef - Metabolic Effects of Gastrectomy and Duodenal Bypass in Early Gastric Cancer Patients with T2DM: A Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study
Young Ki Lee, Eun Kyung Lee, You Jin Lee, Bang Wool Eom, Hong Man Yoon, Young-Il Kim, Soo Jeong Cho, Jong Yeul Lee, Chan Gyoo Kim, Sun-Young Kong, Min Kyong Yoo, Yul Hwangbo, Young-Woo Kim, Il Ju Choi, Hak Jin Kim, Mi Hyang Kwak, Keun Won Ryu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(17): 4008. CrossRef - Chromium picolinate balances the metabolic and clinical markers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Fateme Kooshki, Fardin Moradi, Arash Karimi, Hamid Reza Niazkar, Manouchehr Khoshbaten, Vahid Maleki, Bahram Pourghassem Gargari
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2021; 33(10): 1298. CrossRef - Specificities of lipotoxicity of free fatty acids and cytokine profile in patients with chronic diffuse liver diseases
V. I. Didenko, I. A. Klenina, О. M. Tatarchuk, O. I. Hrabovska, O. P. Petishko
Regulatory Mechanisms in Biosystems.2021; 13(1): 3. CrossRef - Markers of progression of liver fibrotic changes in patients with chronic toxic drug-induced hepatitis
V.I. Didenko, O.M. Tatarchuk, O.P. Petishko, I.S. Konenko, S.L. Melanich
GASTROENTEROLOGY.2021; 55(2): 91. CrossRef - Long-term abuse of a high-carbohydrate diet is as harmful as a high-fat diet for development and progression of liver injury in a mouse model of NAFLD/NASH
Simona Pompili, Antonella Vetuschi, Eugenio Gaudio, Alessandra Tessitore, Roberta Capelli, Edoardo Alesse, Giovanni Latella, Roberta Sferra, Paolo Onori
Nutrition.2020; 75-76: 110782. CrossRef - Targeted Analysis of Three Hormonal Systems Identifies Molecules Associated with the Presence and Severity of NAFLD
Stergios A Polyzos, Nikolaos Perakakis, Chrysoula Boutari, Jannis Kountouras, Wael Ghaly, Athanasios D Anastasilakis, Asterios Karagiannis, Christos S Mantzoros
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(3): e390. CrossRef - Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development
Maria Grazia Refolo, Caterina Messa, Vito Guerra, Brian Irving Carr, Rosalba D’Alessandro
Cancers.2020; 12(3): 641. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Fibrosis Development in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Robert F. Schwabe, Ira Tabas, Utpal B. Pajvani
Gastroenterology.2020; 158(7): 1913. CrossRef - Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat Ratio Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis
Chan-Hee Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyemi Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 165. CrossRef - Alpha-syntrophin deficiency protects against non-alcoholic steatohepatitis associated increase of macrophages, CD8+ T-cells and galectin-3 in the liver
Lisa Rein-Fischboeck, Elisabeth M. Haberl, Ganimete Bajraktari, Susanne Feder, Rebekka Pohl, Elke Eggenhofer, Christa Buechler
Experimental and Molecular Pathology.2020; 113: 104363. CrossRef - Targeting of Secretory Proteins as a Therapeutic Strategy for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
Kyeongjin Kim, Kook Hwan Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(7): 2296. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; New Kids on the Block
Vasilios G. Athyros, Stergios A. Polyzos, Jiannis Kountouras, Niki Katsiki, Panagiotis Anagnostis, Michael Doumas, Christos S. Mantzoros
Current Vascular Pharmacology.2020; 18(2): 172. CrossRef - High body mass index hinders fibrosis improvement in patients receiving long‐term tenofovir therapy in hepatitis B virus‐related cirrhosis
Young Eun Chon, Kyu Sik Jung, Yeonjung Ha, Mi Na Kim, Joo Ho Lee, Seong Gyu Hwang, Sang Hoon Ahn, Do Young Kim, Kwang‐Hyub Han, Jun Yong Park
Journal of Viral Hepatitis.2020; 27(11): 1119. CrossRef - The role of omics in the pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Nikolaos Perakakis, Konstantinos Stefanakis, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2020; 111: 154320. CrossRef - The Selective Peroxisome Proliferator‐Activated Receptor Gamma Modulator CHS‐131 Improves Liver Histopathology and Metabolism in a Mouse Model of Obesity and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Nikolaos Perakakis, Aditya Joshi, Natia Peradze, Konstantinos Stefanakis, Georgia Li, Michael Feigh, Sanne Skovgard Veidal, Glenn Rosen, Michael Fleming, Christos S. Mantzoros
Hepatology Communications.2020; 4(9): 1302. CrossRef - Osteocalcin and osteoprotegerin levels and their relationship with adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Doaa El Amrousy, Dalia El-Afify
Cytokine.2020; 135: 155215. CrossRef - The effect of saffron supplementation on some inflammatory and oxidative markers, leptin, adiponectin, and body composition in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A double‐blind randomized clinical trial
Farnaz Kavianipour, Naheed Aryaeian, Marjan Mokhtare, Reyhanesadat Mirnasrollahiparsa, Leila Jannani, Shahram Agah, Sodabeh Fallah, Nariman Moradi
Phytotherapy Research.2020; 34(12): 3367. CrossRef - Hepatic Lipidomics and Molecular Imaging in a Murine Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model: Insights into Molecular Mechanisms
Ricardo Rodríguez-Calvo, Sara Samino, Josefa Girona, Neus Martínez-Micaelo, Pere Ràfols, María García-Altares, Sandra Guaita-Esteruelas, Alexandra Junza, Mercedes Heras, Oscar Yanes, Xavier Correig, Lluis Masana
Biomolecules.2020; 10(9): 1275. CrossRef - The effect of adiponectin in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the potential role of polyphenols in the modulation of adiponectin signaling
Samukelisiwe C. Shabalala, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla, Lawrence Mabasa, Abidemi P. Kappo, Albertus K. Basson, Carmen Pheiffer, Rabia Johnson
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 131: 110785. CrossRef - NAD+ metabolism: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential
Na Xie, Lu Zhang, Wei Gao, Canhua Huang, Peter Ernst Huber, Xiaobo Zhou, Changlong Li, Guobo Shen, Bingwen Zou
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Neurochemical regulators of food behavior for pharmacological treatment of obesity: current status and future prospects
Gayane Sargis Vardanyan, Hasmik Samvel Harutyunyan, Michail Iosif Aghajanov, Ruben Sargis Vardanyan
Future Medicinal Chemistry.2020; 12(20): 1865. CrossRef - Unraveling the Role of Leptin in Liver Function and Its Relationship with Liver Diseases
Maite Martínez-Uña, Yaiza López-Mancheño, Carlos Diéguez, Manuel A. Fernández-Rojo, Marta G. Novelle
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(24): 9368. CrossRef - Roles of Adipokines in Digestive Diseases: Markers of Inflammation, Metabolic Alteration and Disease Progression
Ming-Ling Chang, Zinger Yang, Sien-Sing Yang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(21): 8308. CrossRef - CHANGES IN CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM AND ADIPOCYTOKINES UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ALCOHOLIC CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER IN COMBINATION WITH OBESITY USING ADAMETHIONINUM AND ARGININE GLUTAMATE
N. R. Matkovska
Medical and Clinical Chemistry.2020; (3): 17. CrossRef - Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Ex quo et quo vadimus?
Niki Katsiki, Nikolaos Perakakis, Christos Mantzoros
Metabolism.2019; 98: iii. CrossRef - Role of Soluble Adiponectin Receptor 2 in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children
Gulsah Kaya Aksoy, Reha Artan, Cihat Aksoy, Sebahat Özdem, Atike Atalay, Aygen Yılmaz
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2019; 22(5): 470. CrossRef - Determinants of ectopic liver fat in metabolic disease
Anja Bosy-Westphal, Wiebke Braun, Viktoria Albrecht, Manfred J. Müller
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2019; 73(2): 209. CrossRef - Involvement of the hepatic branch of the vagus nerve in the regulation of plasma adipokine levels in rats fed a high-fructose diet
Naoto Hashimoto, Manabu Wakagi, Katsunari Ippoushi, Yuko Takano-Ishikawa
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2019; 71: 90. CrossRef - Fat and Sugar—A Dangerous Duet. A Comparative Review on Metabolic Remodeling in Rodent Models of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Ines C.M. Simoes, Justyna Janikiewicz, Judith Bauer, Agnieszka Karkucinska-Wieckowska, Piotr Kalinowski, Agnieszka Dobrzyń, Andrzej Wolski, Maciej Pronicki, Krzysztof Zieniewicz, Paweł Dobrzyń, Marcin Krawczyk, Hans Zischka, Mariusz R. Wieckowski, Yaiza P
Nutrients.2019; 11(12): 2871. CrossRef - Childhood obesity: increased risk for cardiometabolic disease and cancer in adulthood
Susann Weihrauch-Blüher, Peter Schwarz, Jan-Henning Klusmann
Metabolism.2019; 92: 147. CrossRef - Effects of moderate-intensity continuous training and high-intensity interval training on serum levels of Resistin, Chemerin and liver enzymes in Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide induced Type-2 diabetic rats
Parastesh Mohammad, Khosravi Zadeh Esfandiar, Saremi Abbas, Rekabtalae Ahoora
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2019; 18(2): 379. CrossRef - Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics
Stergios A. Polyzos, Jannis Kountouras, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2019; 92: 82. CrossRef - The Latest Insights into Adipokines in Diabetes
Won Kon Kim, Kwang-Hee Bae, Sang Chul Lee, Kyoung-Jin Oh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(11): 1874. CrossRef - Postprandial leptin and adiponectin in response to sugar and fat in obese and normal weight individuals
M. A. Larsen, V. T. Isaksen, E. J. Paulssen, R. Goll, J. R. Florholmen
Endocrine.2019; 66(3): 517. CrossRef - First demonstration of protective effects of purified mushroom polysaccharide-peptides against fatty liver injury and the mechanisms involved
Shuang Zhao, Shuman Zhang, Weiwei Zhang, Yi Gao, Chengbo Rong, Hexiang Wang, Yu Liu, Jack Ho Wong, Tzibun Ng
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Applying Non-Invasive Fibrosis Measurements in NAFLD/NASH: Progress to Date
Somaya Albhaisi, Arun J. Sanyal
Pharmaceutical Medicine.2019; 33(6): 451. CrossRef - Adiponectin rs2241766 and rs266729 gene polymorphisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Aida A. Mahmoud, Hoda M. Moghazy, Laila M. Yousef, Asmaa N. Mohammad
Gene Reports.2019; 15: 100381. CrossRef - Non-invasive diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis with the use of omics and supervised learning: A proof of concept study
Nikolaos Perakakis, Stergios A. Polyzos, Alireza Yazdani, Aleix Sala-Vila, Jannis Kountouras, Athanasios D. Anastasilakis, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2019; 101: 154005. CrossRef - Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver
Rongqiang Liu, Qiuli Liu, Ying He, Wenqing Shi, Qianhui Xu, Qing Yuan, Qi Lin, Biao Li, Lei Ye, Youlan Min, Peiwen Zhu, Yi Shao
Medicine.2019; 98(44): e17781. CrossRef - CHANGES IN CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM IN PATIENTS WITH ALCOHOLIC CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER ASSOCIATED WITH NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE DEPENDING ON THE STAGE OF DECOMPENSATION
Nataliia Matkovska, Nataliia Virstiuk, Uliana Balan
International Academy Journal Web of Scholar.2019; (6(36)): 17. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and colorectal cancer: A marker of risk or common causation?
Niki Katsiki, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis, Christos Mantzoros
Metabolism.2018; 87: A10. CrossRef - Critical Roles of microRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Fatty Liver: New Advances, Challenges, and Potential Directions
Chenggui Miao, Zhongwen Xie, Jun Chang
Biochemical Genetics.2018; 56(5): 423. CrossRef - Alpha-syntrophin dependent expression of tubulin alpha 8 protein in hepatocytes
Lisa Rein-Fischboeck, Ganimete Bajraktari, Rebekka Pohl, Susanne Feder, Kristina Eisinger, Wolfgang Mages, Elisabeth M. Haberl, Christa Buechler
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry.2018; 74(4): 511. CrossRef - Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hormone-Based Therapeutic Approaches
Kook Hwan Kim, Myung-Shik Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Helicobacter pyloriand extragastric diseases: A review
Antonietta Gerarda Gravina, Rocco Maurizio Zagari, Cristiana De Musis, Lorenzo Romano, Carmelina Loguercio, Marco Romano
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 24(29): 3204. CrossRef - Thiazolidinedione induces a therapeutic effect on hepatosteatosis by regulating stearoyl‑CoA desaturase‑1, lipase activity, leptin and resistin
Hessah Al‑Muzafar, Kamal Amin
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of weight cycling on CTRP3 expression, adipose tissue inflammation and insulin sensitivity in C57BL/6J mice
Xin Li, Li Jiang, Miao Yang, Yu‑Wen Wu, Jia‑Zhong Sun
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of non‑alcoholic fatty liver disease microRNA expression spectra in rat liver tissues
Jiao Nie, Chang‑Ping Li, Jue‑Hong Li, Xia Chen, Xiaoling Zhong
Molecular Medicine Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Proanthocyanidins-Based Synbiotics as a Novel Strategy for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Risk Reduction

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Plasma Adiponectin Levels in Elderly Patients with Prediabetes
- Si Eun Kong, Yea Eun Kang, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):326-333. Published online August 4, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.326
- 3,200 View
- 34 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The significance of adiponectin levels in elderly individuals with prediabetes has yet to be determined. Thus, the present study was performed to evaluate the relationships between adiponectin levels and anthropometric variables, body composition parameters, insulin sensitivity, and lipid profiles in elderly prediabetic patients.
Methods The present study included 120 subjects with prediabetes who were >65 years of age and were selected from among 1,993 subjects enrolled in the Korea Rural Genomic Cohort Study. All subjects underwent a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test and tests for measurement of insulin sensitivity. All diagnoses of prediabetes satisfied the criteria of the American Diabetes Association.
Results Plasma adiponectin levels were lower in elderly prediabetic subjects than elderly subjects with normal glucose tolerance (
P <0.01) as well as in elderly prediabetic patients with metabolic syndrome (MetS) than in those without MetS (P <0.02). When the subjects were categorized into two groups according to plasma adiponectin levels, the waist-to-hip ratio and 2-hour insulin levels were significantly lower in individuals with high plasma adiponectin levels than in those with low plasma adiponectin levels. Additionally, the plasma adiponectin levels of elderly prediabetic subject were inversely correlated with body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), waist-to-hip ratio, visceral fat, visceral fat ratio, and 2-hour insulin levels.Conclusion The present findings demonstrated that the major factors correlated with adiponectin levels in elderly prediabetic subjects were BMI, WC, waist-to-hip ratio, visceral fat, visceral fat ratio, and 2-hour insulin levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study
Mohammad Muzaffar Mir, Rashid Mir, Mushabab Ayed Abdullah Alghamdi, Javed Iqbal Wani, Zia Ul Sabah, Mohammed Jeelani, Vijaya Marakala, Shahzada Khalid Sohail, Mohamed O’haj, Muffarah Hamid Alharthi, Mohannad Mohammad S. Alamri
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(5): 735. CrossRef - Postloading insulinemia is independently associated with arterial stiffness in young Japanese persons
Norimitsu Murai, Naoko Saito, Sayuri Nii, Yuto Nishikawa, Asami Suzuki, Eriko Kodama, Tatsuya Iida, Kentaro Mikura, Hideyuki Imai, Mai Hashizume, Yasuyoshi Kigawa, Rie Tadokoro, Chiho Sugisawa, Kei Endo, Toru Iizaka, Fumiko Otsuka, Shun Ishibashi, Shoichi
Hypertension Research.2021; 44(11): 1515. CrossRef - Association of Adiponectin and rs1501299 of the ADIPOQ Gene with Prediabetes in Jordan
Mahmoud Alfaqih, Faheem Al-Mughales, Othman Al-Shboul, Mohammad Al Qudah, Yousef Khader, Muhammad Al-Jarrah
Biomolecules.2018; 8(4): 117. CrossRef
- Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study

- Impact of Serum Adiponectin Concentration on Progression of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Chul Sik Kim, Ju Ri Park, Sung Hoon Yu, Jun Goo Kang, Ohk Hyun Ryu, Seong Jin Lee, Eun Gyung Hong, Doo Man Kim, Jae Myung Yoo, Sung Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(1):31-38. Published online March 1, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.1.31
- 2,069 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Increased cardiovascular events, which is the leading cause of death in type 2 diabetic patients, are mainly caused by accelerated atherosclerosis. Adiponectin has been suggested as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in cross-sectional studies. However, little is known about the impact of adiponectin on the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients. This study was conducted to evaluate the impact of early adiponectin levels on the progression of carotid atherosclerosis. METHODS: From March 2009, 150 patients with type 2 diabetes were consecutively enrolled in our affiliated outpatient clinic. Anthropometric and biochemical data, including adiponectin levels, were measured in each participant. We measured the carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) at baseline and at 1-year follow-up (n = 111). Then, we prospectively studied the relationship between the serum adiponectin levels and the progression of CIMT for 1 year. RESULTS: Adiponectin levels negatively correlated with CIMT (r = -0.219, P = 0.015). Moreover, mean progression of CIMT was 0.016 +/- 0.040 mm. However, there was no correlation between adiponectin levels and the progression of CIMT within 1-year follow-up period (r = -0.156, P = 0.080). Age (beta = 0.556, P = 0.004), LDL cholesterol (beta = 0.276, P = 0.042), and A1C (beta = 0.309, P = 0.038) were found to be independent risk factors for CIMT. However, A1C (beta = 0.311, P = 0.042) was found to be the only independent risk factor for the progression of CIMT. CONCLUSION: In our study, adiponectin levels were negatively associated with CIMT. However, it did not affect the progression of CIMT at 1-year follow-up. Overall glycemic control is the most important factor in the progression of CIMT in patients with type 2 diabetes.

- Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Low Density Lipoprotein Subfraction, Adiponectin and Apolipoprotein B in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Haejung Jun, Junghae Ko, Hyesook Jung, Changshin Yoon, Taekyoon Kim, Minjeong Kwon, Soonhee Lee, Jihye Suk, Mikyung Kim, Dukkyu Kim, Jeong Hyun Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(3):218-224. Published online September 1, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.3.218
- 22,131 View
- 43 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Omega-3 fatty acids derived from fish oil have been reported to exert a beneficial effect on reducing cardiovascular disease. Reports about their mechanism have generated several interesting findings, including a change in small dense low density lipoprotein (sdLDL) cholesterol proportion, adiponectin, and apolipoprotein B (apoB), in addition to changes in the lipid profile. The principal objective of our study was to evaluate the effects of omega-3 fatty acids on plasma sdLDL, adiponectin, apoB100, and B48 in type 2 diabetic patients with hypertriglyceridemia. METHODS: We randomized 28 type 2 diabetic patients in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial to receive either omega-3 fatty acids or placebo, both administered at a dose of 4 g daily for 12 weeks. LDL subfractions prior to and after treatment were separated via low-speed ultracentrifugation and analyzed via immunoelectrophoresis. Adiponectin, apoB100, and B48 levels were measured using an ELISA kit. RESULTS: sdLDL proportions were reduced in the omega-3 fatty acids group by 11% after 12 weeks of treatment (n = 17, P = 0.001), and were reduced by 4% in the control group (n = 11, P = 0.096). The patients receiving the omega-3 fatty acids evidenced a significant reduction in the levels of triglyceride (P = 0.001), apoB100, and B48 after 12 weeks (P = 0.038 and P = 0.009, respectively) relative to the baseline. Omega-3 fatty acids supplementation increased fasting blood glucose (P = 0.011), but the levels of HbA1c in each group did not change to a statistically significance degree. The adiponectin value was not reduced in the omega-3 fatty acids group (P = 0.133); by way of contrast, the placebo group evidenced a significant reduction in adiponectin value after 12 weeks (P = 0.002). CONCLUSION: Omega-3 fatty acid treatment proved effective in the reduction of atherogenic sdLDL and apoB in type 2 diabetic patients (Clinical trials reg. no. NCT 00758927, clinicaltrials.gov). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Blood Flow Improvement Effect of Bokbunja (Rubus coreanus) Seed Oil in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mouse Model
Hyelin Jeon, Sungmin Kwak, Su-Jin Oh, Hyun Soo Nam, Doo Won Han, Yoon Seok Song, Jinwoo Song, Kyung-Chul Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(8): 1105. CrossRef - Fatty Acid Compositions, Mineral and Vitamin Contents of the Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba)
Han-Soo Kim, Min-A Kim, Duan Yishan, Seong-Ho Jang, Dong-Soo Kang, Won-Ki Lee, Chun-Sik Lee, Jae-Young Ryu
Journal of Environmental Science International.2014; 23(1): 47. CrossRef
- Blood Flow Improvement Effect of Bokbunja (Rubus coreanus) Seed Oil in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mouse Model

- The Relation of Serum Adiponectin and Resistin Concentrations with Metabolic Risk Factors.
- Seong Tae Ryu, Seok O Park, Se Hwa Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(5):444-451. Published online October 1, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.5.444
- 1,746 View
- 17 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Adiponectin is a fat cell-secreted cytokine, which has been reported to improve insulin sensitivity and have antiatherogenic properties. However, it is still unclear whether resistin plays a significant role in the development of insulin resistance in humans. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship of the adiponectin and resistin concentrations with insulin resistance, metabolic markers and adiposity in healthy and type 2 diabetic subjects. METHODS: Eighty-three type 2 diabetic and 139 healthy subjects were studied. Blood samples were drawn after fasting to determine the fasting plasma glucose, insulin, resistin, adiponectin, total cholesterol, triglyceride and HDL-cholesterol levels. The subcutaneous and visceral fat areas were measured at the umbilical level using computed tomography. RESULTS: The serum adiponectin concentrations were significantly lower in the diabetic(6.7+/-2.3microgram/mL) than in the obese(8.2+/-2.4microgram/mL, P<0.01) and non-obese subjects(9.9+/-4.5microgram/mL, P<0.01). The serum resistin concentrations were Similar between the non-obese, obese and type 2 diabetic subjects. From a multiple regression analysis, the fasting glucose, HDL-cholesterol and HOMA-IR were found to be independent determinants of the log of the adiponectin level in the diabetes group. In healthy subjects, the gender, BMI, HOMA-IR, visceral fat area and HDL-cholesterol were associated with the log of the adiponectin level. However, the log of the resistin level was not associated with the markers of insulin resistance and obesity. CONCLUSION: This study showed that the serum adiponectin concentration was closely related to the insulin resistance marker in both healthy and type 2 diabetic subjects. However, the resistin concentration was not associated with the markers of insulin resistance and/or obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Simvastatin on induced apical periodontitis in rats: a tomographic and biochemical analysis
Jussara Machado PEREIRA, Alex SEMENOFF-SEGUNDO, Natalino Francisco da SILVA, Álvaro Henrique BORGES, Tereza Aparecida Delle Vedove SEMENOFF
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2016; 45(4): 189. CrossRef - Relationships among Serum Adiponectin, Leptin and Vitamin D Concentrations and the Metabolic Syndrome in Farmers
Seo-Eun Yeon, Hee-Ryoung Son, Jung-Sook Choi, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(1): 12. CrossRef - Comparison of Serum Adiponectin Levels According to Body Mass Index and Dietary Behaviors of Female University Students in Seoul
Mi Joung Kim, Hyun Young Jun, Hye Bog Rha
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(4): 354. CrossRef - The Effects of 12-Weeks Intensive Intervention Program on Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Adipocytokines and Nutrients Intakes in Industrial Male Workers
Kieun Moon, Ill Keun Park, Yeon Sang Jo, Yun Kyun Chang, Yun Mi Paek, Tae In Choi
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2011; 44(4): 292. CrossRef - The Effects of D-Chiro-Inositol on Glucose Metabolism in 3T3-L1 Cells
Kang Seo Park, Jae Min Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Young Suk Jo, Seong Kyu Lee, Kyung Wan Min, Kyung Ah Han, Hyo Jeong Kim, Hyun Jin Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2008; 32(3): 196. CrossRef
- Effect of Simvastatin on induced apical periodontitis in rats: a tomographic and biochemical analysis

- Adiponectin Gene Polymorphism and Carotid Artery Intima-Media thickness in Type 2 Diabetes.
- Eun Seok Kang, So Young Park, So Hun Kim, Hyun Joo Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Jin Han, Se Eun Park, Hyeong Jin Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(1):29-39. Published online February 1, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.1.29
- 1,769 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to examine the association between the common polymorphisms of the adiponectin gene(ACDC) and the intima-media thickness(IMT) of the common carotid arteries in type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: The B mode ultrasound examination of carotid artery was performed on 133 type 2 diabetic patients. The carotid IMT was calculated using the Intimascope computer program. The SNP45 and SNP276 of the ACDC were examined. RESULTS: There was no significant difference in the carotid IMT among the SNP45 genotypes(0.66+/-0.18mm for TT, 0.71+/-0.12mm for TG and 0.64+/-0.15mm for GG, P=NS). Subjects carrying the SNP276 GG genotype had a markedly lower serum adiponectin concentration than those carrying the TT genotype(3.35+/-2.00microgram/mL vs. 4.98+/-2.24microgram/mL, P=0.029) The carotid IMT was significantly higher in patients with the SNP276 GG genotype than those with the TT genotype (0.70+/-0.17mm vs. 0.59+/-0.13mm, P=0.032). Patients with the +45GG/+276GG genotype combination showed significantly higher mean carotid IMT than the other genotype combinations(0.78+/-0.09mm vs. 0.71+/-0.15mm, P=0.013) CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that the adiponectin gene, SNP276 is associated with the carotid IMT in type 2 diabetic patients. Further studies are will be needed to confirm these genotypephenotype associations.

- Relationship between Serum Adiponectin and Development of the Metabolic Syndrome.
- S S Park, K M Choi, S B Kwon, O H Ryu, H J Ryu, S Y Park, H Y Kim, J A Seo, K W Lee, S G Kim, N H Kim, D S Choi, S H Baik
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(5):492-500. Published online October 1, 2004
- 1,168 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
We investigated whether low serum adiponectin concentrations are able to predict the future development of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. METHODS: This was a prospective cohort study, which included 372 elderly Koreans that participated in the South-West Seoul (SWS) study, conducted in 1999 and 2002 in Seoul, Korea. Fasting and post-challenge 2-hour plasma glucose, body mass index (BMI), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), blood pressure, lipid profiles, and serum adiponectin data were examined. RESULTS: Adiponectin concentrations obtained in 1999 and 2002 were highly correlated (r = 0.63, P < 0.0001), and the three-year within-person variation of the adiponectin concentrations was not significant (P=0.61). The serum adiponectin level was closely correlated with metabolic syndrome; negatively with BMI, WHR, blood pressure, triglyceride and blood glucose, and positively with HDL cholesterol. Subjects with metabolic syndrome showed lower serum adiponectin concentrations than those without (P < 0.0001). The baseline adiponectin levels were found to be correlated with subsequent changes in the WHR, LDL cholesterol, and fasting and post-load 2h glucose over the 3-year period, after adjusting the baseline values. A multiple logistic regression analysis showed that lower baseline serum adiponectin concentrations were significantly associated with the developments of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome after adjusting for age, gender, obesity, history of impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance, hypertension and dyslipidemia. CONCLUSION: Reduced concentrations of adiponectin were found to be independently associated with increase risks of both type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome in elderly Koreans

- Relationship between Adiponectin, Leptin and Body Fat in Men with Hypogonadism Before and After Testosterone Treatment.
- Sang Wan Kim, Joon Ku Kang, Do Joon Park, Chan Soo Shin, Kyung Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(5):473-484. Published online October 1, 2004
- 1,099 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Testosterone replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism improves sexual function, decreases body fat, and increases the mass and function of lean muscle. These beneficial effects of testosterone replacement therapy are accompanied by slight lowering of the high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, increase in the hematocrit/hemoglobin ratio and size of the prostate gland. It is presently unknown whether the effect of testosterone on body fat could also reduce the risk of atherosclerotic disease associated with obesity. We investigated the relationship between body fat and blood leptin and adiponectin levels to elucidate the effect of testosterone on body fat metabolism, as well as the effect of testosterone on lipid and bone metabolism. METHODS: We selected 28 men, who were hypogonadal (mean serum testosterone+/-SD, 22.3+/-35.3 ng/dL) due to an organic disease, and them with oral testosterone (testosterone undecanoate) for 12 months. We measured the body composition, serum leptin, plasma adiponectin, biochemical bone markers, bone mineral density, prostate-specific antigen, and serum lipids before and 3, 6 and 12 months after treatment. We analyzed the relationship between body fat and blood leptin and adiponectin levels. RESULTS: The mean serum testosterone concentration reached the subnormal range after 6 months of treatment, which remained for the duration of treatment. The fat mass decreased and muscle mass increased, not within the first 6 months, but principally within 12 months (p<0.05). Although the decrease in the serum leptin level was not statistically significant, there were positive correlations between the leptin level and fat mass before and after 6 months of treatment (p<0.05). The plasma adiponectin did not increase or correlate with body fat parameters. The bone mineral densities of the lumbar spine (L2-L4) and femoral neck did not increased, but the serum osteocalcin and urine N-telopeptide were significantly decreased (p<0.05 and <0.01, respectively). The HDL-cholesterol decreased, principally within the first 6 months (p<0.01), but the total and LDL cholesterols, and the triglycerides remained unchanged during the course of treatment. There was also no change in prostate-specific antigen. CONCLUSION: Twelve months of oral testosterone replacement in men with hypogonadism improved body composition and bone metabolism, but demonstrated subnormal serum testosterone levels, had no effect on the leptin and adiponectin levels and decrease in HDL-cholesterol levels. It will be necessary to examine the long-term effects of testosterone replacement on the incidence of cardiovascular events as well as cardiovascular risk factors in men with hypogonadism

- Association of Serum Adiponectin Levels with Insulin Resistance in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Young Sun Hong, Jee Young Oh, Eun Kyung Byun, Yeon Ah Sung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(4):369-378. Published online August 1, 2004
- 1,045 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is known to be associated with obesity and insulin resistance. The exact mechanism of insulin resistance in PCOS is not completely understood, but there are several pieces of evidence suggesting humoral mediator involvement. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-secreted protein, could be a possible link between adiposity and insulin resistance. This study was performed to see whether the serum adiponectin levels are suppressed in woman with PCOS and if this is associated with the characteristic hormonal and metabolic features of PCOS. METHODS: 20 women with PCOS and 8 normal controls with regular cycles were recruited. The serum adiponectin levels were measured by RIA, and the fasting glucose to insulin ratio (GIR) used as an insulin sensitivity index. RESULTS: The patients with PCOS were classified as lean (BMI < 23 kg/m2, n=9) and obese groups (BMI 25 kg/m2, n=11) based on the WPRO criteria. The GIR was significantly lower in the obese compared to the control group. The adiponectin level was lower in women with PCOS than the controls, but without statistical significance. In 5 of the 20 patients, the GIR was higher than 0.30, which was the lowest limit in the controls, and the adiponectin level was significantly higher than in those patients with a lower GIR. The adiponectin level was significantly correlated with the BMI, subcutaneous and visceral fat areas, post challenge 2 hr glucose, fasting insulin, GIR and SHBG. After adjustment for BMI, adiponectin was significantly correlated with the GIR in all subjects, including the controls. CONCLUSION: The serum adiponectin level was associated with and related to adiposity in women with PCOS; however, adiponectin might be associated with insulin resistance independently from adiposity

- Relationship with Serum Adiponectin Concentrations and Obesity in Korean Children.
- Hyoun Ah Kim, Hyoung Suk Lee, Chul Sik Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Yoon Sok Chung, Kwan Woo Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Dae Jung Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(5):473-480. Published online October 1, 2003
- 1,155 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Adiponectin is an adipocytokine that is highly specific to adipose tissue. In contrast to other adipocytokine, the adiponectin levels are decreased in obesity and/or type 2 diabetes. There are few studies regarding the correlation between the adiponectin concentration and obesity in children. Thus, whether the serum adiponectin concentrations are associated with adiposity in children was investigated. METHODS: One hundred and sixty four subjects were selected from the participants in an ongoing study on the relationship between birth weight and insulin resistance in children. The current weights, heights, body fat percentages, waist circumferences, blood pressures, lipid profiles and insulin resistance, by the HOMA method, were measured in all the subjects. The serum adiponectin concentrations were determined by a validated sandwich ELISA, using a human adiponectin-specific antibody. RESULTS: The serum adiponectin concentration was negatively correlated with the body mass index, waist circumference, systolic blood pressure, insulin resistance by HOMA and serum triglycerides, and positively correlated with the serum HDL cholesterol level. The serum adiponectin concentrations in the boys were significantly lower than in the girls. In a multiple regression analysis, the serum adiponectin concentration was strongly associated with waist circumference and gender. CONCLUSION: It is concluded that there was an inverse relationship between the serum adiponectin concentration and abdominal adiposity in children. However, further studies on independent gender differences on adiponectin are needed.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



