Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > BROWSE ARTICLES > Previous issues
Review Articles
- Thyroid
- Prenatal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, Maternal Thyroid Dysfunction, and Child Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Hyeong-Moo Shin, Jiwon Oh, Rebecca J. Schmidt, Elizabeth N. Pearce
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):819-829. Published online November 23, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1598

- 6,288 View
- 130 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Autism spectrum disorder (ASD), with its high economic and societal costs, is a growing public health concern whose prevalence has risen steadily over the last two decades. Although actual increased incidence versus improved diagnosis remains controversial, the increased prevalence of ASD suggests non-inherited factors as likely contributors. There is increasing epidemiologic evidence that abnormal maternal thyroid function during pregnancy is associated with increased risk of child ASD and other neurodevelopmental disorders. Prenatal exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals such as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) is known to disrupt thyroid function and can affect early brain development; thus, thyroid dysfunction is hypothesized to mediate this relationship. The concept of a potential pathway from prenatal PFAS exposure through thyroid dysfunction to ASD etiology is not new; however, the extant literature on this topic is scant. The aim of this review is to evaluate and summarize reports with regard to potential mechanisms in this pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endocrine Disruptors and Thyroid Health
Elizabeth N. Pearce
Endocrine Practice.2024; 30(2): 172. CrossRef - Maternal Thyroid Dysfunction During Pregnancy as an Etiologic Factor in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Challenges and Opportunities for Research
Zoe B. Kaplan, Elizabeth N. Pearce, Sun Y. Lee, Hyeong-Moo Shin, Rebecca J. Schmidt
Thyroid®.2024; 34(2): 144. CrossRef - Effects of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals on Human Health
Jun Hyung Lee, Sung-Eun Cho
Laboratory Medicine Online.2023; 13(3): 129. CrossRef
- Endocrine Disruptors and Thyroid Health

- Thyroid
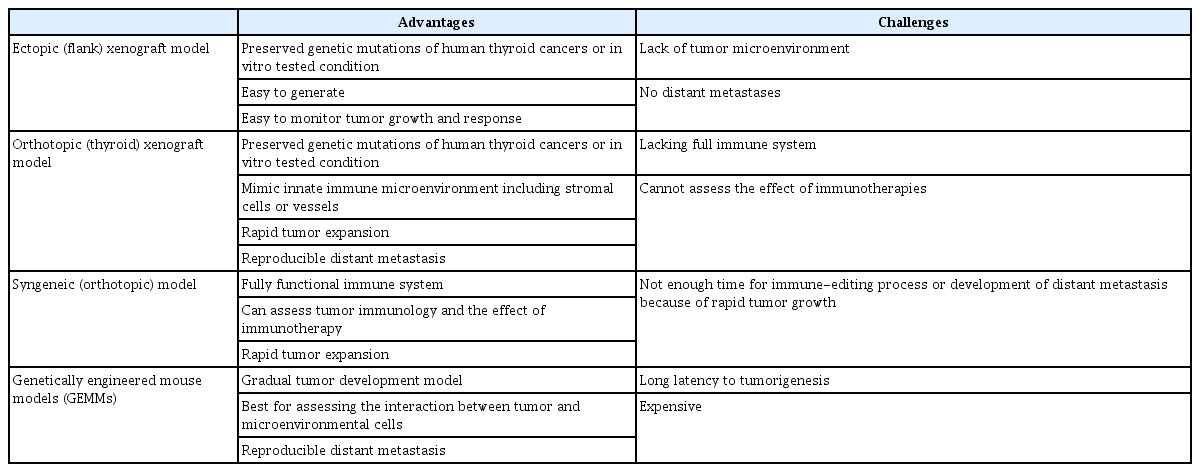
- Preclinical Models of Follicular Cell-Derived Thyroid Cancer: An Overview from Cancer Cell Lines to Mouse Models
- Min Ji Jeon, Bryan R. Haugen
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):830-838. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1636
- 2,330 View
- 195 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The overall prognosis of thyroid cancer is excellent, but some patients have grossly invasive disease and distant metastases with limited responses to systemic therapies. Thus, relevant preclinical models are needed to investigate thyroid cancer biology and novel treatments. Different preclinical models have recently emerged with advances in thyroid cancer genetics, mouse modeling and new cell lines. Choosing the appropriate model according to the research question is crucial to studying thyroid cancer. This review will discuss the current preclinical models frequently used in thyroid cancer research, from cell lines to mouse models, and future perspectives on patient-derived and humanized preclinical models in this field.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advancements of 3D bioprinting in regenerative medicine: Exploring cell sources for organ fabrication
Yue Ma, Bo Deng, Runbang He, Pengyu Huang
Heliyon.2024; 10(3): e24593. CrossRef - Strategies to investigate migration and metastases in thyroid cancer
Daniel M. Chopyk, Priya H. Dedhia
Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research.2024; 34: 100502. CrossRef - Mouse Models to Examine Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Pathogenesis: Recent Updates
Hye Choi, Kwangsoon Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 11138. CrossRef - Modeling the tumor microenvironment of anaplastic thyroid cancer: an orthotopic tumor model in C57BL/6 mice
Zhen Xu, Hyo Shik Shin, Yoo Hyung Kim, Seong Yun Ha, Jae-Kyung Won, Su-jin Kim, Young Joo Park, Sareh Parangi, Sun Wook Cho, Kyu Eun Lee
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient-derived tumor models: a suitable tool for preclinical studies on esophageal cancer
Fan Liang, Hongyan Xu, Hongwei Cheng, Yabo Zhao, Junhe Zhang
Cancer Gene Therapy.2023; 30(11): 1443. CrossRef - Mechanistic Insights of Thyroid Cancer Progression
Luis Javier Leandro-García, Iñigo Landa
Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances of Osteosarcoma Models for Drug Discovery and Precision Medicine
Linyun Tan, Yitian Wang, Xin Hu, Guifeng Du, Xiaodi Tang, Li Min
Biomolecules.2023; 13(9): 1362. CrossRef
- Advancements of 3D bioprinting in regenerative medicine: Exploring cell sources for organ fabrication

Special Article
- Miscellaneous
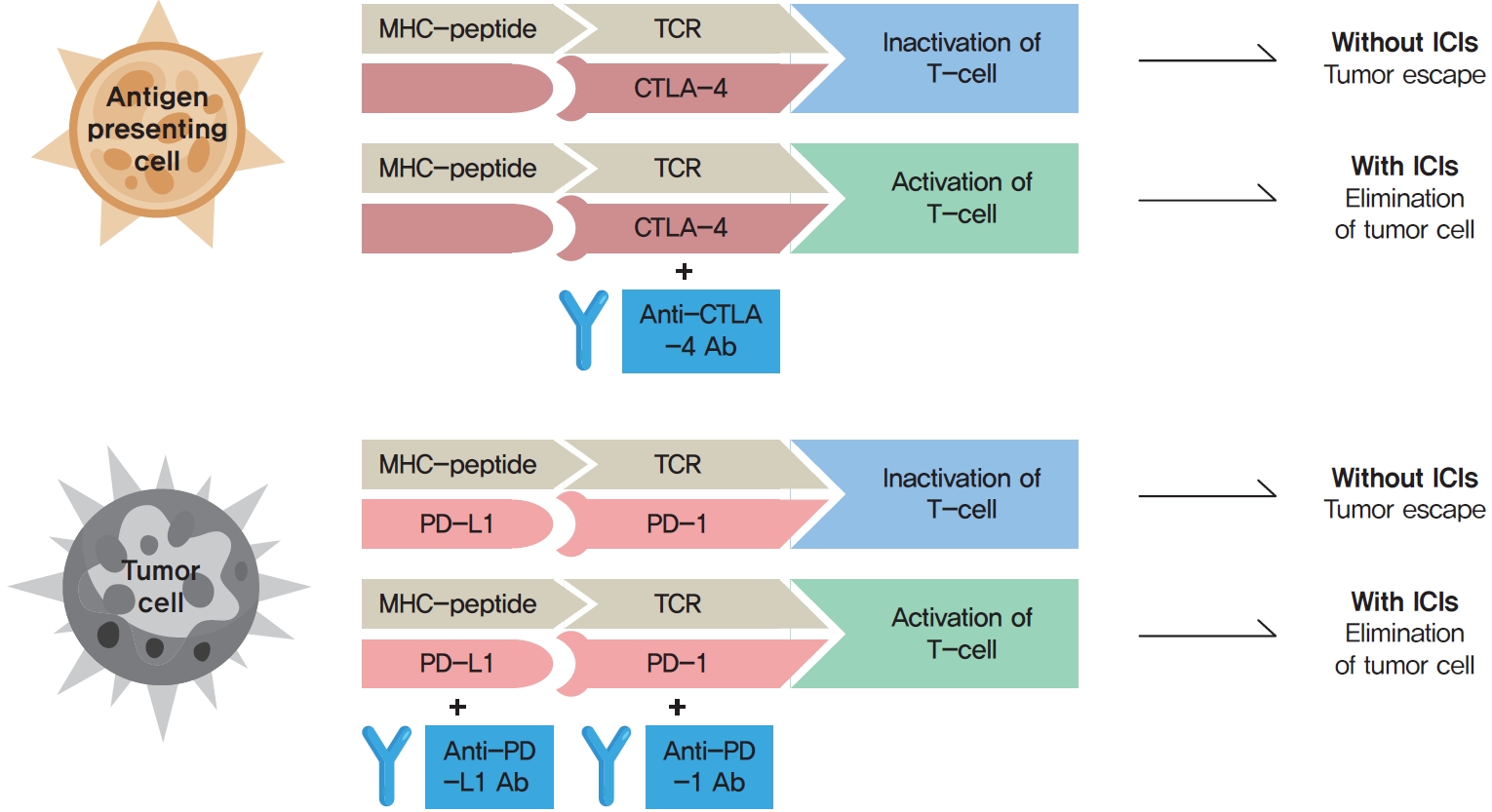
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Endocrine Disorders: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
- Hyemi Kwon, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Kyung Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of the Korean Endocrine Society
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):839-850. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1627
- 3,428 View
- 320 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) including an anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 inhibitor, anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitors, and anti-PD-ligand 1 inhibitors are representative therapeutics for various malignancies. In oncology, the application of ICIs is currently expanding to a wider range of malignancies due to their remarkable clinical outcomes. ICIs target immune checkpoints which suppress the activity of T-cells that are specific for tumor antigens, thereby allowing tumor cells to escape the immune response. However, immune checkpoints also play a crucial role in preventing autoimmune reactions. Therefore, ICIs targeting immune checkpoints can trigger various immune-related adverse events (irAEs), especially in endocrine organs. Considering the endocrine organs that are frequently involved, irAEs associated endocrinopathies are frequently life-threatening and have unfavorable clinical implications for patients. However, there are very limited data from large clinical trials that would inform the development of clinical guidelines for patients with irAEs associated endocrinopathies. Considering the current clinical situation, in which the scope and scale of the application of ICIs are increasing, position statements from clinical specialists play an essential role in providing the appropriate recommendations based on both medical evidence and clinical experience. As endocrinologists, we would like to present precautions and recommendations for the management of immune-related endocrine disorders, especially those involving the adrenal, thyroid, and pituitary glands caused by ICIs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib for radically unresectable or metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the Japanese population
Ryo Fujiwara, Takeshi yuasa, kenichi kobayashi, tetsuya yoshida, susumu kageyama
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2023; 23(5): 461. CrossRef - Incidence of Endocrine-Related Dysfunction in Patients Treated with New Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review
Won Sang Yoo, Eu Jeong Ku, Eun Kyung Lee, Hwa Young Ahn
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 750. CrossRef
- Pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib for radically unresectable or metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the Japanese population

Editorials
- Miscellaneous
- Forty Years Together, New Leap Forward! The 40th Anniversary of the Korean Endocrine Society
- Jong Chul Won, Ki-Hyun Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):851-857. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.604

- 1,403 View
- 164 Download

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- DPP-4 Inhibitor in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patient with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Achieving Two Goals at Once?
- Ji Cheol Bae
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):858-860. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.605
- 1,876 View
- 205 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Vildagliptin inhibits high fat and fetuin-A mediated DPP-4 expression, intracellular lipid accumulation and improves insulin secretory defects in pancreatic beta cells
Snehasish Nag, Samanwita Mandal, Oindrila Mukherjee, Tanmay Majumdar, Satinath Mukhopadhyay, Rakesh Kundu
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2024; 1870(3): 167047. CrossRef - Physiology, pharmacology and prospects for dipeptidilpeptidase-4 inhibitors use
D. V. Kurkin, D. A. Bakulin, E. I. Morkovin, A. V. Strygin, Yu. V. Gorbunova, E. V. Volotova, I. E. Makarenko, V. B. Saparova, R. V. Drai, V. I. Petrov
Pharmacy & Pharmacology.2023; 11(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparative effects between old and new antidiabetic agents on metabolic- associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)
André J. Scheen
Diabetes Epidemiology and Management.2023; 11: 100145. CrossRef - Pharmacokinetic, toxicological, and clinical considerations for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients with liver disease: a comprehensive update
André J. Scheen
Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology.2023; 19(8): 543. CrossRef
- Vildagliptin inhibits high fat and fetuin-A mediated DPP-4 expression, intracellular lipid accumulation and improves insulin secretory defects in pancreatic beta cells

Original Articles
- Thyroid
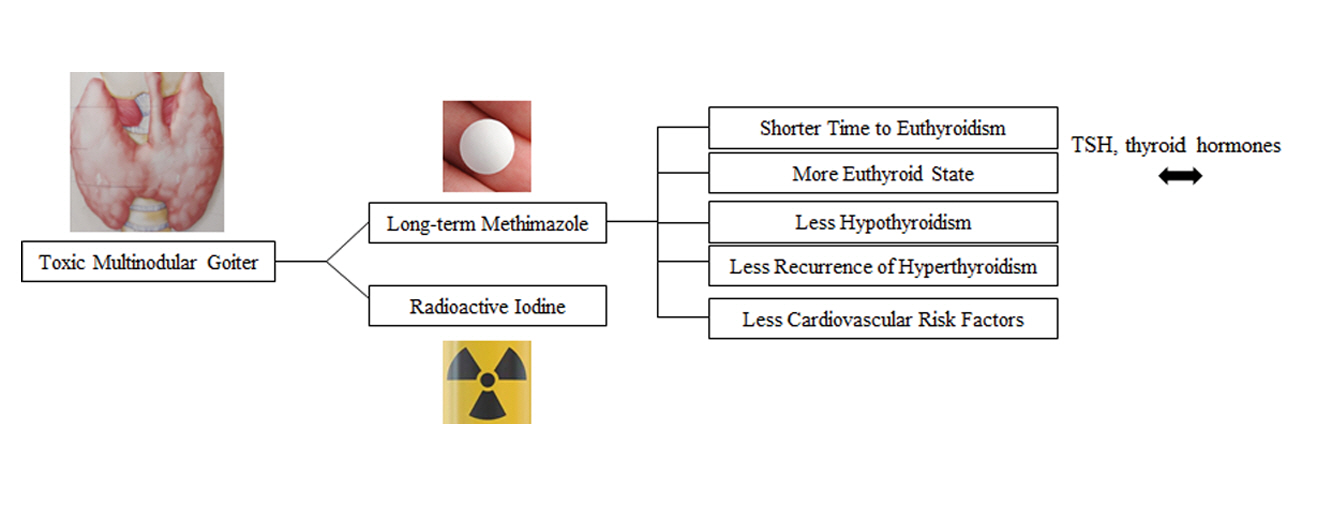
- Efficacy and Safety of Long-Term Methimazole versus Radioactive Iodine in the Treatment of Toxic Multinodular Goiter
- Fereidoun Azizi, Navid Saadat, Mir Alireza Takyar, Hengameh Abdi, Ladan Mehran, Atieh Amouzegar
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):861-869. Published online November 23, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1476
- 3,844 View
- 369 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study compared the degree of sustained control of hyperthyroidism in patients with toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG) treated with long-term methimazole (LT-MMI) or radioactive iodine (RAI).
Methods
In this clinical trial, 130 untreated patients with TMNG were randomized to either LT-MMI or RAI treatment. Both groups were followed for 108 to 148 months, with median follow-up durations of 120 and 132 months in the LT-MMI and RAI groups, respectively. Both groups of patients were followed every 1 to 3 months in the first year and every 6 months thereafter.
Results
After excluding patients in whom the treatment modality was changed and those who were lost to follow-up, 53 patients in the LT-MMI group and 54 in the RAI group completed the study. At the end of the study period, 50 (96%) and 25 (46%) patients were euthyroid, and two (4%) and 25 (46%) were hypothyroid in LT-MMI and RAI groups, respectively. In the RAI group, four (8%) patients had subclinical hyperthyroidism. The mean time to euthyroidism was 4.3±1.3 months in LT-MMI patients and 16.3± 15.0 months in RAI recipients (P<0.001). Patients treated with LT-MMI spent 95.8%±5.9% of the 12-year study period in a euthyroid state, whereas this proportion was 72.4%±14.8% in the RAI-treated patients (P<0.001). No major treatment-related adverse events were observed in either group.
Conclusion
In patients with TMNG, LT-MMI therapy is superior to RAI treatment, as shown by the earlier achievement of euthyroidism and the longer duration of sustained normal serum thyrotropin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanism of Huatan Sanjie Fang in improving goiter in Graves' disease mice based on the Hippo signaling pathway
Huimin Yuan, Wenxin Ma, Yifei Song, Hang Wang, Shuxin Yan, Silan Hao, Xiaoyun Zhu, Yang Tang
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medical Sciences.2023; 10(3): 289. CrossRef
- Mechanism of Huatan Sanjie Fang in improving goiter in Graves' disease mice based on the Hippo signaling pathway

- Thyroid
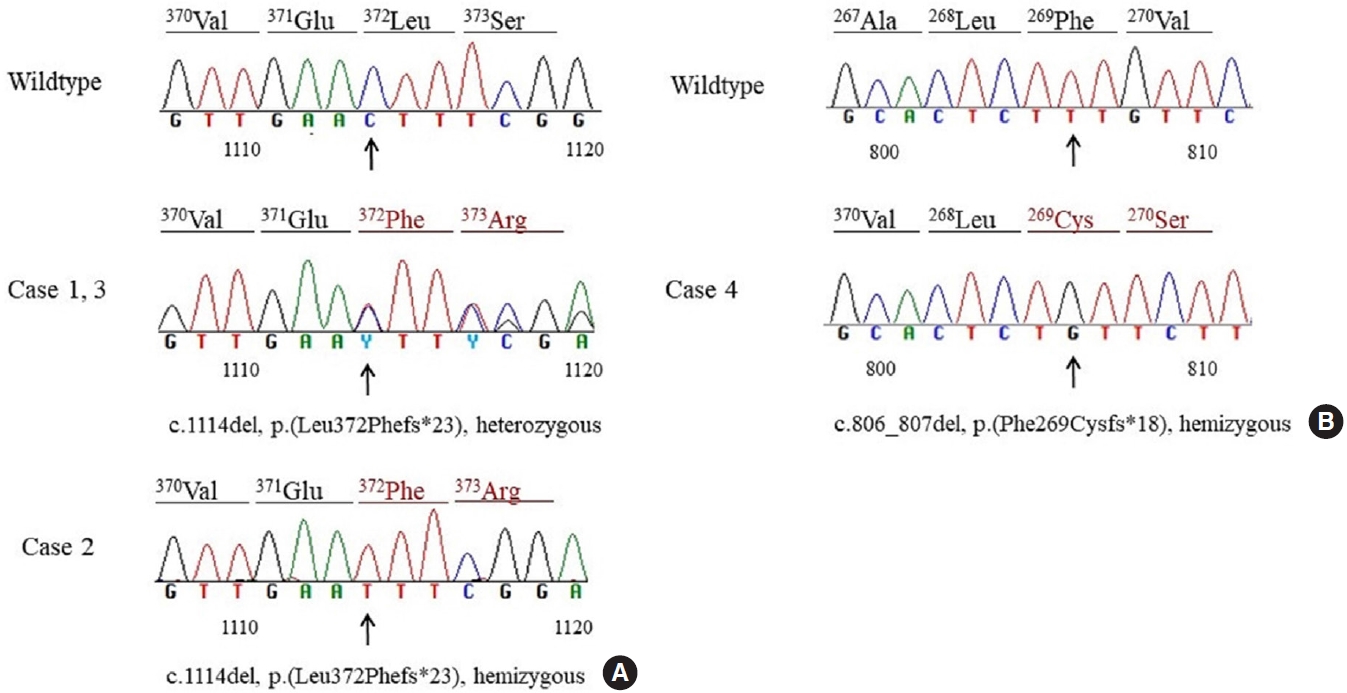
- Identification of Mutations in the Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG) Gene in Patients with TBG Deficiency in Korea
- Jung Heo, Sang-Mi Kim, Hyun Jin Ryu, Hyunju Park, Tae Hyuk Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Hyung-Doo Park, Sun Wook Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):870-878. Published online December 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1591
- 1,715 View
- 197 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) is a major transporter protein for thyroid hormones. The serpin family A member 7 (SERPINA7) gene codes for TBG, and mutations of the SERPINA7 gene result in TBG deficiency. Although more than 40 mutations have been reported in several countries, only a few studies of TBG deficiency and SERPINA7 gene mutation have been performed in Korea. The aim of this study is to review the clinical presentations and laboratory findings of patients with TBG deficiency and to investigate the types of SERPINA7 gene mutation.
Methods
Five unrelated Korean adults with TBG deficiency attending endocrinology clinic underwent SERPINA7 gene sequencing. Four patients harbored a SERPINA7 gene mutation. Serum thyroid hormones, anti-microsomal antibodies, and TBG were measured. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood. All exons and intron-exon boundaries of the TBG gene were amplified and sequencing was performed.
Results
Two patients were heterozygous females, and the other two were hemizygous males. One heterozygous female had coexisting hypothyroidism. The other heterozygous female was erroneously prescribed levothyroxine at a local clinic. One hemizygous male harbored a novel mutation, p.Phe269Cysfs*18, which caused TBG partial deficiency. Three patients had the p.Leu372Phefs*23 mutation, which is known as TBG-complete deficiency Japan (TBG-CDJ) and was also presented in previous mutation analyses in Korea.
Conclusion
This study presents four patients diagnosed with TBG deficiency and provides the results of SERPINA7 gene sequencing. One novel mutation, p.Phe269Cysfs*18, causing TBD-partial deficiency and three cases of TBG-CDJ were demonstrated. It is necessary to identify TBG deficiency to prevent improper treatment. Also, sequencing of the SERPINA7 gene would provide valuable information about the TBG variants in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and basic performance verification of a rapid homogeneous bioassay for agonistic antibodies against the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor
Motoki Hoshina, Shiomi Ojima, Atsushi Kawasaki, Kosuke Doi, Satoshi Ohta, Asuka Inoue, Hiroshi Murayama
Journal of Immunological Methods.2024; 528: 113655. CrossRef
- Development and basic performance verification of a rapid homogeneous bioassay for agonistic antibodies against the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor

- Thyroid
- BRAFV600E Mutation Enhances Estrogen-Induced Metastatic Potential of Thyroid Cancer by Regulating the Expression of Estrogen Receptors
- Minjun Kim, Su-jin Kim, Seong Yun Ha, Zhen Xu, Youngjin Han, Hyeon-Gun Jee, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Kyu Eun Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):879-890. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1563
- 2,731 View
- 214 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
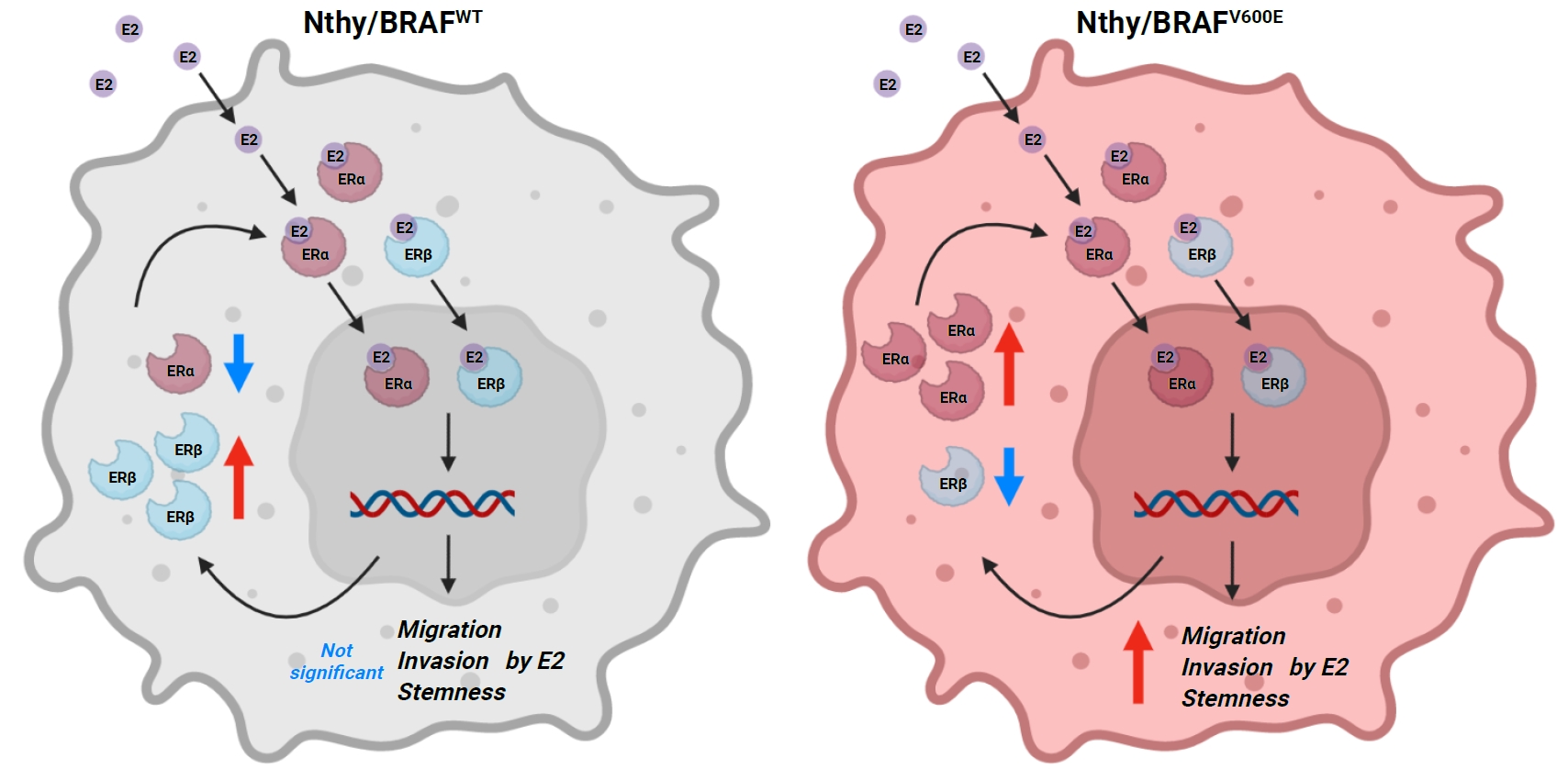
Cross-talk between mitogen-activated protein kinase and estrogen has been reported; however, the role of BRAFV600E in the estrogen responsiveness of thyroid cancer is unknown. We elucidated the effect of BRAFV600E on the estrogen-induced increase in metastatic potential in thyroid cancer.
Methods
Using a pair of cell lines, human thyroid cell lines which harbor wild type BRAF gene (Nthy/WT) and Nthy/BRAFV600E (Nthy/V600E), the expression of estrogen receptors (ERs) and estrogen-induced metastatic phenotypes were evaluated. Susceptibility to ERα- and ERβ-selective agents was evaluated to confirm differential ER expression. ESR expression was analyzed according to BRAFV600E status and age (≤50 years vs. >50 years) using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data.
Results
Estradiol increased the ERα/ERβ expression ratio in Nthy/V600E, whereas the decreased ERα/ERβ expression ratio was found in Nthy/WT. BRAFV600E-mutated cell lines showed a higher E2-induced increase in metastatic potential, including migration, invasion, and anchorage-independent growth compared with Nthy/WT. An ERα antagonist significantly inhibited migration in Nthy/V600E cells, whereas an ERβ agonist was more effective in Nthy/WT. In the BRAFV600E group, ESR1/ESR2 ratio was significantly higher in younger age group (≤50 years) compared with older age group (>50 years) by TCGA data analysis.
Conclusion
Our data show that BRAFV600E mutation plays a crucial role in the estrogen responsiveness of thyroid cancer by regulating ER expression. Therefore, BRAFV600E might be used as a biomarker when deciding future hormone therapies based on estrogen signaling in thyroid cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The importance of protein domain mutations in cancer therapy
Kiran Kumar Chitluri, Isaac Arnold Emerson
Heliyon.2024; 10(6): e27655. CrossRef - Three cases of thyroid cancer in transgender female veterans receiving gender-affirming estrogen treatment
John D. Christensen, Hiba T. Basheer
Endocrine and Metabolic Science.2024; 15: 100177. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Prevalence, Risk Exposure, and Clinical Features Among Transgender Female Veterans
John David Christensen, Hiba T Basheer, Jose Joaquin Lado Abeal
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of DNA Promoter Methylation and BRAF Mutation in Thyroid Cancer
Farzana Jasmine, Briseis Aschebrook-Kilfoy, Mohammad M. Rahman, Garrett Zaagman, Raymon H. Grogan, Mohammed Kamal, Habibul Ahsan, Muhammad G. Kibriya
Current Oncology.2023; 30(3): 2978. CrossRef - Editorial: Recent advances in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Progression, treatment and survival predictors
Erivelto Martinho Volpi, Margarita Carmen Ramirez-Ortega, Jose Federico Carrillo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The importance of protein domain mutations in cancer therapy

- Thyroid
- Metabolite Changes during the Transition from Hyperthyroidism to Euthyroidism in Patients with Graves’ Disease
- Ho Yeop Lee, Byeong Chang Sim, Ha Thi Nga, Ji Sun Moon, Jingwen Tian, Nguyen Thi Linh, Sang Hyeon Ju, Dong Wook Choi, Daiki Setoyama, Hyon-Seung Yi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):891-900. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1590
- 2,460 View
- 253 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
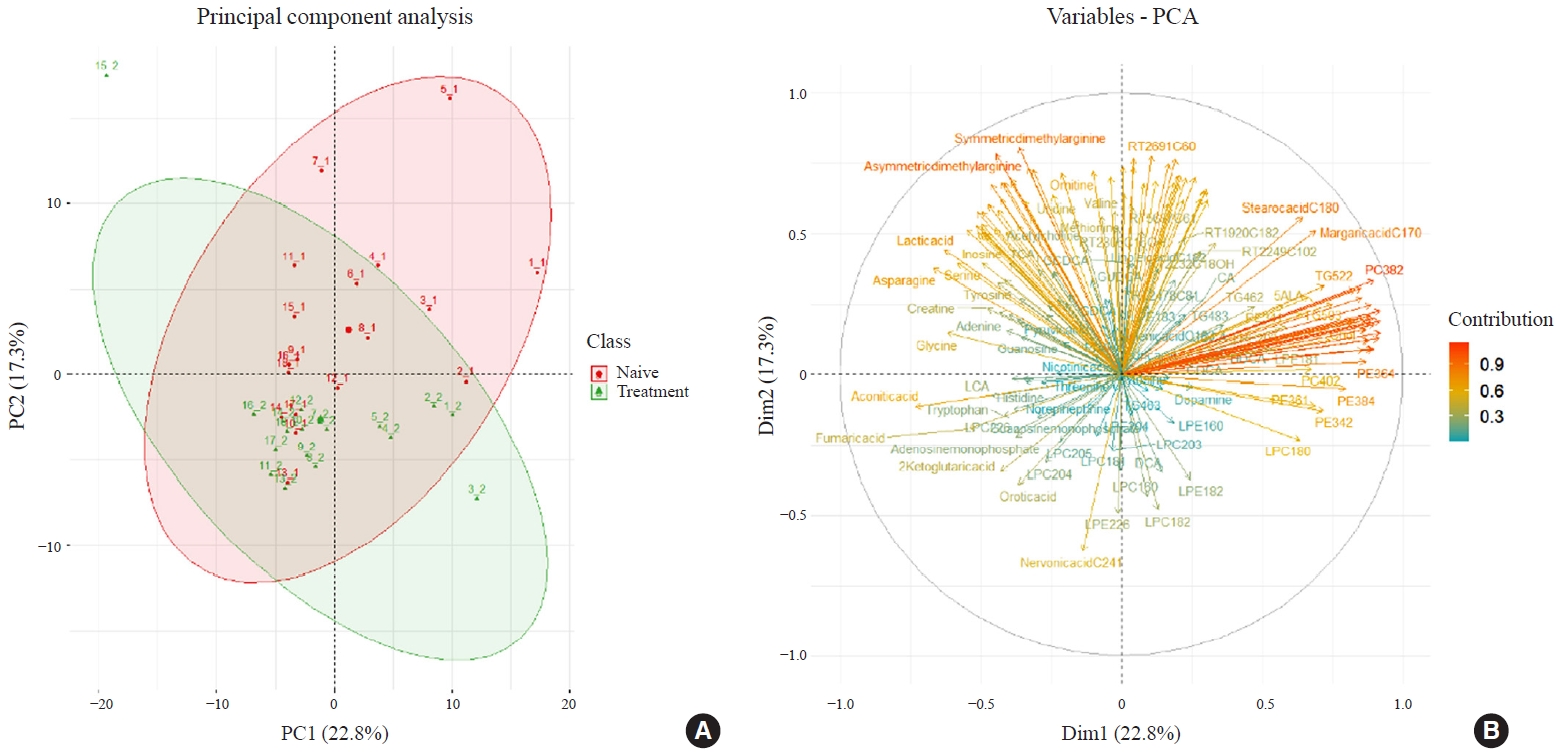
ePub - Background
An excess of thyroid hormones in Graves’ disease (GD) has profound effects on systemic energy metabolism that are currently partially understood. In this study, we aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the metabolite changes that occur when patients with GD transition from hyperthyroidism to euthyroidism with methimazole treatment.
Methods
Eighteen patients (mean age, 38.6±14.7 years; 66.7% female) with newly diagnosed or relapsed GD attending the endocrinology outpatient clinics in a single institution were recruited between January 2019 and July 2020. All subjects were treated with methimazole to achieve euthyroidism. We explored metabolomics by performing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of plasma samples of these patients and then performed multivariate statistical analysis of the metabolomics data.
Results
Two hundred metabolites were measured before and after 12 weeks of methimazole treatment in patients with GD. The levels of 61 metabolites, including palmitic acid (C16:0) and oleic acid (C18:1), were elevated in methimazole-naïve patients with GD, and these levels were decreased by methimazole treatment. The levels of another 15 metabolites, including glycine and creatinine, were increased after recovery of euthyroidism upon methimazole treatment in patients with GD. Pathway analysis of metabolomics data showed that hyperthyroidism was closely related to aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid biosynthesis and branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis pathways.
Conclusion
In this study, significant variations of plasma metabolomic patterns that occur during the transition from hyperthyroidism to euthyroidism were detected in patients with GD via untargeted metabolomics analysis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of serum keratin 1 with thyroid function and immunity in Graves’ disease
Chao-Wen Cheng, Wen-Fang Fang, Jiunn-Diann Lin, Appuwawadu Mestri Nipun Lakshitha de Silva
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0289345. CrossRef
- Associations of serum keratin 1 with thyroid function and immunity in Graves’ disease

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Inhibition of miR-146a-5p and miR-8114 in Insulin-Secreting Cells Contributes to the Protection of Melatonin against Stearic Acid-Induced Cellular Senescence by Targeting Mafa
- Shenghan Su, Qingrui Zhao, Lingfeng Dan, Yuqing Lin, Xuebei Li, Yunjin Zhang, Chunxiao Yang, Yimeng Dong, Xiaohan Li, Romano Regazzi, Changhao Sun, Xia Chu, Huimin Lu
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):901-917. Published online December 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1565
- 2,322 View
- 219 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
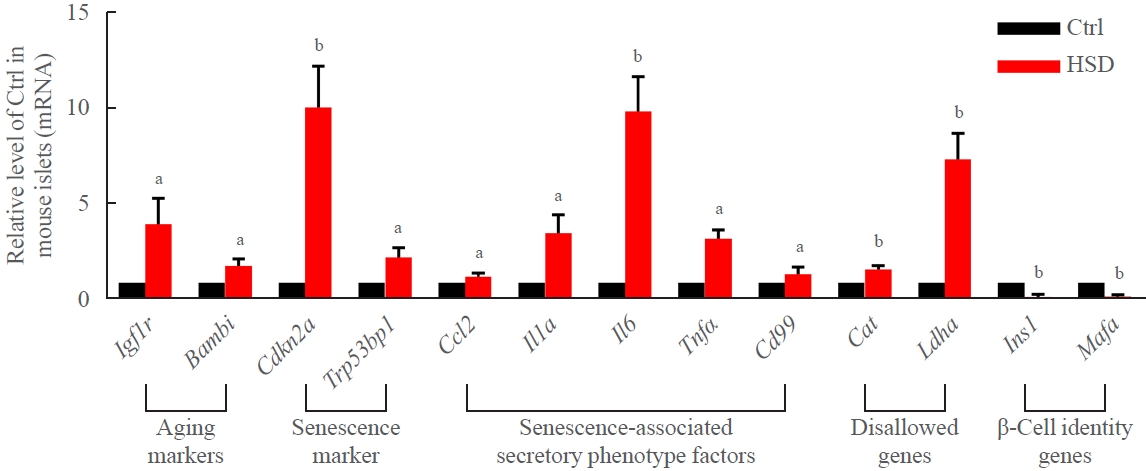
ePub - Background
Chronic exposure to elevated levels of saturated fatty acids results in pancreatic β-cell senescence. However, targets and effective agents for preventing stearic acid-induced β-cell senescence are still lacking. Although melatonin administration can protect β-cells against lipotoxicity through anti-senescence processes, the precise underlying mechanisms still need to be explored. Therefore, we investigated the anti-senescence effect of melatonin on stearic acid-treated mouse β-cells and elucidated the possible role of microRNAs in this process.
Methods
β-Cell senescence was identified by measuring the expression of senescence-related genes and senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining. Gain- and loss-of-function approaches were used to investigate the involvement of microRNAs in stearic acid-evoked β-cell senescence and dysfunction. Bioinformatics analyses and luciferase reporter activity assays were applied to predict the direct targets of microRNAs.
Results
Long-term exposure to a high concentration of stearic acid-induced senescence and upregulated miR-146a-5p and miR- 8114 expression in both mouse islets and β-TC6 cell lines. Melatonin effectively suppressed this process and reduced the levels of these two miRNAs. A remarkable reversibility of stearic acid-induced β-cell senescence and dysfunction was observed after silencing miR-146a-5p and miR-8114. Moreover, V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A (Mafa) was verified as a direct target of miR-146a-5p and miR-8114. Melatonin also significantly ameliorated senescence and dysfunction in miR-146a-5pand miR-8114-transfected β-cells.
Conclusion
These data demonstrate that melatonin protects against stearic acid-induced β-cell senescence by inhibiting miR-146a- 5p and miR-8114 and upregulating Mafa expression. This not only provides novel targets for preventing stearic acid-induced β-cell dysfunction, but also points to melatonin as a promising drug to combat type 2 diabetes progression. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genome-wide analysis in PC6 electroacupuncture to ameliorate carfilzomib-induced cardiotoxicity in mice
Yuxuan Chen, Rou Peng, Yi Qian, Yizhou Lu, Liyao Chen, Meiling Yu, Minjiao Jiang, Wei Wu, Shengfeng Lu
Gene.2024; 897: 148090. CrossRef - MiR-126 and miR-146a as Melatonin-Responsive Biomarkers for Neonatal Brain Ischemia
Maria Cristina Albertini, Tania Vanzolini, Serafina Perrone, Michael D. Weiss, Giuseppe Buonocore, Valentina Dell’Orto, Walter Balduini, Silvia Carloni
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience.2023; 73(9-10): 763. CrossRef
- Genome-wide analysis in PC6 electroacupuncture to ameliorate carfilzomib-induced cardiotoxicity in mice

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Gemigliptin Alleviates Succinate-Induced Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation by Ameliorating Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- Giang Nguyen, So Young Park, Dinh Vinh Do, Dae-Hee Choi, Eun-Hee Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):918-928. Published online November 15, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1530
- 3,403 View
- 227 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
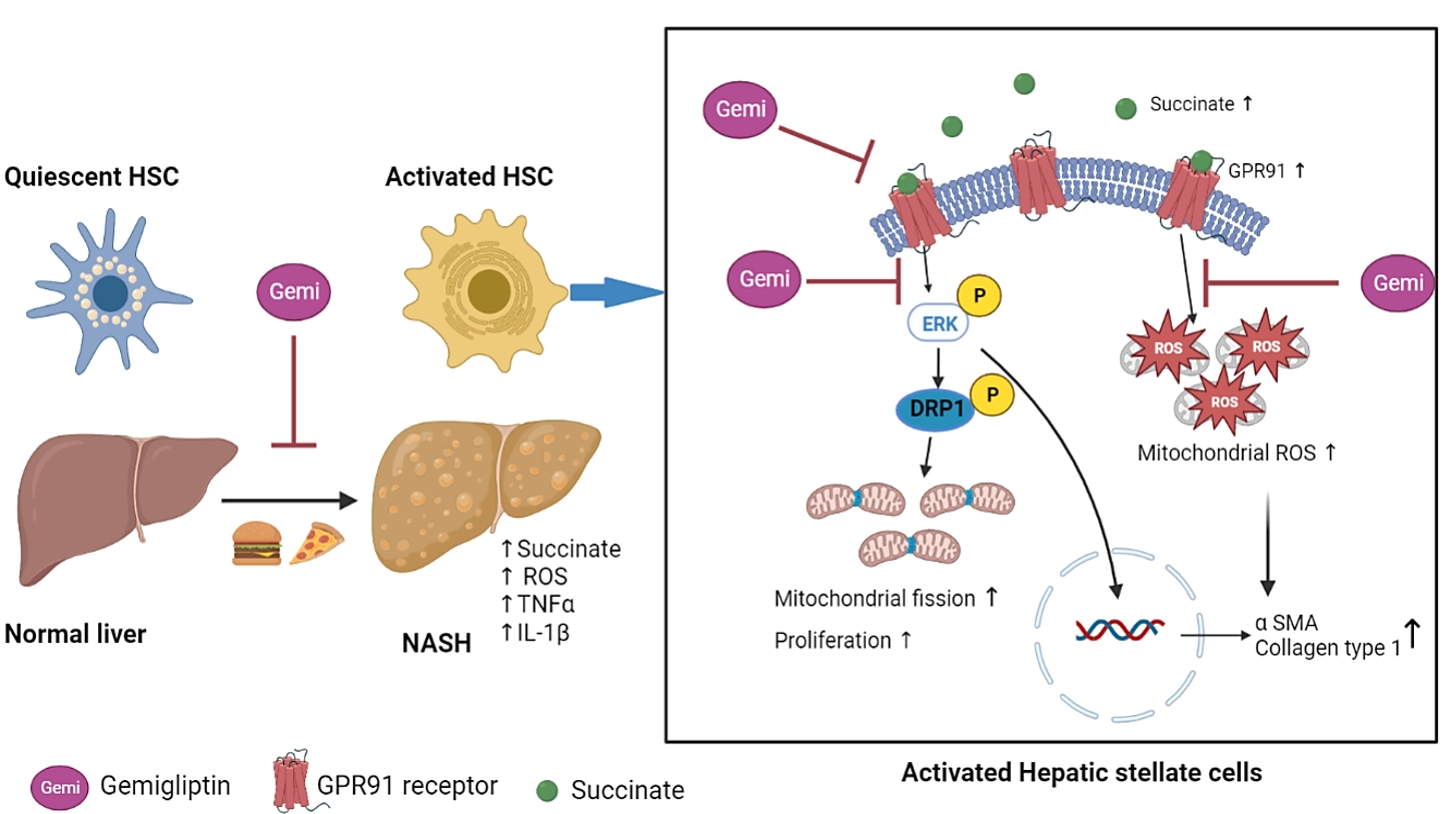
ePub - Background
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4Is) are used clinically as oral antidiabetic agents. Although DPP-4Is are known to ameliorate liver fibrosis, the protective mechanism of DPP-4Is in liver fibrosis remains obscure. In this study, gemigliptin was used to investigate the potential of DPP-4Is to alleviate the progression of liver fibrosis.
Methods
To clarify the effects and mechanisms of gemigliptin, we conducted various experiments in LX-2 cells (immortalized human hepatic stellate cells [HSCs], the principal effectors of hepatic fibrogenesis), which were activated by succinate and exhibited elevated expression of α-smooth muscle actin, collagen type 1, and pro-inflammatory cytokines and increased cell proliferation. In vivo, we examined the effects and mechanisms of gemigliptin on a high-fat, high-cholesterol–induced mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Results
Gemigliptin decreased the expression of fibrogenesis markers and reduced the abnormal proliferation of HSCs. In addition, gemigliptin reduced the succinate-induced production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS), intracellular ROS, and mitochondrial fission in HSCs. Furthermore, in the mouse model of NASH-induced liver fibrosis, gemigliptin alleviated both liver fibrosis and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Conclusion
Gemigliptin protected against HSC activation and liver fibrosis by alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production, indicating its potential as a strategy for preventing the development of liver disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improvement effect of gemigliptin on salivary gland dysfunction in exogenous methylglyoxal-injected rats
Woo Kwon Jung, Su-Bin Park, Hwa Young Yu, Junghyun Kim
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29362. CrossRef - Gemigliptin, a DPP4 inhibitor, ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through AMP-activated protein kinase-independent and ULK1-mediated autophagy
Youngmi Song, Hyekyung Yang, Juhee Kim, Yoonjin Lee, Sung-Ho Kim, In-Gu Do, Cheol-Young Park
Molecular Metabolism.2023; 78: 101806. CrossRef - DPP-4 Inhibitor in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patient with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Achieving Two Goals at Once?
Ji Cheol Bae
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 858. CrossRef
- Improvement effect of gemigliptin on salivary gland dysfunction in exogenous methylglyoxal-injected rats

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
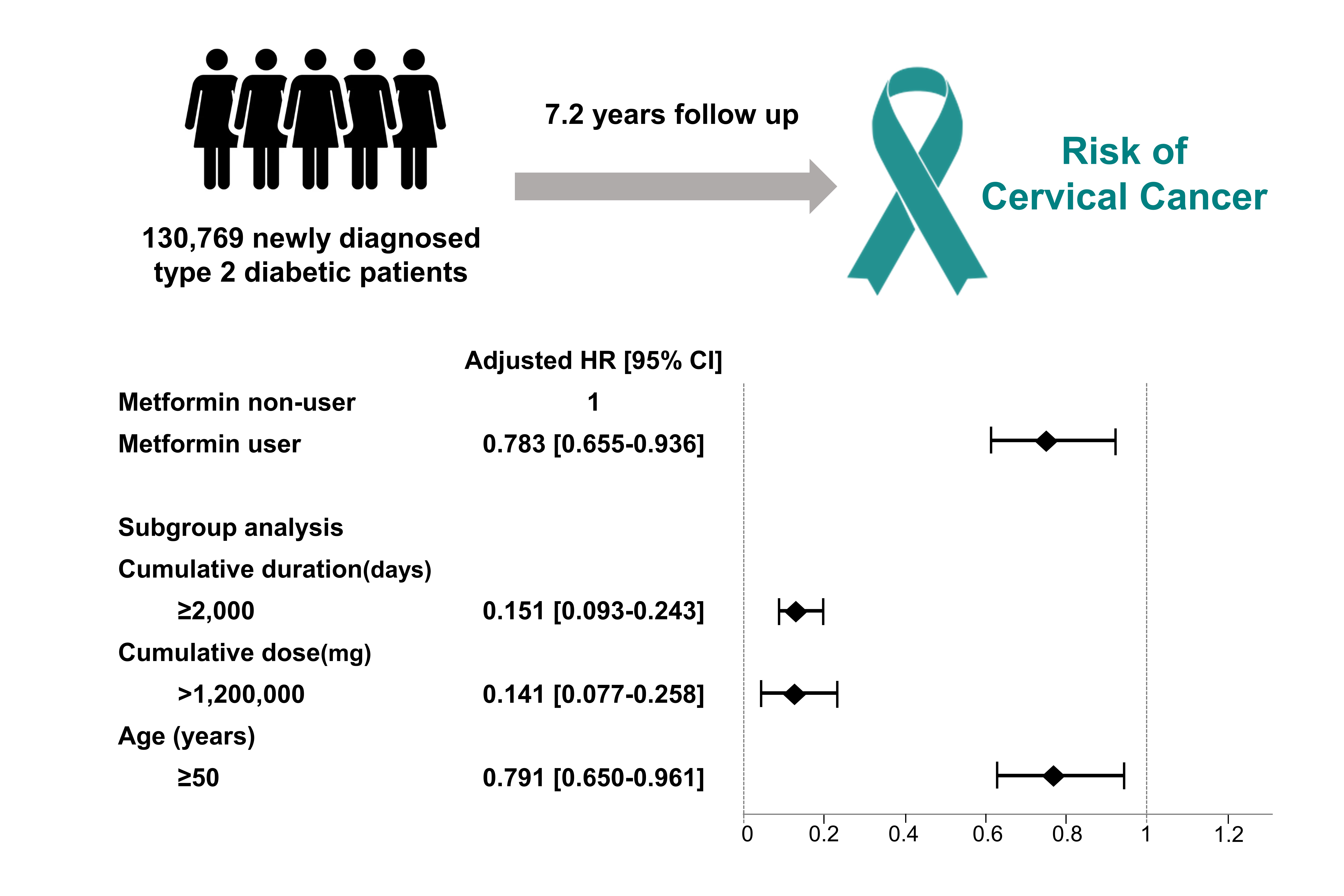
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Metformin and Cervical Cancer Risk in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
- Hyun Min Kim, Min Jin Kang, Sun Ok Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):929-937. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1613
- Correction in: Endocrinol Metab 2023;38(1):174
- 2,395 View
- 217 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Cervical cancer is a prevalent malignancy that is a major health problem for women worldwide. The cancer-preventive properties of metformin are well-known, but insufficient data have been reported regarding its relationship to cervical cancer. Therefore, in a nationwide population-based study, we investigated the association between metformin use and cervical cancer incidence in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study used the Korean National Health Insurance claims database. Individuals newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes between January 2005 and December 2009 were included. The occurrence of cervical cancer was explored by matching for age, economic status, region of residence, and use of anti-diabetic medication.
Results
In total, 66,013 metformin users and 64,756 non-users were analyzed. Cervical cancer occurred in 219 metformin users (0.33%) and 274 metformin non-users (0.42%) (hazard ratio [HR], 0.783; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.655 to 0.036; P=0.007). Moreover, cervical cancer risk was considerably reduced in those treated with a high dose (>1,200,000 mg) or for an extended period (≥2,000 days) compared to non-users (HR, 0.151; 95% CI, 0.093 to 0.243; P<0.001; and HR, 0.141; 95% CI, 0.077 to 0.258; P<0.001). The incidence was also significantly lower in metformin users among those over 50 years old (HR, 0.791; 95% CI, 0.650 to 0.961; P<0.001).
Conclusion
Metformin use in patients with newly diagnosed diabetes was associated with a lower risk of cervical cancer in Korea. Furthermore, a significant association was found between the use of metformin and cervical cancer in a dose- and duration-dependent manner and among those over 50 years old. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Repurposing of Chronically Used Drugs in Cancer Therapy: A Chance to Grasp
Mohamad Ali Hijazi, André Gessner, Nahed El-Najjar
Cancers.2023; 15(12): 3199. CrossRef - Network-based drug repurposing for HPV-associated cervical cancer
Faheem Ahmed, Young Jin Yang, Anupama Samantasinghar, Young Woo Kim, Jeong Beom Ko, Kyung Hyun Choi
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2023; 21: 5186. CrossRef - The Use of Metformin and Postoperative Insulin Pump Were Predictive Factors for Outcomes of Diabetic Colorectal Cancer Patients after Surgery
Xu-Rui Liu, Fei Liu, Zi-Wei Li, Quan Lv, Xin-Peng Shu, Lian-Shuo Li, Yue Tong, Wei Zhang, Dong Peng
Nutrition and Cancer.2023; 75(10): 1926. CrossRef
- Repurposing of Chronically Used Drugs in Cancer Therapy: A Chance to Grasp

Brief Report
- Adrenal Gland
- Aldosterone Immunoassay-Specific Cutoff Value for Seated Saline Suppression Test for Diagnosing Primary Aldosteronism
- So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, So Hee Park, So Hyun Cho, You-Bin Lee, Soo-Youn Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):938-942. Published online December 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1535
- 1,746 View
- 193 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
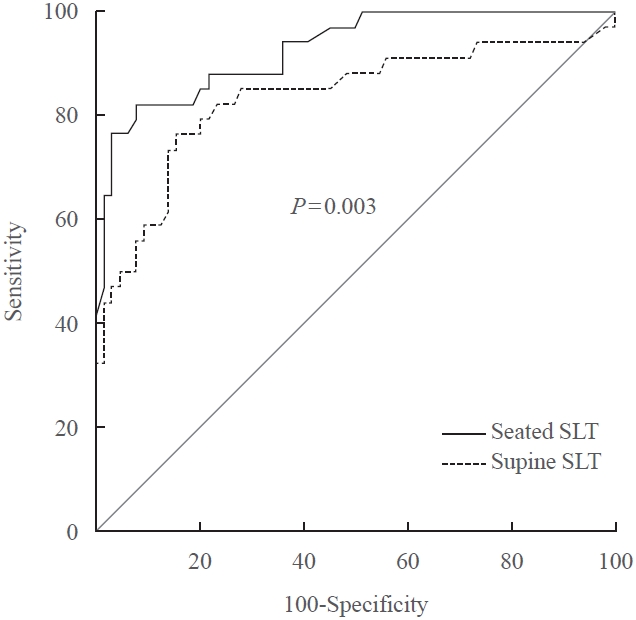
ePub - A seated saline loading test (SLT) using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is one of the most accepted confirmatory tests of primary aldosteronism. However, LC-MS/MS is time-consuming and is not widely available in diagnostic laboratories compared to immunoassay. With immunoassay, it is unknown whether SLT in the seated position is more accurate than that of the supine position, and a cutoff value of post-seated SLT plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) must be established in the Korean population. Ninety-eight patients underwent SLT in both positions, and post-SLT PAC was measured by LC-MS/MS and radioimmunoassay. We confirmed primary aldosteronism if post-seated SLT PAC by LC-MS/MS exceeded 5.8 ng/dL. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was greater for seated than supine SLT (0.928 vs. 0.834, P=0.003). The optimal cutoff value of post-seated SLT by radioimmunoassay was 6.6 ng/dL (sensitivity 83.3%, specificity 92.2%).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating the cut-off values of captopril challenge test for primary aldosteronism using the novel chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay method: a retrospective cohort study
Yuta Tezuka, Kei Omata, Yoshikiyo Ono, Kengo Kambara, Hiroki Kamada, Sota Oguro, Yuto Yamazaki, Celso E. Gomez-Sanchez, Akihiro Ito, Hironobu Sasano, Kei Takase, Tetsuhiro Tanaka, Hideki Katagiri, Fumitoshi Satoh
Hypertension Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Investigating the cut-off values of captopril challenge test for primary aldosteronism using the novel chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay method: a retrospective cohort study

Letter
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:641-51, Han-sang Baek et al.)
- May Thu Hla Aye, Sajid Adhi Raja, Vui Heng Chong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):943-944. Published online November 23, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1601

- 1,721 View
- 164 Download

Response
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:641-51, Han-sang Baek et al.)
- Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):945-946. Published online December 2, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.602
- [Original]
- 1,698 View
- 164 Download


 KES
KES



 First
First Prev
Prev



