Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > BROWSE ARTICLES > Previous issues
Namgok Lecture 2020
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Cellular and Intercellular Homeostasis in Adipose Tissue with Mitochondria-Specific Stress
- Min Jeong Choi, Saet-Byel Jung, Joon Young Chang, Minho Shong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):1-11. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.956
- 5,411 View
- 226 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
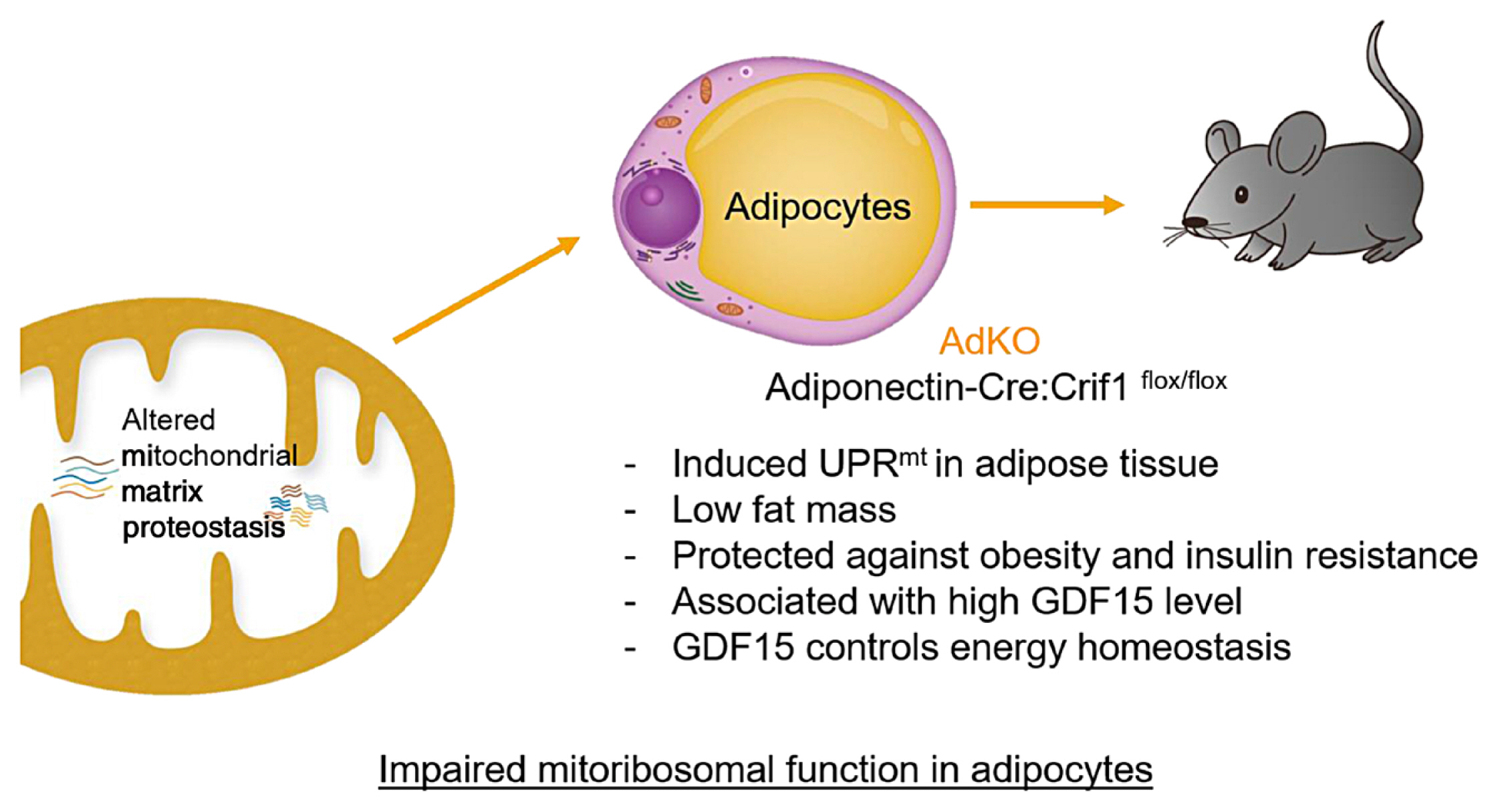
ePub - Paracrine interactions are imperative for the maintenance of adipose tissue intercellular homeostasis, and intracellular organelle dysfunction results in local and systemic alterations in metabolic homeostasis. It is currently accepted that mitochondrial proteotoxic stress activates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) in vitro and in vivo. The induction of mitochondrial chaperones and proteases during the UPRmt is a key cell-autonomous mechanism of mitochondrial quality control. The UPRmt also affects systemic metabolism through the secretion of cell non-autonomous peptides and cytokines (hereafter, metabokines). Mitochondrial function in adipose tissue plays a pivotal role in whole-body metabolism and human diseases. Despite continuing interest in the role of the UPRmt and quality control pathways of mitochondria in energy metabolism, studies on the roles of the UPRmt and metabokines in white adipose tissue are relatively sparse. Here, we describe the role of the UPRmt in adipose tissue, including adipocytes and resident macrophages, and the interactive roles of cell non-autonomous metabokines, particularly growth differentiation factor 15, in local adipose cellular homeostasis and systemic energy metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial stress-induced GFRAL signaling controls diurnal food intake and anxiety-like behavior
Carla Igual Gil, Bethany M Coull, Wenke Jonas, Rachel N Lippert, Susanne Klaus, Mario Ost
Life Science Alliance.2022; 5(11): e202201495. CrossRef - Stress-induced FGF21 and GDF15 in obesity and obesity resistance
Susanne Keipert, Mario Ost
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 32(11): 904. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial stress-induced GFRAL signaling controls diurnal food intake and anxiety-like behavior

Review Articles
- Adrenal gland
- The Genotype-Based Morphology of Aldosterone-Producing Adrenocortical Disorders and Their Association with Aging
- Xin Gao, Yuto Yamazaki, Yuta Tezuka, Kei Omata, Yoshikiyo Ono, Ryo Morimoto, Yasuhiro Nakamura, Fumitoshi Satoh, Hironobu Sasano
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):12-21. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.101

- 4,750 View
- 192 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Primary aldosteronism (PA) is the most common cause of secondary hypertension, and is associated with an increased incidence of cardiovascular events. PA itself is clinically classified into the following two types: unilateral PA, mostly composed of aldosteroneproducing adenoma (APA); and bilateral hyperaldosteronism, consisting of multiple aldosterone-producing micronodules (APMs) and aldosterone-producing diffuse hyperplasia. Histopathologically, those disorders above are all composed of compact and clear cells. The cellular morphology in the above-mentioned aldosterone-producing disorders has been recently reported to be closely correlated with patterns of somatic mutations of ion channels including KCNJ5, CACNA1D, ATP1A1, ATP2B3, and others. In addition, in non-pathological adrenal glands, APMs are frequently detected regardless of the status of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Aldosterone-producing nodules have been also proposed as non-neoplastic nodules that can be identified by hematoxylin and eosin staining. These non-neoplastic CYP11B2-positive nodules could represent possible precursors of APAs possibly due to the presence of somatic mutations. On the other hand, aging itself also plays a pivotal role in the development of aldosterone-producing lesions. For instance, the number of APMs was also reported to increase with aging. Therefore, recent studies indicated the novel classification of PA into normotensive PA (RAAS-independent APM) and clinically overt PA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Subtype-specific Body Composition and Metabolic Risk in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism
Seung Shin Park, Chang Ho Ahn, Sang Wan Kim, Ji Won Yoon, Jung Hee Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): e788. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 597. CrossRef - Correlation of Histopathologic Subtypes of Primary Aldosteronism with Clinical Phenotypes and Postsurgical Outcomes
Chang Ho Ahn, You-Bin Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Jung Hee Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Expression of CYP11B1 and CYP11B2 in adrenal adenoma correlates with clinical characteristics of primary aldosteronism
Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park, Hyeong Won Yu, Su‐Jin Kim, June Young Choi, Kyu Eun Lee, Sang Wan Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jung Hee Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2022; 96(1): 30. CrossRef - Pathology of Aldosterone Biosynthesis and its Action
Xin Gao, Yuto Yamazaki, Yuta Tezuka, Kei Omata, Yoshikiyo Ono, Ryo Morimoto, Yasuhiro Nakamura, Takashi Suzuki, Fumitoshi Satoh, Hironobu Sasano
The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine.2021; 254(1): 1. CrossRef - Cellular Senescence in Adrenocortical Biology and Its Disorders
Xin Gao, Faping Li, Bin Liu, Yuxiong Wang, Yishu Wang, Honglan Zhou
Cells.2021; 10(12): 3474. CrossRef
- Subtype-specific Body Composition and Metabolic Risk in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism

- Diabetes
- Peptidyl and Non-Peptidyl Oral Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists
- Hun Jee Choe, Young Min Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):22-29. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.102
- 27,759 View
- 652 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
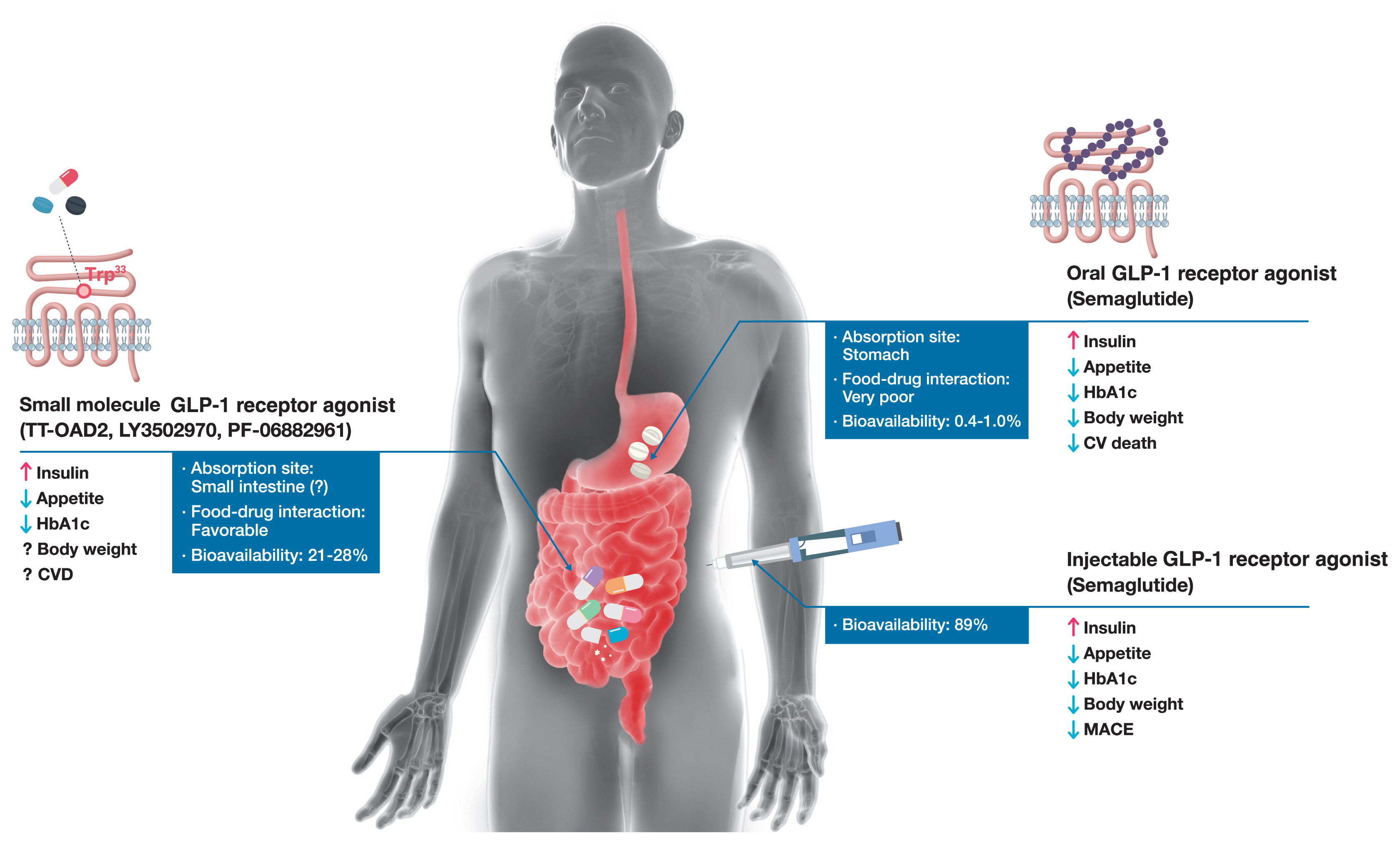
ePub - Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are efficacious glucose-lowering medications with salient benefits for body weight and cardiovascular events. This class of medications is now recommended as the top priority for patients with established cardiovascular disease or indicators of high risk. Until the advent of oral semaglutide, however, GLP-1 receptor agonists were available only in the form of subcutaneous injections. Aversion to needles, discomfort with self-injection, or skin problems at the injection site are commonly voiced problems in people with diabetes, and thus, attempts for non-invasive delivery strategies have continued. Herein, we review the evolution of GLP-1 therapy from its discovery and the development of currently approved drugs to the unprecedented endeavor to administer GLP-1 receptor agonists via the oral route. We focus on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of the recently approved oral GLP-1 receptor agonist, oral semaglutide. Small molecule oral GLP-1 receptor agonists are currently in development, and we introduce how these chemicals have addressed the challenge posed by interactions with the large extracellular ligand binding domain of the GLP-1 receptor. We specifically discuss the structure and pharmacological properties of TT-OAD2, LY3502970, and PF-06882961, and envision an era where more patients could benefit from oral GLP-1 receptor agonist therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sulfobetaine modification of poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles enhances mucus permeability and improves bioavailability of orally delivered liraglutide
Zhenyu Zhao, Ruihuan Ding, Yumei Wang, Ranran Yuan, Houqian Zhang, Tianyang Li, Wei Zheng, Entao Chen, Aiping Wang, Yanan Shi
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2024; 93: 105437. CrossRef - Physiology and pharmacology of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
D. V. Kurkin, D. A. Bakulin, E. I. Morkovin, V. I. Petrov, A. V. Strygin, K. N. Koryanova, Yu. V. Gorbunova, Yu. A. Kolosov, O. V. Ivanova, E. V. Pavlova, M. A. Dzhavakhyan, A. V. Zaborovsky, V. B. Saparova, I. E. Makarenko, R. I. Drai, A. N. Chumachenko
Pharmacy & Pharmacology.2024; 11(4): 347. CrossRef - G protein-coupled receptors driven intestinal glucagon-like peptide-1 reprogramming for obesity: Hope or hype?
Mohan Patil, Ilaria Casari, Leon N. Warne, Marco Falasca
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 172: 116245. CrossRef - Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs: Miracle drugs are blooming?
Binbin Gong, Zhihong Yao, Chenxu Zhou, Wenxi Wang, Lidan Sun, Jing Han
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2024; 269: 116342. CrossRef - Opportunities and challenges of incretin-based hypoglycemic agents treating type 2 diabetes mellitus from the perspective of physiological disposition
Yaochen Xie, Qian Zhou, Qiaojun He, Xiaoyi Wang, Jincheng Wang
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B.2023; 13(6): 2383. CrossRef - Advances in GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Shurui Hong, J. Xiao, Y. He
BIO Web of Conferences.2023; 61: 01006. CrossRef - Safety and efficacy of the new, oral, small-molecule, GLP-1 receptor agonists orforglipron and danuglipron for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Paschalis Karakasis, Dimitrios Patoulias, Konstantinos Pamporis, Panagiotis Stachteas, Konstantinos I. Bougioukas, Aleksandra Klisic, Nikolaos Fragakis, Manfredi Rizzo
Metabolism.2023; 149: 155710. CrossRef - A review of glucoregulatory hormones potentially applicable to the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: mechanism and brain delivery
Reeju Amatya, Kyoung Ah Min, Meong Cheol Shin
Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation.2022; 52(2): 195. CrossRef - Anti-Obesity Medications and Investigational Agents: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2022
Harold E. Bays, Angela Fitch, Sandra Christensen, Karli Burridge, Justin Tondt
Obesity Pillars.2022; 2: 100018. CrossRef - Structural basis of peptidomimetic agonism revealed by small-molecule GLP-1R agonists Boc5 and WB4-24
Zhaotong Cong, Qingtong Zhou, Yang Li, Li-Nan Chen, Zi-Chen Zhang, Anyi Liang, Qing Liu, Xiaoyan Wu, Antao Dai, Tian Xia, Wei Wu, Yan Zhang, Dehua Yang, Ming-Wei Wang
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Improved Split TEV GPCR β-arrestin-2 Recruitment Assays via Systematic Analysis of Signal Peptide and β-arrestin Binding Motif Variants
Yuxin Wu, Isabelle von Hauff, Niels Jensen, Moritz Rossner, Michael Wehr
Biosensors.2022; 13(1): 48. CrossRef - GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects
Xin Zhao, Minghe Wang, Zhitong Wen, Zhihong Lu, Lijuan Cui, Chao Fu, Huan Xue, Yunfeng Liu, Yi Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent developments in GLP‐1RA therapy: A review of the latest evidence of efficacy and safety and differences within the class
Evie K. Bain, Stephen C. Bain
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(S3): 30. CrossRef
- Sulfobetaine modification of poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles enhances mucus permeability and improves bioavailability of orally delivered liraglutide

- Thyroid
- Best Achievements in Clinical Thyroidology in 2020
- Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):30-35. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.103
- 4,418 View
- 244 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This review highlights the most interesting research in thyroidology conducted in 2020. The publications of interest discussed below dealt with the following topics: thyroid dysfunction, risk of thyroid cancer, molecular diagnostics and new therapeutics for thyroid cancer, and thyroid disease in the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic era.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Compensation for iodine deficiency conditions with drugs based on duckweed substrate
M. Kh. Sadulaev, M. I. Usmanova, T. T. Tataev, A. M. Inderbiev, A. S.-A. Zhamalullayla, A. Salamova
BIO Web of Conferences.2023; 76: 03002. CrossRef - Use of long non-coding RNAs for the molecular diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer
Daham Kim, Juyeon Yu, Jiwon Kim, Yoon-a Hwang, Jin Kyong Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Jung Hyun Yoon, Jin Young Kwak, Kee-Hyun Nam, Eun Jig Lee
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration with or without Negative Pressure for Different Types of Thyroid Nodules
Qi Zhou, Wenjun Wu, Fang Wang, Xiaohua Gong, Xiaojun Chen
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 5475. CrossRef
- Compensation for iodine deficiency conditions with drugs based on duckweed substrate

- Thyroid
- Best Achievements in Translational and Basic Thyroidology in 2020
- Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):36-40. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.104
- 3,236 View
- 136 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This review discusses articles published in 2020 that presented noteworthy achievements in translational and basic thyroidology. Previously unresolved questions about thyroid hormone receptor actions and signaling mechanisms were answered using various novel in vitro and in vivo models. Using high resolution cryo-electron microscopy, the fine functional structure of thyroglobulin was demonstrated, and new insights into the pathogenesis of thyroid disease were achieved, with a focus on research into thyroid-disrupting chemicals and the gut microbiome. Novel therapeutic approaches were tried in the field of advanced thyroid cancer treatments.

- Diabetes
- Best Achievements in Clinical Medicine in Diabetes and Dyslipidemia in 2020
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Mee-Kyung Kim, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):41-50. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.106
- 4,261 View
- 176 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Over the last two decades, our understanding of diabetes and treatment strategies have evolved tremendously, from scientific, mechanistic, and human perspectives. The categories of anti-diabetic medications expanded from a few to numerous, enabling clinicians to personalize diabetes care and treatment. Thanks to rapid growth in the field of science and medical engineering, newer treatment options are coming to the market with various advantages and disadvantages to be aware of. Therefore, clinicians should rapidly adopt new trends based on guidelines and data from many clinical trials in the field of diabetes. In the treatment of dyslipidemia, trends and guidelines are changing every year, and novel therapies are being developed. In this review, we would like to summarize the major achievements in clinical medicine in 2020 in the field of diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef - Effects of exercise initiation and smoking cessation after new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus on risk of mortality and cardiovascular outcomes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Effects of Obesity and Dyslipidaemia on the Prevalence of Diabetes Amongst Adults Aged ≥45 Years: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study
Simin Zhang, Donghan Sun, Xiaoyi Qian, Li Li, Wenwen Wu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8036. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Best Achievements in Pituitary and Adrenal Diseases in 2020
- Chang Ho Ahn, Jung Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):51-56. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.108

- 4,465 View
- 160 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Significant progress in pituitary and adrenal diseases was made in 2020. This review presents major translational and clinical advances in research on pituitary and adrenal diseases, encompassing their epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and clinical management. We address the controversy regarding the nomenclature of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors, omics-based molecular classification of pituitary adenomas, and novel drugs for Cushing’s disease in the field of pituitary diseases. In the field of adrenal diseases, we cover big data-driven epidemiology of adrenal tumors, steroid profiling as a new diagnostic tool, and the utility of scoring systems in the decision-making process of managing primary aldosteronism. This brief article will broaden readers’ understanding of pituitary and adrenal diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical management and outcomes of spinal metastasis of malignant adrenal tumor: A retrospective study of six cases and literature review
Xiangzhi Ni, Jing Wang, Jiashi Cao, Kun Zhang, Shuming Hou, Xing Huang, Yuanjin Song, Xin Gao, Jianru Xiao, Tielong Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 597. CrossRef
- Surgical management and outcomes of spinal metastasis of malignant adrenal tumor: A retrospective study of six cases and literature review

Editorial
- Diabetes
- Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Combination for the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes
- Jang Won Son
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):57-59. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.109
- 2,956 View
- 115 Download

Original Articles
- Clinical Study
- Romosozumab in Postmenopausal Korean Women with Osteoporosis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Efficacy and Safety Study
- Ki-Hyun Baek, Yoon-Sok Chung, Jung-Min Koh, In Joo Kim, Kyoung Min Kim, Yong-Ki Min, Ki Deok Park, Rajani Dinavahi, Judy Maddox, Wenjing Yang, Sooa Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Hyungjin Cho, Sung-Kil Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):60-69. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.848
- 6,693 View
- 388 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
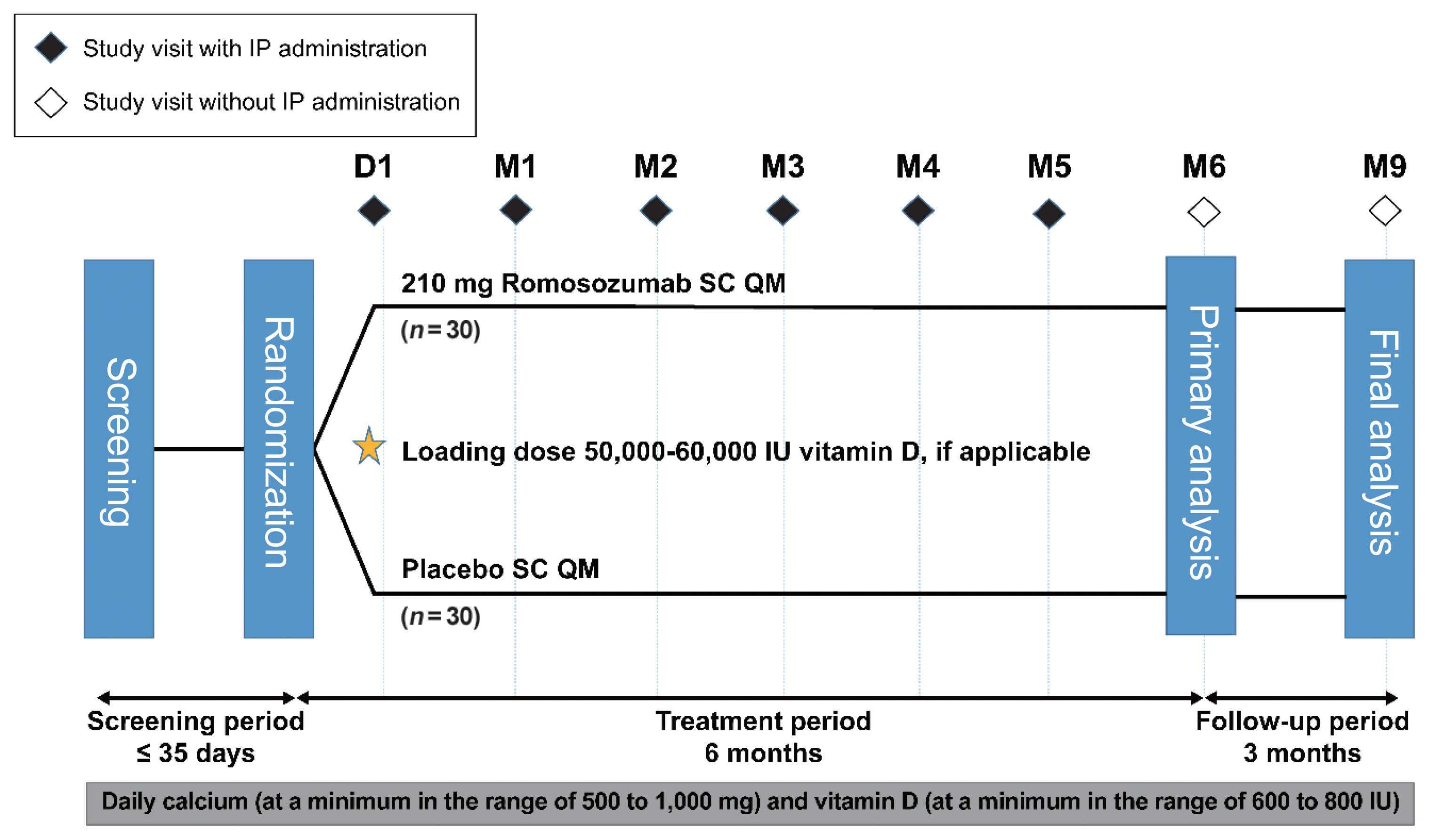
This phase 3 study evaluated the efficacy and safety of 6-month treatment with romosozumab in Korean postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.
Methods
Sixty-seven postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (bone mineral density [BMD] T-scores ≤–2.5 at the lumbar spine, total hip, or femoral neck) were randomized (1:1) to receive monthly subcutaneous injections of romosozumab (210 mg; n=34) or placebo (n=33) for 6 months.
Results
At month 6, the difference in the least square (LS) mean percent change from baseline in lumbar spine BMD (primary efficacy endpoint) between the romosozumab (9.5%) and placebo (–0.1%) groups was significant (9.6%; 95% confidence interval, 7.6 to 11.5; P<0.001). The difference in the LS mean percent change from baseline was also significant for total hip and femoral neck BMD (secondary efficacy endpoints). After treatment with romosozumab, the percent change from baseline in procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide transiently increased at months 1 and 3, while that in C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen showed a sustained decrease. No events of cancer, hypocalcemia, injection site reaction, positively adjudicated atypical femoral fracture or osteonecrosis of the jaw, or positively adjudicated serious cardiovascular adverse events were observed. At month 9, 17.6% and 2.9% of patients in the romosozumab group developed binding and neutralizing antibodies, respectively.
Conclusion
Treatment with romosozumab for 6 months was well tolerated and significantly increased lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck BMD compared with placebo in Korean postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02791516). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A pharmacovigilance analysis of FDA adverse event reporting system events for romosozumab
Zepeng Chen, Ming Li, Shuzhen Li, Yuxi Li, Junyan Wu, Kaifeng Qiu, Xiaoxia Yu, Lin Huang, Guanghui Chen
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2023; 22(4): 339. CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of romosozumab (evenity) for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in postmenopausal women: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials (CDM‐J)
Wenbo Huang, Masashi Nagao, Naohiro Yonemoto, Sen Guo, Takeshi Tanigawa, Yuji Nishizaki
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety.2023; 32(6): 671. CrossRef - Efficacy and Cardiovascular Safety of Romosozumab: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review
Seo-Yong Choi, Jeong-Min Kim, Sang-Hyeon Oh, Seunghyun Cheon, Jee-Eun Chung
Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2023; 33(2): 128. CrossRef - Clinical Studies On Romosozumab: An Alternative For Individuals With A High Risk Of Osteoporotic Fractures: A Current Concepts Review (Part I)
E. Carlos Rodriguez-Merchan, Alonso Moreno-Garcia, Hortensia De la Corte-Rodriguez
SurgiColl.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Romosozumab in osteoporosis: yesterday, today and tomorrow
Dong Wu, Lei Li, Zhun Wen, Guangbin Wang
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of anti-sclerostin antibodies in the treatment of osteoporosis: A meta-analysis and systematic review
Frideriki Poutoglidou, Efthimios Samoladas, Nikolaos Raikos, Dimitrios Kouvelas
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2022; 25(3): 401. CrossRef - Benefits of lumican on human bone health: clinical evidence using bone marrow aspirates
Yun Sun Lee, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Eunah Choi, Beom-Jun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(4): 821. CrossRef - What is the risk of cardiovascular events in osteoporotic patients treated with romosozumab?
I. R. Reid
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2022; 21(12): 1441. CrossRef - Proxied Therapeutic Inhibition on Wnt Signaling Antagonists and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: Multi-Omics Analyses
Yu Qian, Cheng-Da Yuan, Saber Khederzadeh, Ming-Yu Han, Hai-Xia Liu, Mo-Chang Qiu, Jian-Hua Gao, Wei-Lin Wang, Yun-Piao Hou, Guo-Bo Chen, Ke-Qi Liu, Lin Xu, David Karasik, Shu-Yang Xie, Hou-Feng Zheng
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi-Omics Analyses Identify Pleiotropy and Causality Between Circulating Sclerostin and Atrial Fibrillation
Yu Qian, Peng-Lin Guan, Saber Khederzadeh, Ke-Qi Liu, Cheng-Da Yuan, Ming-Yu Han, Hai-Xia Liu, Mo-Chang Qiu, Jian-Hua Gao, Wei-Lin Wang, Yun-Piao Hou, Guo-Bo Chen, Lin Xu, David Karasik, Shu-Yang Xie, sheng zhifeng, Hou-Feng Zheng
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- A pharmacovigilance analysis of FDA adverse event reporting system events for romosozumab

- Clinical Study
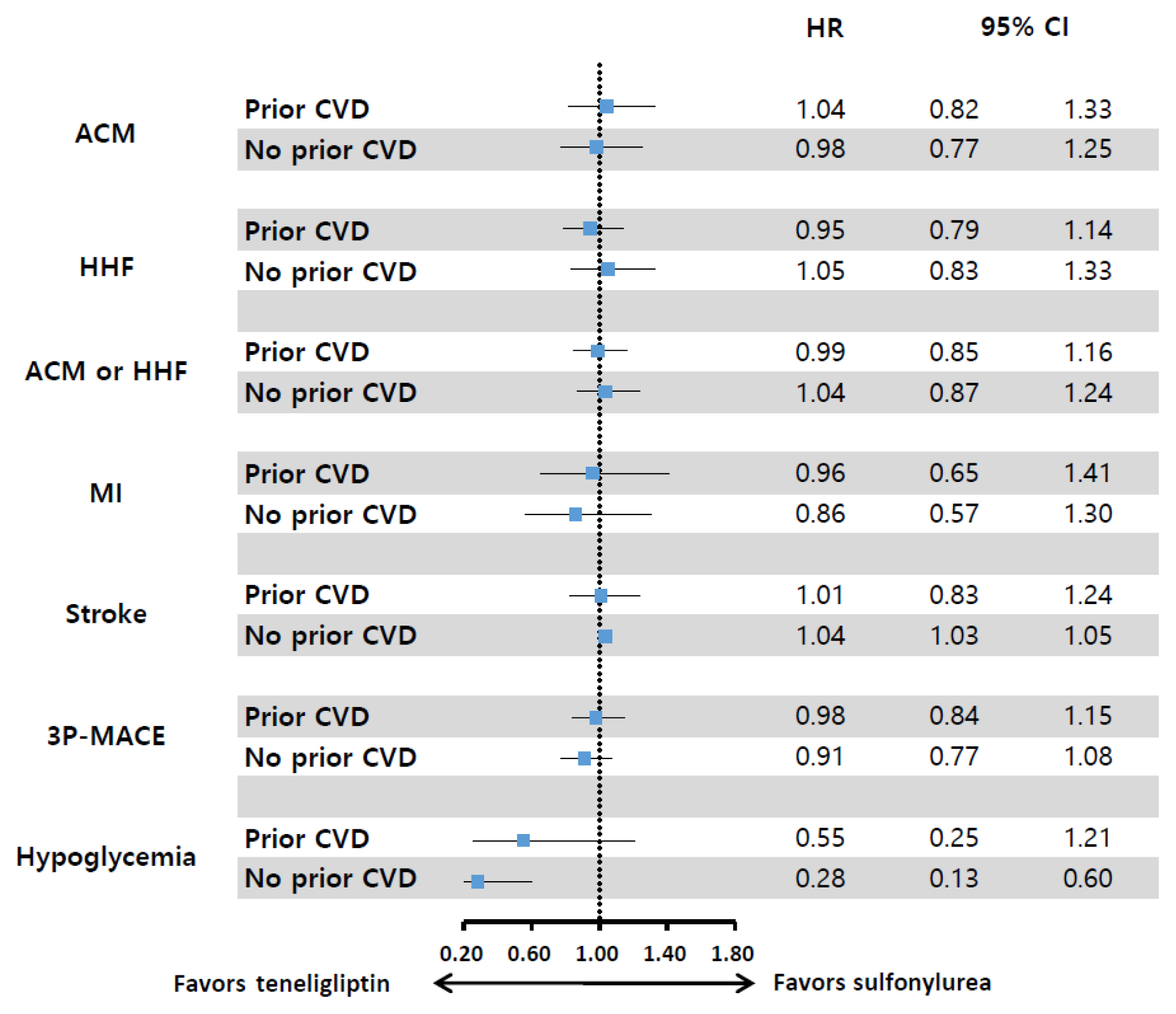
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Effect of Teneligliptin versus Sulfonylurea on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Real-World Study in Korea
- Da Hea Seo, Kyoung Hwa Ha, So Hun Kim, Dae Jung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):70-80. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.777
- 4,914 View
- 190 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Results regarding the cardiovascular (CV) effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors are inconsistent. This study aimed to assess the effects of teneligliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, on the risk of major CV outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients compared to sulfonylurea.
Methods
From January 1, 2015 to December 31, 2017, we conducted a retrospective cohort study using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. A total of 6,682 T2DM patients who were newly prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors or sulfonylurea were selected and matched in a 1:1 ratio by propensity score. The hazard ratios (HRs) for all-cause mortality, hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), all-cause mortality or HHF, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and hypoglycemia were assessed.
Results
During 641 days of follow-up, the use of teneligliptin was not associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality (HR, 1.00; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85 to 1.19), HHF (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.86 to 1.14), all-cause mortality or HHF (HR, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.90 to 1.14), MI (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.68 to 1.20), and stroke (HR, 1.00; 95% CI, 0.86 to 1.17) compared to the use of sulfonylurea. However, it was associated with a significantly lower risk of hypoglycemia (HR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.49 to 0.94) compared to sulfonylurea therapy.
Conclusion
Among T2DM patients, teneligliptin therapy was not associated with an increased risk of CV events including HHF, but was associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia compared to sulfonylurea therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between age at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality risks: A nationwide population-based study
Da Hea Seo, Mina Kim, Young Ju Suh, Yongin Cho, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111098. CrossRef - Systematic review and meta-analysis of teneligliptin for treatment of type 2 diabetes
R. Pelluri, S. Kongara, V. R. Nagasubramanian, S. Mahadevan, J. Chimakurthy
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 46(5): 855. CrossRef - Finding the most cost-effective option from commonly used Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in India: a systematic study
Harmanjit Singh, Ekta Arora, Seerat Narula, Mandeep Singla, Armaan Otaal, Jatin Sharma
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 18(4): 347. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef
- Association between age at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality risks: A nationwide population-based study

- Clinical Study
- Efficacy of Ethanol Ablation for Benign Thyroid Cysts and Predominantly Cystic Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Cheng-Chun Yang, Yung Hsu, Jyun-Yan Liou
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):81-95. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.833
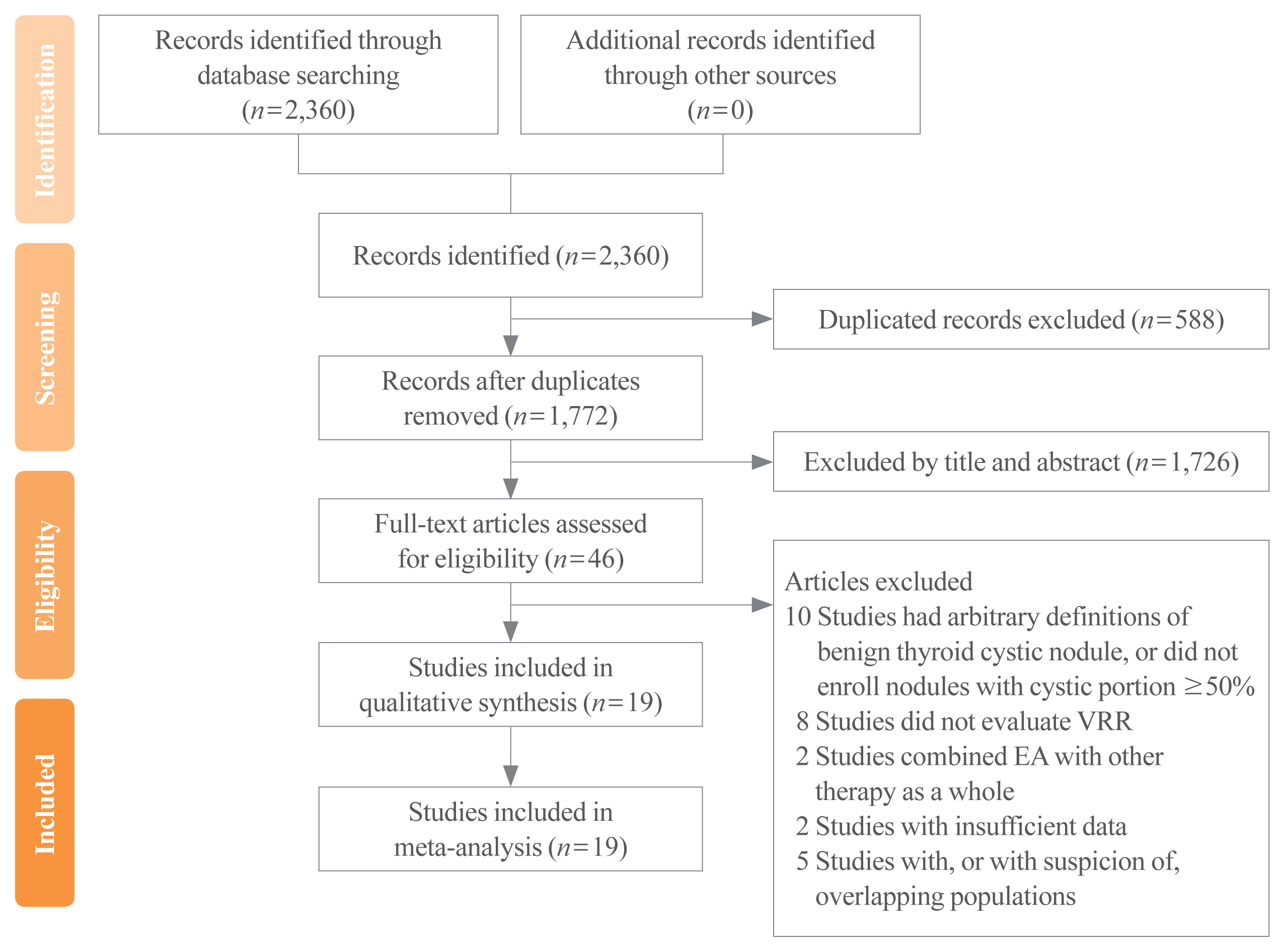
- 5,844 View
- 217 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Ultrasound-guided minimally invasive procedures are widely used to treat thyroid diseases. The objective of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of ethanol ablation (EA) in comparison with other non-surgical options in the treatment of benign thyroid cystic nodules.
Methods
We conducted a systematic search of studies on EA for thyroid cystic nodules, mainly in the Ovid-MEDLINE and Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane databases. The standardized mean difference (SMD) of the volume reduction ratio (VRR) after EA versus other non-surgical treatments comprised the primary outcome, whereas the odds ratio (OR) of therapeutic success rates between the two groups comprised the secondary outcome.
Results
The meta-analysis included 19 studies (four randomized controlled trials and 15 non-randomized studies) with 1,514 participants. The cumulative VRR of EA was 83.908% (95% confidence interval [CI], 79.358% to 88.457%). EA had a significantly higher pooled VRR (SMD, 0.381; 95% CI, 0.028 to 0.734; P=0.030), but not a significantly higher pooled therapeutic success rate (OR, 0.867; 95% CI, 0.132 to 5.689; P=0.880), than other forms of non-surgical management including radiofrequency ablation (RFA), polidocanol sclerotherapy, and simple aspiration with or without saline flush. However, the VRR and therapeutic success rate were not significantly different between EA and RFA. Major complications were recorded only in six patients (0.53%) with self-limiting dysphonia.
Conclusion
The role of EA as the first-line treatment for benign thyroid cysts and predominantly cystic nodules is supported by its high effectiveness and good safety profile compared to other currently available non-surgical options. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrasound-guided ethanol ablation versus the Sistrunk operation as a primary treatment for thyroglossal duct cysts
Dongbin Ahn, Ji Hye Kwak, Gil Joon Lee, Jin Ho Sohn
Ultrasonography.2024; 43(1): 25. CrossRef - The Comparison of Efficacy and Safety between Radiofrequency Ablation Alone and Ethanol Ablation Followed by Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Mixed Cystic and Solid Thyroid Nodule
Min Gang Jo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jae Ho Shin, Min Guk Seo, So Lyung Jung
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasound-Guided Ethanol Ablation for Thyroglossal Duct Cyst: A Review of Technical Issues and Potential as a New Standard Treatment
Dongbin Ahn
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(17): 5445. CrossRef - Ultrasound‐Guided Ethanol Ablation as a Primary Treatment for Thyroglossal Duct Cyst: Feasibility, Characteristics, and Outcomes
Dongbin Ahn, Ji Hye Kwak, Gil Joon Lee, Jin Ho Sohn
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.2023; 168(6): 1381. CrossRef - Ultraschallgeführte lokalablative Verfahren zur Behandlung von Schilddrüsenläsionen
Johannes-Paul Richter, Carl-Philip Richter, Daniel Gröner
Angewandte Nuklearmedizin.2023; 46(02): 169. CrossRef - A Case of Thyroid Abscess Following Ethanol Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodule
Heungrae Cho, Dongbin Ahn, Ji Hye Kwak, Gil Joon Lee
Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2023; 66(9): 624. CrossRef - Sclerotherapy with a Viscum Album Extract for the Two Patients with Cystic Thyroid Nodule
Jae Ha Lee, Seung Won Lee, Ki Nam Park
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 139. CrossRef - Percutaneous ethanol injection in thyroid nodular pathology and metastatic cervical adenopathies: A systematic review, meta-analysis and economic evaluation
Beatriz León-Salas, Aránzazu Hernández-Yumar, Diego Infante-Ventura, Aythami de Armas Castellano, Yadira González Hernández, Renata Linertová, Teresa Téllez Santana, Pedro de Pablos-Velasco, María M. Trujillo-Martín
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición.2023; 70(9): 572. CrossRef - Ultraschallgeführte lokalablative Verfahren zur Behandlung von Schilddrüsenläsionen
Johannes-Paul Richter, Carl-Philip Richter, Daniel Gröner
Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie.2023; 102(12): 916. CrossRef - Percutaneous ethanol injection in thyroid nodular pathology and metastatic cervical adenopathies: A systematic review, meta-analysis and economic evaluation
Beatriz León-Salas, Aránzazu Hernández-Yumar, Diego Infante-Ventura, Aythami de Armas Castellano, Yadira González Hernández, Renata Linertová, Teresa Téllez Santana, Pedro de Pablos-Velasco, María M. Trujillo-Martín
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición (English ed.).2023; 70(9): 572. CrossRef - Safety and Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Nonfunctional Thyroid Nodules in Children: A Retrospective Study of 62 Patients with Over Four Years of Follow-Up
Liwen Li, Xinguang Qiu
Thyroid.2022; 32(5): 525. CrossRef - Ethanol ablation for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules
Gabrielle K. Steinl, Latoya A. Stewart, Catherine McManus, James A. Lee, Jennifer H. Kuo
The American Journal of Surgery.2022; 224(1): 408. CrossRef - Minimally-invasive treatments for benign thyroid nodules: recommendations for information to patients and referring physicians by the Italian Minimally-Invasive Treatments of the Thyroid group
Giovanni Mauri, Stella Bernardi, Andrea Palermo, Roberto Cesareo, Enrico Papini, Luigi Solbiati, Daniele Barbaro, Salvatore Monti, Maurilio Deandrea, Laura Fugazzola, Giovanni Gambelunghe, Roberto Negro, Stefano Spiezia, Fulvio Stacul, Luca Maria Sconfien
Endocrine.2022; 76(1): 1. CrossRef - Image-Guided Percutaneous Ablation for Primary and Metastatic Tumors
Arian Mansur, Tushar Garg, Apurva Shrigiriwar, Vahid Etezadi, Christos Georgiades, Peiman Habibollahi, Timothy C. Huber, Juan C. Camacho, Sherif G. Nour, Alan Alper Sag, John David Prologo, Nariman Nezami
Diagnostics.2022; 12(6): 1300. CrossRef - Approach to FNA of Thyroid Gland Cysts
Esther Diana Rossi, Pietro Tralongo, Vincenzo Fiorentino, Mariangela Curatolo, Carmine Bruno, Carmen De Crea, Marco Raffaelli, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Luigi Maria Larocca
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2022; 29(6): 358. CrossRef
- Ultrasound-guided ethanol ablation versus the Sistrunk operation as a primary treatment for thyroglossal duct cysts

- Clinical Study
- Lactate Dehydrogenase A as a Potential New Biomarker for Thyroid Cancer
- Eun Jeong Ban, Daham Kim, Jin Kyong Kim, Sang-Wook Kang, Jandee Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Kee-Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Kunhong Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):96-105. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.819

- 5,761 View
- 185 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Several cancers show increased levels of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), which are associated with cancer progression. However, it remains unclear whether LDHA levels are associated with papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) aggressiveness or with the presence of the PTC prognostic marker, the BRAFV600E mutation. This study aimed to evaluate the potential of LDHA as a PTC prognostic marker.
Methods
LDHA expression was examined in 83 PTC tissue specimens by immunohistochemistry. Human thyroid cell lines were genetically manipulated to overexpress BRAFV600E or were treated with a BRAF-specific short hairpin RNA (shBRAF), whose effects on LDHA expression were evaluated by Western blotting. Data from 465 PTC patients were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and analyzed to validate the in vitro results.
Results
LDHA was aberrantly overexpressed in PTC. Intense immunostaining for LDHA was observed in PTC specimens carrying mutated BRAF, whereas the intensity was less in wild-type BRAF samples. Overexpression of BRAFV600E resulted in LDHA upregulation, whereas treatment with shBRAF downregulated LDHA in human thyroid cell lines. Furthermore, LDHA mRNA expression was significantly elevated and associated with BRAFV600E expression in thyroid cancer tissues from TCGA database. Additionally, LDHA overexpression was found to be correlated with aggressive clinical features of PTC, such as lymph node metastases and advanced tumor stages.
Conclusion
LDHA overexpression is associated with the BRAFV600E mutation and an aggressive PTC behavior. Therefore, LDHA may serve as a biomarker and therapeutic target in PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrated proteogenomic and metabolomic characterization of papillary thyroid cancer with different recurrence risks
Ning Qu, Di Chen, Ben Ma, Lijun Zhang, Qiuping Wang, Yuting Wang, Hongping Wang, Zhaoxian Ni, Wen Wang, Tian Liao, Jun Xiang, Yulong Wang, Shi Jin, Dixin Xue, Weili Wu, Yu Wang, Qinghai Ji, Hui He, Hai-long Piao, Rongliang Shi
Nature Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral lymphocytes and lactate dehydrogenase correlate with response and survival in head and neck cancers treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
Cassie Pan, Qian Vicky Wu, Jenna Voutsinas, Jeffrey J. Houlton, Brittany Barber, Zain H. Rizvi, Emily Marchiano, Neal Futran, George E. Laramore, Jay J. Liao, Upendra Parvathaneni, Renato G. Martins, Jonathan R. Fromm, Cristina P. Rodriguez
Cancer Medicine.2023; 12(8): 9384. CrossRef - LncRNA GLTC targets LDHA for succinylation and enzymatic activity to promote progression and radioiodine resistance in papillary thyroid cancer
Liang Shi, Rui Duan, Zhenhua Sun, Qiong Jia, Wenyu Wu, Feng Wang, Jianjun Liu, Hao Zhang, Xue Xue
Cell Death & Differentiation.2023; 30(6): 1517. CrossRef - Integrated analysis of circulating and tissue proteomes reveals that fibronectin 1 is a potential biomarker in papillary thyroid cancer
Guochao Ye, Xiaomei Zhang, Mansheng Li, Zixiang Lin, Yongcan Xu, Haoru Dong, Jie Zhou, Jiaqi Zhang, Sheng Wang, Yunping Zhu, Xiaobo Yu, Xu Qian
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting metabolism by B-raf inhibitors and diclofenac restrains the viability of BRAF-mutated thyroid carcinomas with Hif-1α-mediated glycolytic phenotype
Marianna Aprile, Simona Cataldi, Caterina Perfetto, Antonio Federico, Alfredo Ciccodicola, Valerio Costa
British Journal of Cancer.2023; 129(2): 249. CrossRef - circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
Hongguo Xie, Xiaopeng Lu
Open Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The potential role of reprogrammed glucose metabolism: an emerging actionable codependent target in thyroid cancer
Sai-li Duan, Min Wu, Zhe-Jia Zhang, Shi Chang
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - CENPE and LDHA were potential prognostic biomarkers of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
Hui-feng Wu, Hao Liu, Zhe-wei Zhang, Ji-min Chen
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Classification for Staging and Managing Patients with Biopolymer-induced Human Adjuvant Disease
Jaime Eduardo Pachón Suárez, Marcela C. Salazar, Victor Z. Rizo
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open.2022; 10(2): e4137. CrossRef - Development of Metabolic Synthetic Lethality and Its Implications for Thyroid Cancer
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Seong Eun Lee, Yea Eun Kang, Minho Shong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 53. CrossRef - Drug delivery for metabolism targeted cancer immunotherapy
Taravat Khodaei, Sahil Inamdar, Abhirami P. Suresh, Abhinav P. Acharya
Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews.2022; 184: 114242. CrossRef - Sulfur quantum dot based fluorescence assay for lactate dehydrogenase activity detection
Shengnan Fan, Xiaoqing Li, Fanghui Ma, Minghui Yang, Juan Su, Xiang Chen
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2022; 430: 113989. CrossRef - STAT3/LINC00671 axis regulates papillary thyroid tumor growth and metastasis via LDHA-mediated glycolysis
Nan Huo, Rui Cong, Zhi-jia Sun, Wen-chao Li, Xiang Zhu, Chun-yuan Xue, Zhao Chen, Lu-yuan Ma, Zhong Chu, Yu-chen Han, Xiao-feng Kang, Song-hao Jia, Nan Du, Lei Kang, Xiao-jie Xu
Cell Death & Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Integrated proteogenomic and metabolomic characterization of papillary thyroid cancer with different recurrence risks

- Clinical Study
- Association of Vitamin D Deficiency with Diabetic Nephropathy
- So-hyeon Hong, Young Bin Kim, Hoon Sung Choi, Tae-Dong Jeong, Jin Taek Kim, Yeon Ah Sung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):106-113. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.826

- 8,417 View
- 222 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) levels are associated with the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, the association between 25OHD and metabolic health status or diabetic complications is inconclusive. We evaluated this relationship between vitamin D status and metabolic parameters and complications of T2DM.
Methods
This study included 1,392 patients with T2DM who visited Eulji and Ewha Diabetes Center between January 2011 and August 2016. Anthropometric parameters and laboratory tests including glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), lipid profile, liver and kidney function, and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) were evaluated. Diabetic macro- and microvascular complications were determined through a medical record review. Serum 25OHD concentrations were measured by chemiluminescent immunoassay.
Results
The mean 25OHD level was 16.8±9.6 ng/mL. Vitamin D deficiency (<20 ng/mL) and severe deficiency (<10 ng/mL) were observed in 990 (71.1%) and 351 (25.2%) participants, respectively. 25OHD level was positively correlated with age and highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) level and negatively correlated with HbA1c, triglyceride level, and UACR. HDL-C and UACR were significantly associated with 25OHD after adjusting for other variables. Vitamin D deficiency was independently related to nephropathy after adjusting for confounding variables.
Conclusion
Vitamin D deficiency was common among Korean T2DM patients; it was independently associated with microalbuminuria and HDL level, and positively related to diabetic nephropathy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ED-71 ameliorates bone regeneration in type 2 diabetes by reducing ferroptosis in osteoblasts via the HIF1α pathway
Maoshan Wang, Yingxue Liu, Houda Gui, Gaoqiang Ma, Binyang Li, Zhanwei Zhang, Gyeonghwi Yu, Ailin Wu, Xin Xu, Dongjiao Zhang
European Journal of Pharmacology.2024; 969: 176303. CrossRef - Vitamin D metabolism in diabetic nephropathy
Z. V. Abilov, R. Kh. Salimkhanov, A. A. Povaliaeva, A. Yu. Zhukov, E. A. Pigarova, L. K. Dzeranova, L. Ya. Rozhinskaya
Obesity and metabolism.2024; 20(4): 283. CrossRef - COVID-19 infection and metabolic comorbidities: Mitigating role of nutritional sufficiency and drug – nutraceutical combinations of vitamin D
Sumit Kumar Mandal, Meghana Tare, P.R. Deepa
Human Nutrition & Metabolism.2023; 31: 200179. CrossRef - Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review
Thais de Oliveira e Silva Ullmann, Beatrys Juliani Ramalho, Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Ricardo José Tofano, Claudio José Rubira, Elen Landgraf Guiguer, Sandra Maria Barbalho, Uri Adrian Prync Flato, Katia Portero Sloan, Adriano Cressoni Araujo
Journal of Renal Nutrition.2023; 33(5): 618. CrossRef - Diabetic Nephropathy: Significance of Determining Oxidative Stress and Opportunities for Antioxidant Therapies
Marina Darenskaya, Sergey Kolesnikov, Natalya Semenova, Lyubov Kolesnikova
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12378. CrossRef - Association between serum 25- hydroxyvitamin D and albuminuiria in middle-aged and older Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes
Luyan Zhang, Qian Guo, Yanjia Xu, Wenzhen Wei, Yu Wang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D deficiency and its associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mitku Mammo Taderegew, Gashaw Garedew Woldeamanuel, Alemayehu Wondie, Atsede Getawey, Abera Nesiru Abegaz, Fentahun Adane
BMJ Open.2023; 13(10): e075607. CrossRef - Progression of diabetic nephropathy and vitamin D serum levels: A pooled analysis of 7722 patients
Yomna E. Dean, Sameh Samir Elawady, Wangpan Shi, Ahmed A. Salem, Arinnan Chotwatanapong, Haya Ashraf, Tharun Reddi, Prashant Obed Reddy Dundi, Waleed Yasser Habash, Mohamed Yasser Habash, Safaa Ahmed, Hana M. Samir, Ahmed Elsayed, Aryan Arora, Abhinav Aro
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence of Vitamin D Deficiency and Its Association With Microalbuminuria in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Muhammad Hamza Riaz, Ammar Jamil, Hira Yousaf, Muhammad Hassan, Muhammad Ahmer Sohaib, Sharjeel Babar, Muhammad Hassan Ahmad, Ibtesam Allahi, Muhammad Zeshan Mehmood, Tayyab Mumtaz Khan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Vitamin D in Diabetic Nephropathy: A Translational Approach
Charlotte Delrue, Reinhart Speeckaert, Joris R. Delanghe, Marijn M. Speeckaert
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(2): 807. CrossRef - Associations of serum amyloid A and 25‐hydroxyvitamin D with diabetic nephropathy: A cross‐sectional study
Qian Liu, Jin Sun, Tongdao Xu, Guangrong Bian, Fumeng Yang
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Formulation Strategies for Improving the Stability and Bioavailability of Vitamin D-Fortified Beverages: A Review
Elsa F. Vieira, Suene Souza
Foods.2022; 11(6): 847. CrossRef - Association between Vitamin D Status and Mortality among Adults with Diabetic Kidney Disease
Feng Xu, Hongyu Lu, Tianwen Lai, Ling Lin, Yongsong Chen, Pratibha V. Nerurkar
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Assessment of the relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D and albuminuria in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Seyed Alireza Zomorodian, Maryam Shafiee, Zeinab Karimi, Fatemeh Masjedi, Amirhossein Roshanshad
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Serum 25 (OH) Vitamin D With Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in Type 2 Diabetes
Suyan Duan, Fang Lu, Buyun Wu, Chengning Zhang, Guangyan Nie, Lianqin Sun, Zhimin Huang, Honglei Guo, Bo Zhang, Changying Xing, Yanggang Yuan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Dietary Supplementations on Neuropathic Pain
Francesco D’Egidio, Giorgia Lombardozzi, Housem E. Kacem Ben Haj M’Barek, Giada Mastroiacovo, Margherita Alfonsetti, Annamaria Cimini
Life.2022; 12(8): 1125. CrossRef - Emergence of Ectopic Adrenal Tissues-What are the Probable Mechanisms?
Gürkan Tarçın, Oya Ercan
Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology.2022; 14(3): 258. CrossRef - Nutritional Supplements for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
Khaled M. Abdelrahman, Kevin V. Hackshaw
Biomedicines.2021; 9(6): 674. CrossRef - Vitamin D Deficiency as a Predictor of a High Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease in Pancreas Transplant Candidates With Type 1 Diabetes
Małgorzata Buksińska-Lisik, Przemysław J. Kwasiborski, Robert Ryczek, Wojciech Lisik, Artur Mamcarz
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and Metabolic Parameters in Healthy Korean Adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI
Jeonghoon Ha, Hansang Baek, Chaiho Jeong, Hyunsam Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Moo Il Kang, Dong-Jun Lim
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 5233. CrossRef - Association Between 25(OH)Vitamin D, HbA1c and Albuminuria in Diabetes Mellitus: Data From a Population-Based Study (VIDAMAZON)
João Soares Felício, Hana Andrade de Rider Britto, Pedro Celeira Cortez, Fabrício de Souza Resende, Manuela Nascimento de Lemos, Lorena Vilhena de Moraes, Vitória Teixeira de Aquino, Fernanda de Souza Parente, Natércia Neves Marques de Queiroz, João Felíc
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D Analogs Can Retard the Onset or Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review
Samuel N. Uwaezuoke
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- ED-71 ameliorates bone regeneration in type 2 diabetes by reducing ferroptosis in osteoblasts via the HIF1α pathway

- Clinical Study
- Longitudinal Changes of High Molecular Weight Adiponectin are Associated with Postpartum Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Dong-Hwa Lee, Jung Ah Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):114-122. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.831
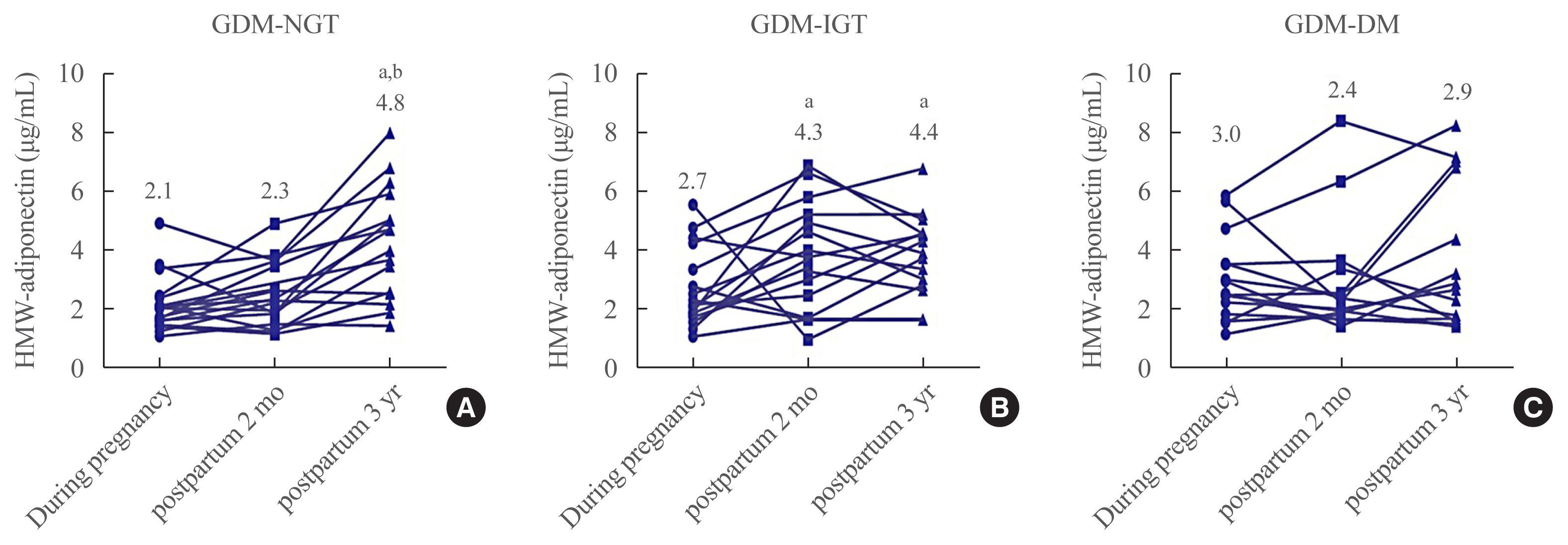
- 3,900 View
- 102 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The influence of serial changes of adipokines on maternal glucose metabolism from pregnancy to postpartum periods in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus (pGDM) has not been thoroughly explored. We tried to examine the relationship between the serial changes of adipokines and the development of diabetes mellitus (DM) in women with pGDM.
Methods
We longitudinally measured following adipokines: high molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin, retinol-binding protein-4 (RBP-4), lipocalin-2, and chemerin, during pregnancy, and at 2 months and 3 years after delivery. Based on glucose status at postpartum 3 years, we divided into three groups: normal glucose tolerance (GDM-NGT, n=20), impaired glucose tolerance (GDM-IGT, n=23), and GDM-DM (n=22). We analyzed the correlations between adipokines and various metabolic parameters.
Results
Plasma HMW adiponectin levels were not different among the three groups during pregnancy. However, HMW adiponectin levels increased at 3 years after the delivery in women with GDM-NGT compared with women with GDM-DM. In the GDM-IGT group, HMW adiponectin levels increased at 2 months postpartum compared to pregnancy period. In contrast, HMW adiponectin levels showed no alternation after parturition in women with GDM-DM. HMW adiponectin was negatively correlated with body mass index and a homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance. Other adipokines such as RBP-4, lipocalin-2, and chemerin neither showed any differences among the groups nor any significant correlations with 3 years postpartum status of glucose intolerance.
Conclusion
Serial changes of HMW adiponectin are associated with the maintenance of glucose metabolism in women with pGDM after delivery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reproductive risk factors across the female lifecourse and later metabolic health
Amy R. Nichols, Jorge E. Chavarro, Emily Oken
Cell Metabolism.2024; 36(2): 240. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Colostral Appetite-Regulating Adipokines
Jolanta Lis-Kuberka, Marta Berghausen-Mazur, Magdalena Orczyk-Pawiłowicz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3853. CrossRef - The levels of osteopontin in human milk of Chinese mothers and its associations with maternal body composition
Huijuan Ruan, Qingya Tang, Xuan Zhao, Yajie Zhang, Xuelin Zhao, Yi Xiang, Wei Geng, Yi Feng, Wei Cai
Food Science and Human Wellness.2022; 11(5): 1419. CrossRef - Association of circulatory adiponectin with the parameters of Madras Diabetes Research Foundation-Indian Diabetes Risk Score
MohdD Khan, MohammadK Ahmad, Roshan Alam, Saba Khan, Geeta Jaiswal, MohammadM Khan
Journal of Diabetology.2022; 13(4): 331. CrossRef
- Reproductive risk factors across the female lifecourse and later metabolic health

- Clinical Study
- Molecular Correlates and Nuclear Features of Encapsulated Follicular-Patterned Thyroid Neoplasms
- Chan Kwon Jung, Andrey Bychkov, Dong Eun Song, Jang-Hee Kim, Yun Zhu, Zhiyan Liu, Somboon Keelawat, Chiung-Ru Lai, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Kaori Kameyama, Kennichi Kakudo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):123-133. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.860

- 5,032 View
- 147 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Assessing nuclear features is diagnostically challenging in the aspect of thyroid pathology. The aim of this study was to determine whether pathologists could distinguish BRAF-like and RAS-like nuclear features morphologically and identify morphological features to differentiate thyroid tumors with RAS-like mutations from encapsulated papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) with predominant follicular growth and BRAFV600E mutation.
Methods
Representative whole slide images of 16 encapsulated thyroid tumors with predominant follicular growth were reviewed by 12 thyroid pathologists using a web browser-based image viewer. Total nuclear score was calculated from semi-quantitatively scored eight nuclear features. The molecular profile of RAS and BRAF genes was determined by Sanger sequencing.
Results
Total nuclear score ranging 0 to 24 could differentiate BRAF-like tumors from RAS-like tumors with a cut-off value of score 14. The interobserver agreement was the highest for the assessment of nuclear pseudoinclusions (NPIs) but the lowest for nuclear elongation and sickle-shaped nuclei. NPIs were found in tumors with BRAFV600E mutation, but not in tumors with RAS-like mutations. Total nuclear scores were significantly higher for tumors with BRAFV600E than for those with RAS-like mutations (P<0.001).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that NPIs and high nuclear scores have diagnostic utility as rule-in markers for differentiating PTC with BRAFV600E mutation from benign or borderline follicular tumors with RAS-like mutations. Relaxation of rigid criteria for nuclear features resulted in an overdiagnosis of PTC. Immunostaining or molecular testing for BRAFV600E mutation is a useful adjunct for cases with high nuclear scores to identify true PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differentiating BRAF V600E- and RAS-like alterations in encapsulated follicular patterned tumors through histologic features: a validation study
Chankyung Kim, Shipra Agarwal, Andrey Bychkov, Jen-Fan Hang, Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Kennichi Kakudo, Somboon Keelawat, Chih-Yi Liu, Zhiyan Liu, Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Chanchal Rana, Huy Gia Vuong, Yun Zhu, Chan Kwon Jung
Virchows Archiv.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Presence of Typical “BRAFV600E-Like” Atypia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma is Highly Specific for the Presence of the BRAFV600E Mutation
John Turchini, Loretta Sioson, Adele Clarkson, Amy Sheen, Leigh Delbridge, Anthony Glover, Mark Sywak, Stan Sidhu, Anthony J. Gill
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(1): 112. CrossRef - Could Oxidative Stress Play a Role in the Development and Clinical Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer?
Maria Kościuszko, Angelika Buczyńska, Adam Jacek Krętowski, Anna Popławska-Kita
Cancers.2023; 15(12): 3182. CrossRef - Pitfalls in thyroid pathology and the medicolegal aspects of error
David N Poller
Diagnostic Histopathology.2023; 29(11): 495. CrossRef - Developing Models to Predict BRAFV600E and RAS Mutational Status in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Clinicopathological Features and pERK1/2 Immunohistochemistry Expression
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Imam Subekti, Sonar Soni Panigoro, Asmarinah, Lisnawati, Retno Asti Werdhani, Hasrayati Agustina, Dina Khoirunnisa, Mutiah Mutmainnah, Fajar Lamhot Gultom, Abdillah Hasbi Assadyk, Maria Francisca Ham
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2803. CrossRef - The Asian Thyroid Working Group, from 2017 to 2023
Kennichi Kakudo, Chan Kwon Jung, Zhiyan Liu, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Andrey Bychkov, Huy Gia Vuong, Somboon Keelawat, Radhika Srinivasan, Jen-Fan Hang, Chiung-Ru Lai
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(6): 289. CrossRef - Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features (NIFTP): Tumour Entity with a Short History. A Review on Challenges in Our Microscopes, Molecular and Ultrasonographic Profile
Ivana Kholová, Elina Haaga, Jaroslav Ludvik, David Kalfert, Marie Ludvikova
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 250. CrossRef - Update from the 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Thyroid Tumors: A Standardized Diagnostic Approach
Chan Kwon Jung, Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 703. CrossRef - Different Threshold of Malignancy for RAS-like Thyroid Tumors Causes Significant Differences in Thyroid Nodule Practice
Kennichi Kakudo
Cancers.2022; 14(3): 812. CrossRef - The Incidence of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: A Meta-Analysis Assessing Worldwide Impact of the Reclassification
Chanchal Rana, Huy Gia Vuong, Thu Quynh Nguyen, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Chan Kwon Jung, Kennichi Kakudo, Andrey Bychkov
Thyroid.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Differentiating BRAF V600E- and RAS-like alterations in encapsulated follicular patterned tumors through histologic features: a validation study


 KES
KES



 First
First Prev
Prev



