Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > BROWSE ARTICLES > Previous issues
Review Articles
- Miscellaneous
- Encountering COVID-19 as Endocrinologists
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung Hee Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):197-205. Published online June 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.197
- 13,225 View
- 277 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The world is entering an era of disaster and chaos due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Since its first emergence in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, COVID-19 has swept through Asia and propagated throughout the world to Europe and North America. As of April 13, 1,773,084 people were infected and 111,652 people had died from COVID-19 globally, and new record levels of infection are being reported every day. Based on the data that have been amassed so far, the primary risk factors for a severe disease course or even mortality from COVID-19 are underlying diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. As the global prevalence of diabetes continues to increase, patients with endocrine diseases such as diabetes mellitus and those who are on long-term corticosteroid therapy due to adrenal insufficiency or hypopituitarism are at risk for a poor prognosis of COVID-19. As endocrinologists, we would like to briefly review the current knowledge about the relationship between COVID-19 and endocrine diseases and to discuss what we can do for the safety and health of our patients with endocrine diseases in this globally threatening situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adverse Events Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents with Endocrinological Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study
İbrahim Mert Erbaş, İrem Ceren Erbaş, Gözde Akın Kağızmanlı, Kübra Yüksek Acinikli, Özge Besci, Korcan Demir, Ece Böber, Nurşen Belet, Ayhan Abacı
Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology.2023; 15(3): 248. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - New-onset and relapsed Graves’ disease following COVID-19 vaccination: a comprehensive review of reported cases
Kan Chen, Yiyang Gao, Jing Li
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Neuroendocrine Changes and Hypothalamo-Pituitary
Autoimmunity in Patients with COVID-19
Mustafa Sait Gonen, Annamaria De Bellis, Emre Durcan, Giuseppe Bellastella, Paolo Cirillo, Lorenzo Scappaticcio, Miriam Longo, Basak Ecem Bircan, Serdar Sahin, Cem Sulu, Hande Mefkure Ozkaya, Dildar Konukoglu, Fatma Ferda Kartufan, Fahrettin Kelestimur
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2022; 54(03): 153. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: Association intensify risk factors for morbidity and mortality
Prateek Sharma, Tapan Behl, Neelam Sharma, Sukhbir Singh, Ajmer Singh Grewal, Ali Albarrati, Mohammed Albratty, Abdulkarim M. Meraya, Simona Bungau
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 151: 113089. CrossRef - The Relationship between COVID-19 and Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis: A Large Spectrum from Glucocorticoid Insufficiency to Excess—The CAPISCO International Expert Panel
Mojca Jensterle, Rok Herman, Andrej Janež, Wael Al Mahmeed, Khalid Al-Rasadi, Kamila Al-Alawi, Maciej Banach, Yajnavalka Banerjee, Antonio Ceriello, Mustafa Cesur, Francesco Cosentino, Massimo Galia, Su-Yen Goh, Sanjay Kalra, Peter Kempler, Nader Lessan,
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(13): 7326. CrossRef - WhatsApp-Based virtual consultation in clinical practice during COVID times: A prospective institutional study
RamakanthBhargav Panchangam, Pradeep Puthenveetil, SunilKumar Kota, Sabaretnam Mayilvaganan
Annals of African Medicine.2022; 21(2): 132. CrossRef - Thyroid and COVID-19: a review on pathophysiological, clinical and organizational aspects
G. Lisco, A. De Tullio, E. Jirillo, V. A. Giagulli, G. De Pergola, E. Guastamacchia, V. Triggiani
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(9): 1801. CrossRef - Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeongwoo Lee, Hyewon Nam, Dae-Sung Kyoung, Dong Wook Shin, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 251. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - Collateral Damage of the COVID‐19 Pandemic on Nutritional Quality and Physical Activity: Perspective from South Korea
Soo Lim, Hyunjung Lim, Jean‐Pierre Després
Obesity.2020; 28(10): 1788. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 in the post-acute phase patients - possible links with physical and rehabilitation medicine and balneotherapy
Constantin Munteanu, Diana-Loreta PĂUN, Alina-Maria ȘUȚĂ, Simin Aysel FLORESCU, Gelu ONOSE, Mihail Hoteteu
Balneo Research Journal.2020; 11(Vol.11, no): 350. CrossRef - Managing Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic
John Doupis, Konstantinos Avramidis
European Endocrinology.2020; 16(2): 85. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sung-Rae Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 737. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and the Endocrine System
Michelle D Lundholm, Caroline Poku, Nicholas Emanuele, Mary Ann Emanuele, Norma Lopez
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adverse Events Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents with Endocrinological Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
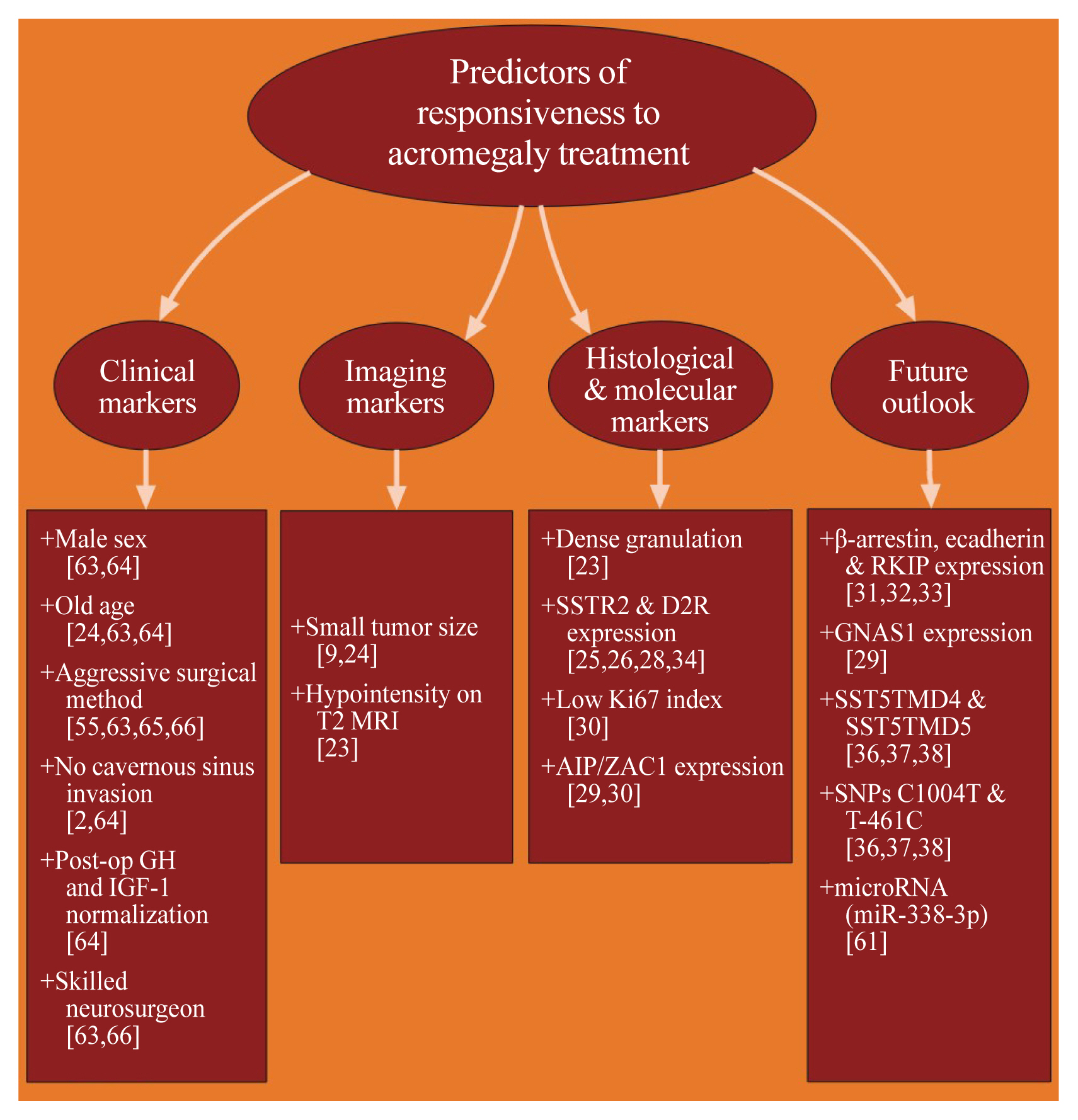
- Precision Therapy in Acromegaly Caused by Pituitary Tumors: How Close Is It to Reality?
- Cheol Ryong Ku, Vladimir Melnikov, Zhaoyun Zhang, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):206-216. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.206
- 6,672 View
- 250 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Acromegaly presents with an enigmatic range of symptoms and comorbidities caused by chronic and progressive growth hormone elevations, commonly due to endocrinologic hypersecretion from a pituitary gland tumor. Comprehensive national acromegaly databases have been appearing over the years, allowing for international comparisons of data, although still presenting varying prevalence and incidence rates. Lack of large-scale analysis in geographical and ethnic differences in clinical presentation and management requires further research. Assessment of current and novel predictors of responsiveness to distinct therapy can lead to multilevel categorization of patients, allowing integration into new clinical guidelines and reduction of increased morbidity and mortality associated with acromegaly. This review compares current data from epidemiological studies and assesses the present-day application of prognostic factors in medical practice, the reality of precision therapy, as well as its future prospects in acromegaly, with a special focus on its relevance to the South Korean population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomarkers of response to treatment in acromegaly
Leandro Kasuki, Elisa Lamback, Ximene Antunes, Mônica R. Gadelha
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 19(1): 71. CrossRef - Multiomics Approach to Acromegaly: Unveiling Translational Insights for Precision Medicine
Kyungwon Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 463. CrossRef - Risk of depression in patients with acromegaly in Korea (2006-2016): a nationwide population-based study
Shinje Moon, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
European Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 189(3): 363. CrossRef - The Future of Somatostatin Receptor Ligands in Acromegaly
Monica R Gadelha, Luiz Eduardo Wildemberg, Leandro Kasuki
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(2): 297. CrossRef - Innovative therapeutics in acromegaly
Leandro Kasuki, Mônica R. Gadelha
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 36(6): 101679. CrossRef - Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Patients With Acromegaly
Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Kyung-Soo Kim, Cheol-Young Park
Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning-based Prediction Model for Treatment of Acromegaly With First-generation Somatostatin Receptor Ligands
Luiz Eduardo Wildemberg, Aline Helen da Silva Camacho, Renan Lyra Miranda, Paula C L Elias, Nina R de Castro Musolino, Debora Nazato, Raquel Jallad, Martha K P Huayllas, Jose Italo S Mota, Tobias Almeida, Evandro Portes, Antonio Ribeiro-Oliveira, Lucio Vi
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(7): 2047. CrossRef - Skin anomalies in acromegalic patients (Review of the practical aspects)
Florica Sandru, Adelina Popa, Dan Paduraru, Alexandru Filipescu, Mara Carsote, Adina Ghemigian
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Biomarkers of response to treatment in acromegaly

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Effects of Cardiovascular Risk Factor Variability on Health Outcomes
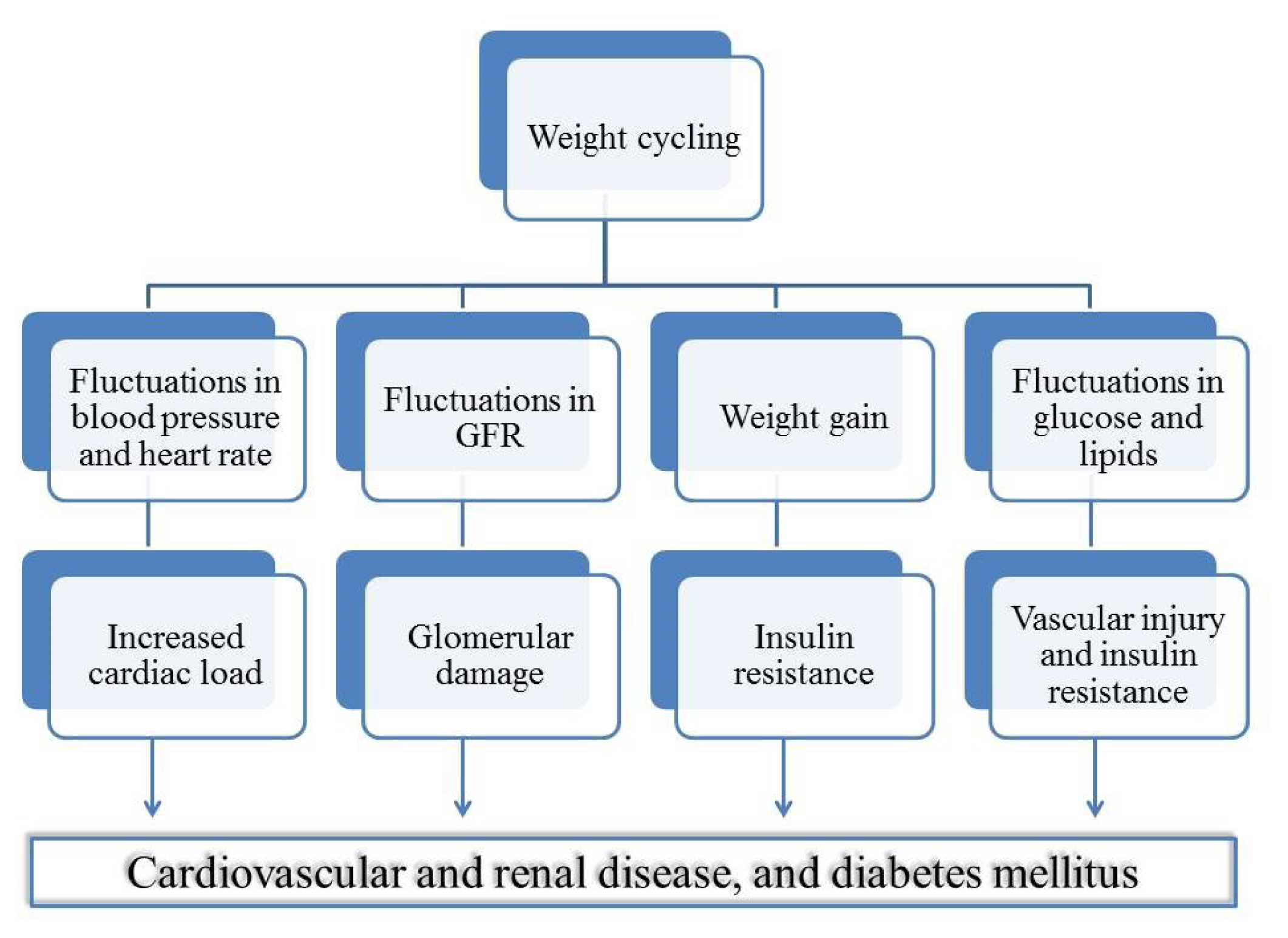
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):217-226. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.217
- 9,165 View
- 193 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Innumerable studies have suggested “the lower, the better” for cardiovascular risk factors, such as body weight, lipid profile, blood pressure, and blood glucose, in terms of health outcomes. However, excessively low levels of these parameters cause health problems, as seen in cachexia, hypoglycemia, and hypotension. Body weight fluctuation is related to mortality, diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, although contradictory findings have been reported. High lipid variability is associated with increased mortality and elevated risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, end-stage renal disease, and dementia. High blood pressure variability is associated with increased mortality, myocardial infarction, hospitalization, and dementia, which may be caused by hypotension. Furthermore, high glucose variability, which can be measured by continuous glucose monitoring systems or self-monitoring of blood glucose levels, is associated with increased mortality, microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes, and hypoglycemic events, leading to hospitalization. Variability in metabolic parameters could be affected by medications, such as statins, antihypertensives, and hypoglycemic agents, and changes in lifestyle patterns. However, other mechanisms modify the relationships between biological variability and various health outcomes. In this study, we review recent evidence regarding the role of variability in metabolic parameters and discuss the clinical implications of these findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sex Differences in Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Treatment Among Young Israeli Patients Following Premature Acute Coronary Syndrome
Feras Haskiah, Karam Abdelhai, Ranin Hilu, Abid Khaskia
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term variability in physiological measures in relation to mortality and epigenetic aging: prospective studies in the USA and China
Hui Chen, Tianjing Zhou, Shaowei Wu, Yaying Cao, Geng Zong, Changzheng Yuan
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Relationship between Short- and Mid-Term Glucose Variability and Blood Pressure Profile Parameters: A Scoping Review
Elena Vakali, Dimitrios Rigopoulos, Petros C. Dinas, Ioannis-Alexandros Drosatos, Aikaterini G. Theodosiadi, Andriani Vazeou, George Stergiou, Anastasios Kollias
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(6): 2362. CrossRef - Lipid treatment status and goal attainment among patients with premature acute coronary syndrome in Israel
Feras Haskiah, Abid Khaskia
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2023; 17(3): 367. CrossRef - Research on obesity using the National Health Information Database: recent trends
Eun-Jung Rhee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(2): 35. CrossRef - Risk of fracture according to temporal changes of low body weight changes in adults over 40 years: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Jung Guel Kim, Jae-Young Hong, Jiwon Park, Sang-Min Park, Kyungdo Han, Ho-Joong Kim, Jin S. Yeom
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High Body Weight Variability
Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 163. CrossRef - Puerarin Attenuates High-Glucose and High-Lipid-Induced Inflammatory Injury in H9c2 Cardiomyocytes via CAV3 Protein Upregulation
YiFu Tian, CaiXia Zhou, XiaoYang Bu, Qian Lv, Qin Huang
Journal of Inflammation Research.2023; Volume 16: 2707. CrossRef - Visit-to-Visit Glucose Variability, Cognition, and Global Cognitive Decline: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Christopher L Schaich, Michael P Bancks, Kathleen M Hayden, Jingzhong Ding, Stephen R Rapp, Alain G Bertoni, Susan R Heckbert, Timothy M Hughes, Morgana Mongraw-Chaffin
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e243. CrossRef - Association between lipid variability and the risk of mortality in cancer patients not receiving lipid-lowering agents
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association of Postprandial Triglyceride Variability with Renal Dysfunction and Microalbuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus: A Retrospective and Observational Study
Natsumi Matsuoka-Uchiyama, Haruhito A. Uchida, Shugo Okamoto, Yasuhiro Onishi, Katsuyoshi Katayama, Mariko Tsuchida-Nishiwaki, Hidemi Takeuchi, Rika Takemoto, Yoshiko Hada, Ryoko Umebayashi, Naoko Kurooka, Kenji Tsuji, Jun Eguchi, Hirofumi Nakajima, Kenic
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Associations of variability in body weight and glucose levels with the risk of hip fracture in people with diabetes
Jeongmin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Sang Hyun Park, Mee Kyoung Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moo-Il Kang, Seung-Hwan Lee
Metabolism.2022; 129: 155135. CrossRef - The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors: Causative Factor or Epiphenomenon?
Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 257. CrossRef - Changes in Underweight Status and Risk of Hip Fracture: A Korean Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Sangsoo Han, Jiwon Park, Hae-Dong Jang, Kyungdo Han, Choungah Lee, Wonseok Kim, Jae-Young Hong
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(7): 1913. CrossRef - Dynamic physical examination indicators of cardiovascular health: A single-center study in Shanghai, China
Rongren Kuang, Yiling Liao, Xinhan Xie, Biao Li, Xiaojuan Lin, Qiang Liu, Xiang Liu, Wenya Yu, Yajing Wang
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0268358. CrossRef - Characteristics and Clinical Course of Diabetes of the Exocrine Pancreas: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Nami Lee, So Jeong Park, Dongwoo Kang, Ja Young Jeon, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan-Woo Lee, Edward J. Boyko, Seung Jin Han
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(5): 1141. CrossRef - Lipid Variability and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
Shuting Li, Leying Hou, Siyu Zhu, Qian Yi, Wen Liu, Yang Zhao, Feitong Wu, Xue Li, An Pan, Peige Song
Nutrients.2022; 14(12): 2450. CrossRef - Impact of Visit-to-Visit Triglyceride-Glucose Index Variability on the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Elderly
Fei Chen, Ying Pan, Ziqing Liu, Rong Huang, Jing Wang, Jian Shao, Yaqin Gong, Xiyi Sun, Xiaobo Jiang, Weihao Wang, Zhaoqiang Li, Shao Zhong, Qi Pan, Kaixin Zhou, Muhammad Furqan Akhtar
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - Mean versus variability of lipid measurements over 6 years and incident cardiovascular events: More than a decade follow-up
Soroush Masrouri, Leila Cheraghi, Niloofar Deravi, Neda Cheraghloo, Maryam Tohidi, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Variability in Physiological Measures in Relation to Mortality and Epigenetic Aging: Prospective Studies in the US and China
Hui Chen, Tianjing Zhou, Shaowei Wu, Yaying Cao, Geng Zong, Changzheng Yuan
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Acute Glucose Shift Induces the Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in THP-1 Cells
Ji Yeon Lee, Yup Kang, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Seung Jin Han
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(18): 9952. CrossRef - Body Weight Change and Cardiovascular Disease: Effect of Weight Gain, Weight Loss, and Weight Cycling
Jung-Hwan Cho, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(4): 73. CrossRef - Fasting Glucose Variability as a Risk Indicator for End-Stage Kidney Disease in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Da Young Lee, Jaeyoung Kim, Sanghyun Park, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A. Seo, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyungdo Han, Nan Hee Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(24): 5948. CrossRef - Characteristics and Clinical Course of Diabetes of the Exocrine Pancreas: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Studybrief Title: Diabetes of the Exocrine Pancreas
Nami Lee, So Jeong Park, Dongwoo Kang, Ja Young Jeon, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan-Woo Lee, Edward J. Boyko, Seung Jin Han
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of a wearable cuff-less wristwatch-type blood pressure monitoring device
Joon Ho Moon, Myung-Kyun Kang, Chang-Eun Choi, Jeonghee Min, Hae-Young Lee, Soo Lim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Sex Differences in Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Treatment Among Young Israeli Patients Following Premature Acute Coronary Syndrome

- Thyroid
- Amino Acid Transporters as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Thyroid Cancer
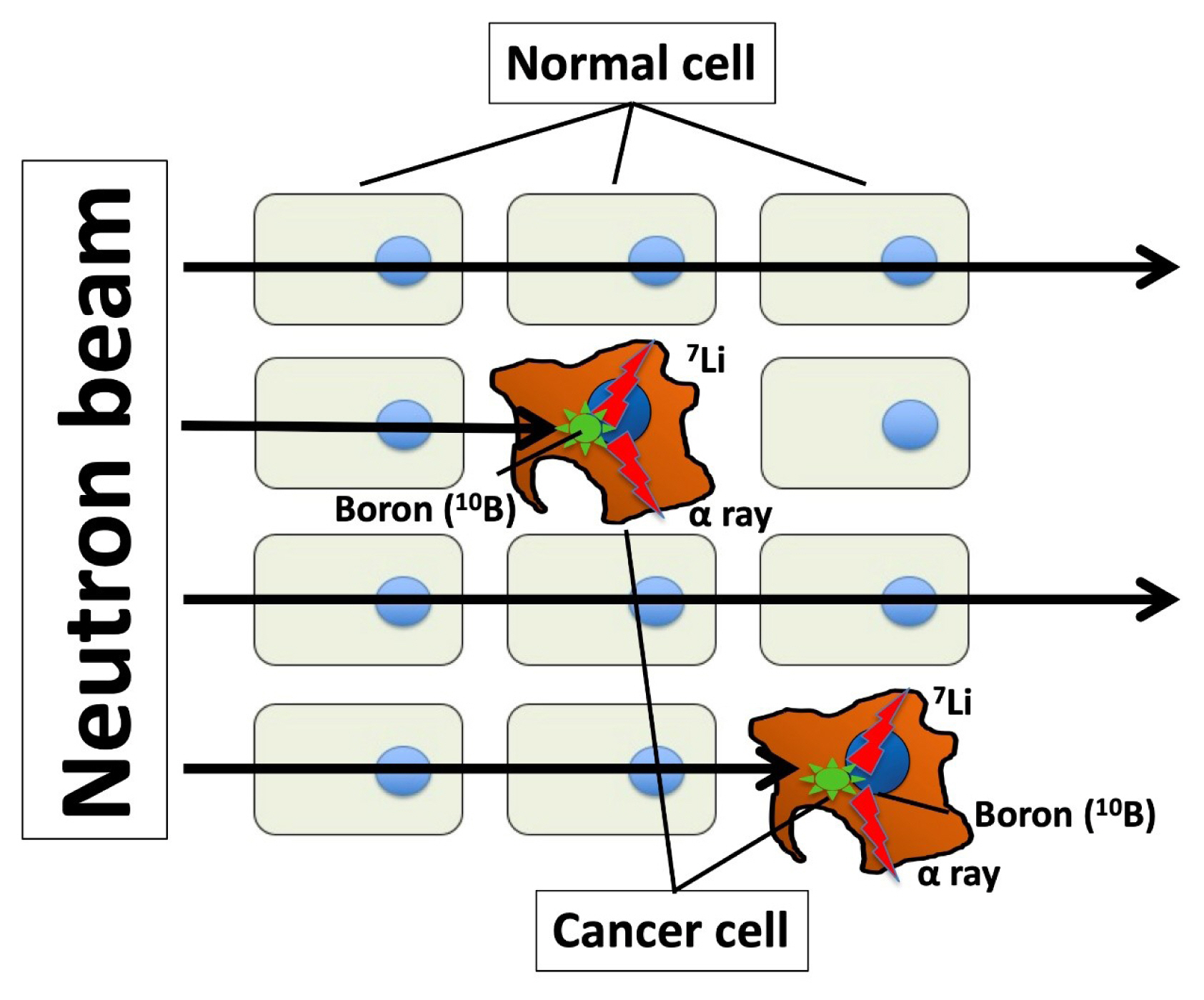
- Keisuke Enomoto, Muneki Hotomi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):227-236. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.227
- 6,718 View
- 171 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Thyroid cancer cells have a high amino acid demand for proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Amino acids are taken up by thyroid cancer cells, both thyroid follicular cell and thyroid parafollicular cells (commonly called “C-cells”), via amino acid transporters. Amino acid transporters up-regulate in many cancers, and their expression level associate with clinical aggressiveness and prognosis. This is the review to discuss the therapeutic potential of amino acid transporters and as molecular targets in thyroid cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Applications of spatially resolved omics in the field of endocrine tumors
Yinuo Hou, Yan Gao, Shudi Guo, Zhibin Zhang, Ruibing Chen, Xiangyang Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Taurine and Creatine Transporters as Potential Drug Targets in Cancer Therapy
Dorota Stary, Marek Bajda
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3788. CrossRef - GLUT1 and ASCT2 Protein Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients and Relation to Hepatitis C Virus: A Propensity-Score Matched Analysis
Afaf T Ibrahiem, Manal S Fawzy, Jawaher A Abdulhakim, Eman A Toraih
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 2929. CrossRef - Excellent physicochemical and sensing characteristics of a RexOy based pH sensor at low post-deposition annealing temperature
Munmun Das, Titisha Chakraborty, Kin Fong Lei, Chan Yu Lin, Chyuan Haur Kao
RSC Advances.2022; 12(22): 13774. CrossRef - SLC6A14 Depletion Contributes to Amino Acid Starvation to Suppress EMT-Induced Metastasis in Gastric Cancer by Perturbing the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 Pathway
Qie Guo, Wen Xu, Xiao Li, Jia-Lin Sun, Xiao-Ce Gu, Fan-Bo Jing, Sercan Ergün
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Genetic Engineering in Combination with Semi‐Synthesis Leads to a New Route for Gram‐Scale Production of the Immunosuppressive Natural Product Brasilicardin A
Alma Botas, Michael Eitel, Paul N. Schwarz, Anina Buchmann, Paula Costales, Luz Elena Núñez, Jesús Cortés, Francisco Morís, Michał Krawiec, Marcin Wolański, Bertolt Gust, Mirna Rodriguez, Wolf‐Nicolas Fischer, Bernd Jandeleit, Jolanta Zakrzewska‐Czerwińsk
Angewandte Chemie.2021; 133(24): 13648. CrossRef - Genetic Engineering in Combination with Semi‐Synthesis Leads to a New Route for Gram‐Scale Production of the Immunosuppressive Natural Product Brasilicardin A
Alma Botas, Michael Eitel, Paul N. Schwarz, Anina Buchmann, Paula Costales, Luz Elena Núñez, Jesús Cortés, Francisco Morís, Michał Krawiec, Marcin Wolański, Bertolt Gust, Mirna Rodriguez, Wolf‐Nicolas Fischer, Bernd Jandeleit, Jolanta Zakrzewska‐Czerwińsk
Angewandte Chemie International Edition.2021; 60(24): 13536. CrossRef - Next-Generation Molecular Imaging of Thyroid Cancer
Yuchen Jin, Beibei Liu, Muhsin H. Younis, Gang Huang, Jianjun Liu, Weibo Cai, Weijun Wei
Cancers.2021; 13(13): 3188. CrossRef - Evaluation of 3-l- and 3-d-[18F]Fluorophenylalanines as PET Tracers for Tumor Imaging
Felicia Krämer, Benedikt Gröner, Chris Hoffmann, Austin Craig, Melanie Brugger, Alexander Drzezga, Marco Timmer, Felix Neumaier, Boris D. Zlatopolskiy, Heike Endepols, Bernd Neumaier
Cancers.2021; 13(23): 6030. CrossRef
- Applications of spatially resolved omics in the field of endocrine tumors

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Epidemiology of Functioning Pituitary Adenomas
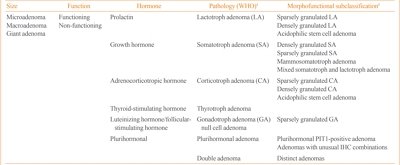
- Sang Ouk Chin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):237-242. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.237
- 7,852 View
- 254 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Pituitary adenomas (PAs) are defined as benign monoclonal tumors in the pituitary gland that cause symptoms due to either hormonal hypersecretion or a space-occupying effect, and are classified as functioning or non-functioning. Because of their rarity and slow-growing with symptomless nature in most cases, it has been challenging to investigate the epidemiology of PAs. Considering their public health impact and association with increased morbidity and mortality, however, it is essential to understand the prevalence and incidence of PAs in order to improve patient outcomes and to minimize the resultant burden on the health care system. Fortunately, developments in imaging modalities and easier access to large-scale population data have enabled investigators to analyze the epidemiology of PAs more accurately. This review summarizes previously reported epidemiologic data on functioning PAs in Korea and other countries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spherical type of amyloidogenic pituitary prolactinoma in a 50 year old male
Madhala Divya, Balasubramanian Archana, Lawrence D Cruze, D. Balasubramanian
Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery.2024; 36: 101957. CrossRef - Transcriptome of GH-producing pituitary neuroendocrine tumours and models are significantly affected by somatostatin analogues
Rihards Saksis, Olesja Rogoza, Helvijs Niedra, Kaspars Megnis, Ilona Mandrika, Inga Balcere, Liva Steina, Janis Stukens, Austra Breiksa, Jurijs Nazarovs, Jelizaveta Sokolovska, Ilze Konrade, Raitis Peculis, Vita Rovite
Cancer Cell International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Models in Growth-Hormone- and Prolactin-Secreting Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Systematic Review
Roxana-Ioana Dumitriu-Stan, Iulia-Florentina Burcea, Teodor Salmen, Catalina Poiana
Diagnostics.2023; 13(12): 2118. CrossRef - Salivary microbiome profiles for different clinical phenotypes of pituitary adenomas by single-molecular long-read sequencing
Xuefei Ji, Pingping Li, Qinglong Guo, Liao Guan, Peng Gao, Bingshan Wu, Hongwei Cheng, Jin Xiao, Lei Ye, Justin R. Kaspar
Microbiology Spectrum.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoscopic endonasal surgical management of giant pituitary adenomas with extension into ventricle system
Mykola O. Guk, Oleksii V. Ukrainets
Ukrainian Neurosurgical Journal.2023; 29(4): 13. CrossRef - Uso de resonancia magnética nuclear intraoperatoria en la resección transesfenoidal de adenomas hipofisiarios: ¿qué resultados se han obtenido?
María Laura Boschetti Saer, Levino Roberto Boschetti, Jose Pastor Linarez Veloz, Michael Ortega-Sierra
Archivos de Neurociencias.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of common and uncommon adult pituitary tumors in the U.S. according to the 2017 World Health Organization classification
Luz E. Castellanos, Catherine Gutierrez, Timothy Smith, Edward R. Laws, J. Bryan Iorgulescu
Pituitary.2022; 25(1): 201. CrossRef - The kinome, cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases of pituitary adenomas, a look into the gene expression profile among tumors from different lineages
Keiko Taniguchi-Ponciano, Lesly A. Portocarrero-Ortiz, Gerardo Guinto, Sergio Moreno-Jimenez, Erick Gomez-Apo, Laura Chavez-Macias, Eduardo Peña-Martínez, Gloria Silva-Román, Sandra Vela-Patiño, Jesús Ordoñez-García, Sergio Andonegui-Elguera, Aldo Ferreir
BMC Medical Genomics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - IL-10 Gene Rs1800871, Rs1800872, and Rs1800896 Polymorphisms and IL-10 Serum Levels Association with Pituitary Adenoma
Migle Palivonaite, Greta Gedvilaite, Brigita Glebauskiene, Loresa Kriauciuniene, Vita Rovite, Rasa Liutkeviciene
Biomedicines.2022; 10(8): 1921. CrossRef - Genome wide analysis of circulating miRNAs in growth hormone secreting pituitary neuroendocrine tumor patients’ plasma
Helvijs Niedra, Raitis Peculis, Helena Daiga Litvina, Kaspars Megnis, Ilona Mandrika, Inga Balcere, Mihails Romanovs, Liva Steina, Janis Stukens, Austra Breiksa, Jurijs Nazarovs, Jelizaveta Sokolovska, Rasa Liutkeviciene, Alvita Vilkevicute, Ilze Konrade,
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of mutant K-RAS in pituitary macroadenoma
Veronica Aran, Manoela Heringer, Paulo Jose da Mata, Leandro Kasuki, Renan Lyra Miranda, Felipe Andreiuolo, Leila Chimelli, Paulo Niemeyer Filho, Monica Roberto Gadelha, Vivaldo Moura Neto
Pituitary.2021; 24(5): 746. CrossRef - Surgery is a safe, effective first-line treatment modality for noninvasive prolactinomas
Ji Yong Park, Wonsuk Choi, A Ram Hong, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim, Woo-Youl Jang, Shin Jung, Ho-Cheol Kang
Pituitary.2021; 24(6): 955. CrossRef
- Spherical type of amyloidogenic pituitary prolactinoma in a 50 year old male

- Obesity and Metabolism
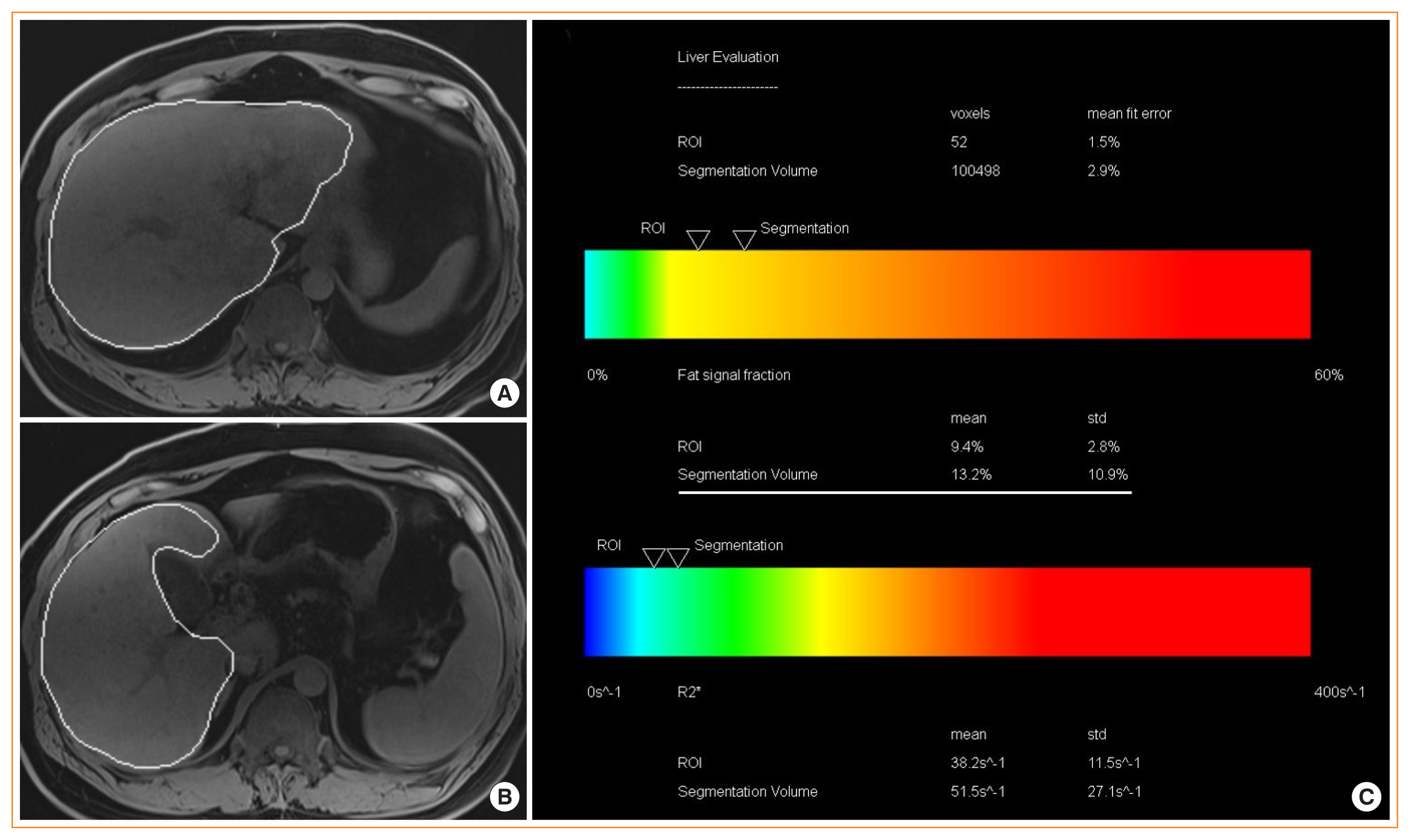
- Noninvasive Evaluation of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Dae Ho Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):243-259. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.243
- 10,997 View
- 296 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent liver diseases and can progress to advanced fibrosis and end-stage liver disease. Thus, intensive research has been performed to develop noninvasive methods for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis. Currently, no single noninvasive tool covers all of the stages of pathologies and conditions of NAFLD, and the cost and feasibility of known techniques are also important issues. Blood biomarkers for NAFLD may be useful to select subjects who need ultrasonography (US) screening for NAFLD, and noninvasive tools for assessing fibrosis may be helpful to exclude the probability of significant fibrosis and to predict advanced fibrosis, thus guiding the decision of whether to perform liver biopsy in patients with NAFLD. Among various methods, magnetic resonance-based methods have been shown to perform better than other methods in assessing steatosis as well as in detecting hepatic fibrosis. Many genetic markers are associated with the development and progression of NAFLD. Further well-designed studies are needed to determine which biomarker panels, imaging studies, genetic marker panels, or combinations thereof perform well for diagnosing NAFLD, differentiating NASH and fibrosis, and following-up NAFLD, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Progresses on Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Therapeutic Modalities,
and Management of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Mahdi Barazesh, Sajad Jalili, Morteza Akhzari, Fouzieyeh Faraji, Ebrahim Khorramdin
Current Drug Therapy.2024; 19(1): 20. CrossRef - Intact ketogenesis predicted reduced risk of moderate-severe metabolic-associated fatty liver disease assessed by liver transient elastography in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Sejeong Lee, Jaehyun Bae, Seung Up Kim, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: A 7-year retrospective cohort study of 3,496 adults using serial echocardiography
Gyuri Kim, Tae Yang Yu, Jae Hwan Jee, Ji Cheol Bae, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; : 101534. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 220. CrossRef - Non-invasive diagnosis and monitoring of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Monica A Tincopa, Rohit Loomba
The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2023; 8(7): 660. CrossRef - Hepatic Involvement across the Metabolic Syndrome Spectrum: Non-Invasive Assessment and Risk Prediction Using Machine Learning
Adelaida Solomon, Călin Remus Cipăian, Mihai Octavian Negrea, Adrian Boicean, Romeo Mihaila, Corina Beca, Mirela Livia Popa, Sebastian Mihai Grama, Minodora Teodoru, Bogdan Neamtu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(17): 5657. CrossRef - Greater Severity of Steatosis Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Incident Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study
Ji Min Han, Jung Hwan Cho, Hye In Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Yu-Ji Lee, Jung Won Lee, Kwang Min Kim, Ji Cheol Bae
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 418. CrossRef - Advances in Noninvasive Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Georgiana-Emmanuela Gîlcă-Blanariu, Daniela Simona Budur, Dana Elena Mitrică, Elena Gologan, Oana Timofte, Gheorghe Gh Bălan, Vasile Andrei Olteanu, Gabriela Ștefănescu
Metabolites.2023; 13(11): 1115. CrossRef - Plasma Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member B10 as a Biomarker Performs Well in the Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis
Aron Park, Seung Joon Choi, Sungjin Park, Seong Min Kim, Hye Eun Lee, Minjae Joo, Kyoung Kon Kim, Doojin Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Jae Been Im, Jaehun Jung, Seung Kak Shin, Byung-Chul Oh, Cheolsoo Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Dae Ho Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(9): 5035. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - The Impact of Insulin Resistance on Hepatic Fibrosis among United States Adults with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: NHANES 2017 to 2018
Ji Cheol Bae, Lauren A. Beste, Kristina M. Utzschneider
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 455. CrossRef - Plasma Metabolomics and Machine Learning-Driven Novel Diagnostic Signature for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Moongi Ji, Yunju Jo, Seung Joon Choi, Seong Min Kim, Kyoung Kon Kim, Byung-Chul Oh, Dongryeol Ryu, Man-Jeong Paik, Dae Ho Lee
Biomedicines.2022; 10(7): 1669. CrossRef - Evaluation of Liver Changes in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients using Computed Tomography
Nayyar Ashfaq, Akash John, Abid Ali, Amina Sharif Bhatti, Hateem Qaiser
DIET FACTOR (Journal of Nutritional & Food Sciences).2022; : 14. CrossRef - Accuracy of FIB-4 to Detect Elevated Liver Stiffness Measurements in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Referral Centers
Mauro Viganò, Nicola Pugliese, Federica Cerini, Federica Turati, Vincenzo Cimino, Sofia Ridolfo, Simone Rocchetto, Francesca Foglio, Maria Terrin, Carlo La Vecchia, Maria Grazia Rumi, Alessio Aghemo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(20): 12489. CrossRef - MAFLD vs. NAFLD: shared features and potential changes in epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and pharmacotherapy
Ying-Xin Xian, Jian-Ping Weng, Fen Xu
Chinese Medical Journal.2021; 134(1): 8. CrossRef - Prognostic accuracy of FIB‐4, NAFLD fibrosis score and APRI for NAFLD‐related events: A systematic review
Jenny Lee, Yasaman Vali, Jerome Boursier, Rene Spijker, Quentin M. Anstee, Patrick M. Bossuyt, Mohammad H. Zafarmand
Liver International.2021; 41(2): 261. CrossRef - Serum syndecan‐4 is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Shu Jing Xia, Li Zhong Tang, Wen Hua Li, Zhao Shan Xu, Li Li Zhang, Feng Gan Cheng, Hong Xia Chen, Zi Hua Wang, Yu Cheng Luo, An Na Dai, Jian Gao Fan
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2021; 22(9): 536. CrossRef - Non-Laboratory-Based Simple Screening Model for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Developed Using Multi-Center Cohorts
Jiwon Kim, Minyoung Lee, Soo Yeon Kim, Ji-Hye Kim, Ji Sun Nam, Sung Wan Chun, Se Eun Park, Kwang Joon Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Joo Young Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 823. CrossRef - Pemafibrate Ameliorates Liver Dysfunction and Fatty Liver in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Hypertriglyceridemia: A Retrospective Study with the Outcome after a Mid-Term Follow-Up
Suguru Ikeda, Takaaki Sugihara, Takuya Kihara, Yukako Matsuki, Takakazu Nagahara, Tomoaki Takata, Sonoko Kitao, Tsuyoshi Okura, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Hajime Isomoto
Diagnostics.2021; 11(12): 2316. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference Is Superior to the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance in Identifying Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Healthy Subjects
Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 11(1): 41. CrossRef - The Leg Fat to Total Fat Ratio Is Associated with Lower Risks of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Less Severe Hepatic Fibrosis: Results from Nationwide Surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011)
Hyun Min Kim, Yong-ho Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1232. CrossRef
- Recent Progresses on Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Therapeutic Modalities,
and Management of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder

- Diabetes
- Recent Updates on Vascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):260-271. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.260
- 7,538 View
- 282 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - It is well known that patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are at an increased risk of morbidity and mortality from atherosclerotic cardiovascular (CV) complications. Previously, the concept that diabetes mellitus (DM) is a “coronary artery disease (CAD) risk equivalent” was widely accepted, implying that all DM patients should receive intensive management. However, considerable evidence exist for wide heterogeneity in the risk of CV events among T2DM patients and the concept of a “CAD risk equivalent” has changed. Recent guidelines recommend further CV risk stratification in T2DM patients, with treatment tailored to the risk level. Although imaging modalities for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been used to improve risk prediction, there is currently no evidence that imaging-oriented therapy improves clinical outcomes. Therefore, controversy remains whether we should screen for CVD in asymptomatic T2DM. The coexistence of T2DM and heart failure (HF) is common. Based on recent CV outcome trials, sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists are recommended who have established ASCVD, indicators of high risk, or HF because of their demonstrated benefits for CVD. These circumstances have led to an increasing emphasis on ASCVD and HF in T2DM patients. In this review, we examine the literature published within the last 5 years on the risk assessment of CVD in asymptomatic T2DM patients. In particular, we review recent guidelines regarding screening for CVD and research focusing on the role of coronary artery calcium, coronary computed tomography angiography, and carotid intima-media thickness in asymptomatic T2DM patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pathways of Coagulopathy and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Orsolya-Zsuzsa Akácsos-Szász, Sándor Pál, Kinga-Ilona Nyulas, Enikő Nemes-Nagy, Ana-Maria Fárr, Lóránd Dénes, Mónika Szilveszter, Erika-Gyöngyi Bán, Mariana Cornelia Tilinca, Zsuzsánna Simon-Szabó
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4319. CrossRef - Increased soluble endoglin levels in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients are associated with endothelial dysfunction
Xiaobing Dou, Xiujing Wang, Xiuhua Yu, Jiaqi Yao, Huiling Shen, Yao Xu, Bojing Zheng, Zhenying Zhang, Qingying Tan, Tianxiao Hu
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(7): 711. CrossRef - Effects of hypertension on subcortical nucleus morphological alternations in patients with type 2 diabetes
Feng Cui, Zhi-Qiang Ouyang, Yi-Zhen Zeng, Bing-Bing Ling, Li Shi, Yun Zhu, He-Yi Gu, Wan-Lin Jiang, Ting Zhou, Xue-Jin Sun, Dan Han, Yi Lu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 568. CrossRef - Exploring Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells to Better Understand the Pathophysiology of Disease: An Updated Review
Qiuwang Zhang, Anthony Cannavicci, Michael J. B. Kutryk, Giuseppe Mandraffino
Stem Cells International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Recent Insights into the Nutritional Antioxidant Therapy in Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Vascular Complications: A Comprehensive Review
Narasimha M. Beeraka, Irina K. Tomilova, Galina A. Batrak, Maria V. Zhaburina, Vladimir N. Nikolenko, Mikhail Y. Sinelnikov, Liudmila M. Mikhaleva
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 29(11): 1920. CrossRef - Topical Reappraisal of Molecular Pharmacological Approaches to Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus Angiopathy
Constantin Munteanu, Mariana Rotariu, Marius-Alexandru Turnea, Aurelian Anghelescu, Irina Albadi, Gabriela Dogaru, Sînziana Calina Silișteanu, Elena Valentina Ionescu, Florentina Carmen Firan, Anca Mirela Ionescu, Carmen Oprea, Gelu Onose
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2022; 44(8): 3378. CrossRef - Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
Fei Xu, Xiang Ning, Tong Zhao, Qinghua Lu, Huiqiang Chen
Open Medicine.2022; 17(1): 1405. CrossRef - Effects of dulaglutide on endothelial progenitor cells and arterial elasticity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dandan Xie, Yutong Li, Murong Xu, Xiaotong Zhao, Mingwei Chen
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum netrin and VCAM-1 as biomarker for Egyptian patients with type IΙ diabetes mellitus
Maher M. Fadel, Faten R. Abdel Ghaffar, Shimaa K. Zwain, Hany M. Ibrahim, Eman AE. badr
Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports.2021; 27: 101045. CrossRef - Decoding the chemical composition and pharmacological mechanisms of Jiedu Tongluo Tiaogan Formula using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with network pharmacology-based investigation
Qi Zhang, Chunli Piao, Wenqi Jin, De Jin, Han Wang, Cheng Tang, Xiaohua Zhao, Naiwen Zhang, Shengnan Gao, Fengmei Lian
Aging.2021; 13(21): 24290. CrossRef
- Pathways of Coagulopathy and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Type 2 Diabetic Patients

Special Article
- Miscellaneous
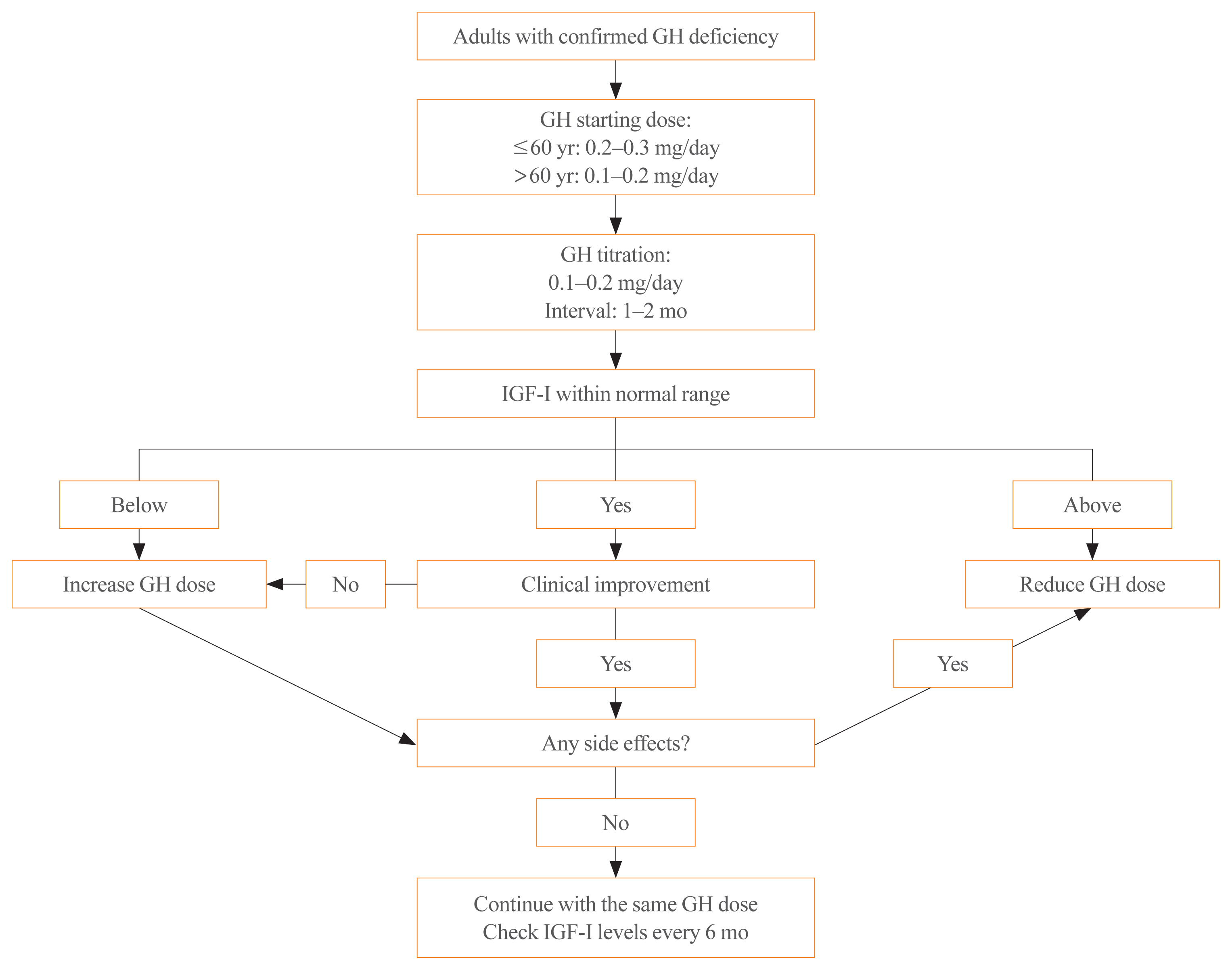
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Position Statement from Korean Endocrine Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology
- Jung Hee Kim, Hyun Wook Chae, Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyeong Hye Park, Dong Jun Lim, Kwang Joon Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Gyuri Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Seong Hee Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Yul Hwangbo, Ju Hee Lee, Bu Kyung Kim, Yong Jun Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Hwa Young Ahn, Hoon Sung Choi, Sang Mo Hong, Dong Yeob Shin, Ji A Seo, Se Hwa Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hoon Yu, Byung Joon Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sung-Woon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):272-287. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.272
- 9,383 View
- 426 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Growth hormone (GH) deficiency is caused by congenital or acquired causes and occurs in childhood or adulthood. GH replacement therapy brings benefits to body composition, exercise capacity, skeletal health, cardiovascular outcomes, and quality of life. Before initiating GH replacement, GH deficiency should be confirmed through proper stimulation tests, and in cases with proven genetic causes or structural lesions, repeated GH stimulation testing is not necessary. The dosing regimen of GH replacement therapy should be individualized, with the goal of minimizing side effects and maximizing clinical improvements. The Korean Endocrine Society and the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology have developed a position statement on the diagnosis and treatment of GH deficiency. This position statement is based on a systematic review of evidence and expert opinions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial
Ghina Tsurayya, Cut Alifiya Nazhifah, Muhammad Rahmat Pirwanja, Putri Oktaviani Zulfa, Muhammad Raihan Ramadhan Tatroman, Fajar Fakri, Muhammad Iqhrammullah
Children.2024; 11(2): 227. CrossRef - Evaluation of Adult Height in Patients with Non-Permanent Idiopathic GH Deficiency
Agnese Murianni, Anna Lussu, Chiara Guzzetti, Anastasia Ibba, Letizia Casula, Mariacarolina Salerno, Marco Cappa, Sandro Loche
Endocrines.2023; 4(1): 169. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests
Soo Yeun Sim, Moon Bae Ahn
Sensors.2023; 23(15): 6892. CrossRef - The risk patients with AGHD have of developing CVD
Eisha Javed, Maha Zehra, Naz Elahi
International Journal of Cardiology Cardiovascular Risk and Prevention.2023; 19: 200221. CrossRef - Diagnosis of GH Deficiency Without GH Stimulation Tests
Anastasia Ibba, Sandro Loche
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Impacts of Discontinuation and Resumption of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment during the Transition Period in Patients with Childhood-Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency
Yun Jeong Lee, Yunha Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Han Saem Choi, Ho-Seong Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Jung Eun Moon, Cheol Woo Ko, Moon Bae Ahn, Byung-Kyu Suh, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 359. CrossRef - A Radiomics-Based Model with the Potential to Differentiate Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature on Sella MRI
Taeyoun Lee, Kyungchul Song, Beomseok Sohn, Jihwan Eom, Sung Soo Ahn, Ho-Seong Kim, Seung-Koo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(9): 856. CrossRef - Phenotypic spectrum of patients with mutations in CHD7: clinical implications of endocrinological findings
Ja Hye Kim, Yunha Choi, Soojin Hwang, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Endocrine Disorders: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Hyemi Kwon, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Kyung Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 839. CrossRef - Laron syndrome: clinic, diagnostics (а clinical case)
P.M. Lіashuk, R.P. Lіashuk, N.I. Stankova, M.B. Kudina
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(3): 193. CrossRef - Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 322. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Guidelines for Adrenal Tumor Ablation
Byung Kwan Park, Masashi Fujimori, Shu-Huei Shen, Uei Pua
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 553. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation guidelines for renal cell carcinoma
Byung Kwan Park, Shu-Huei Shen, Masashi Fujimori, Yi Wang
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2021; 62(4): 378. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency
Jung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2021; 96(5): 400. CrossRef
- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial

Editorial
- Thyroid
- Association of Serum Progranulin Levels with Progression of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- Won Gu Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):288-289. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.288
- 4,116 View
- 81 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Clinical Study
- Fasting and Postprandial Hyperglycemia: Their Predictors and Contributions to Overall Hyperglycemia in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Jaecheol Moon, Ji Young Kim, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):290-297. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.290
- 6,851 View
- 200 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to identify factors that affect fasting hyperglycemia (FHG) and postprandial hyperglycemia (PPG) and their contributions to overall hyperglycemia in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This was a retrospective study conducted on 194 Korean T2DM patients with 7-point self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) profiles plotted in 4 days in 3 consecutive months. We calculated the areas corresponding to FHG and PPG (area under the curve [AUC]FHG and AUCPPG) and contributions (%) in the graph of the 7-point SMBG data. The levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were categorized by tertiles, and the contributions of FHG and PPG were compared.
Results
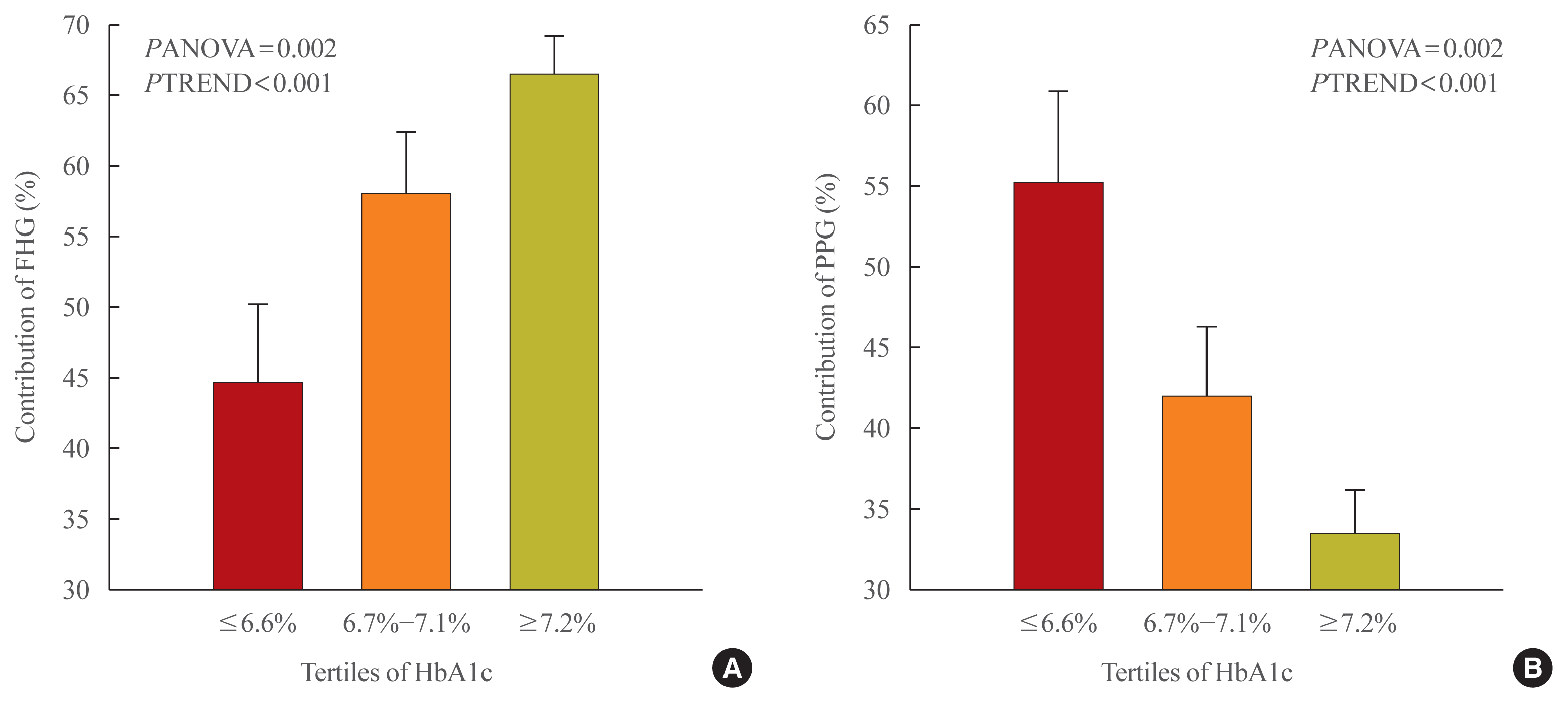
The relative contribution of FHG increased (44.7%±5.6%, 58.0%±4.4%, 66.5%±2.8%; PANOVA=0.002, PTREND <0.001), while that of PPG decreased (55.3%±5.5%, 42.0%±4.4%, 33.5%±2.8%; PANOVA=0.002, PTREND <0.001) with the elevated HbA1c. Multivariate analysis showed that HbA1c (β=0.615, P<0.001), waist circumference (β=0.216, P=0.042), and triglyceride (β=0.121, P=0.048) had a significant association with AUCFHG. Only HbA1c (β=0.231, P=0.002) and age (β=0.196, P=0.009) was significantly associated with AUCPPG.
Conclusion
The data suggested that in Korean T2DM patients, FHG predominantly contributed to overall hyperglycemia at higher HbA1c levels, whereas it contributed to PPG at lower HbA1c levels. It is recommended that certain factors, namely age, degree of glycemic control, obesity, or triglyceride levels, should be considered when prescribing medications for T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prospective study of the association between chronotype and cardiometabolic risk among Chinese young adults
Tingting Li, Yang Xie, Shuman Tao, Liwei Zou, Yajuan Yang, Fangbiao Tao, Xiaoyan Wu
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of mulberry twig alkaloids(Sangzhi alkaloids) and metformin on blood glucose fluctuations in combination with premixed insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes
Ziyu Meng, Chengye Xu, Haoling Liu, Xinyuan Gao, Xinyu Li, Wenjian Lin, Xuefei Ma, Changwei Yang, Ming Hao, Kangqi Zhao, Yuxin Hu, Yi Wang, Hongyu Kuang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - A new approach for investigating the relative contribution of basal glucose and postprandial glucose to HbA1C
Jing Ma, Hua He, Xiaojie Yang, Dawei Chen, Cuixia Tan, Li Zhong, Qiling Du, Xiaohua Wu, Yunyi Gao, Guanjian Liu, Chun Wang, Xingwu Ran
Nutrition & Diabetes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef
- Prospective study of the association between chronotype and cardiometabolic risk among Chinese young adults

- Clinical Study
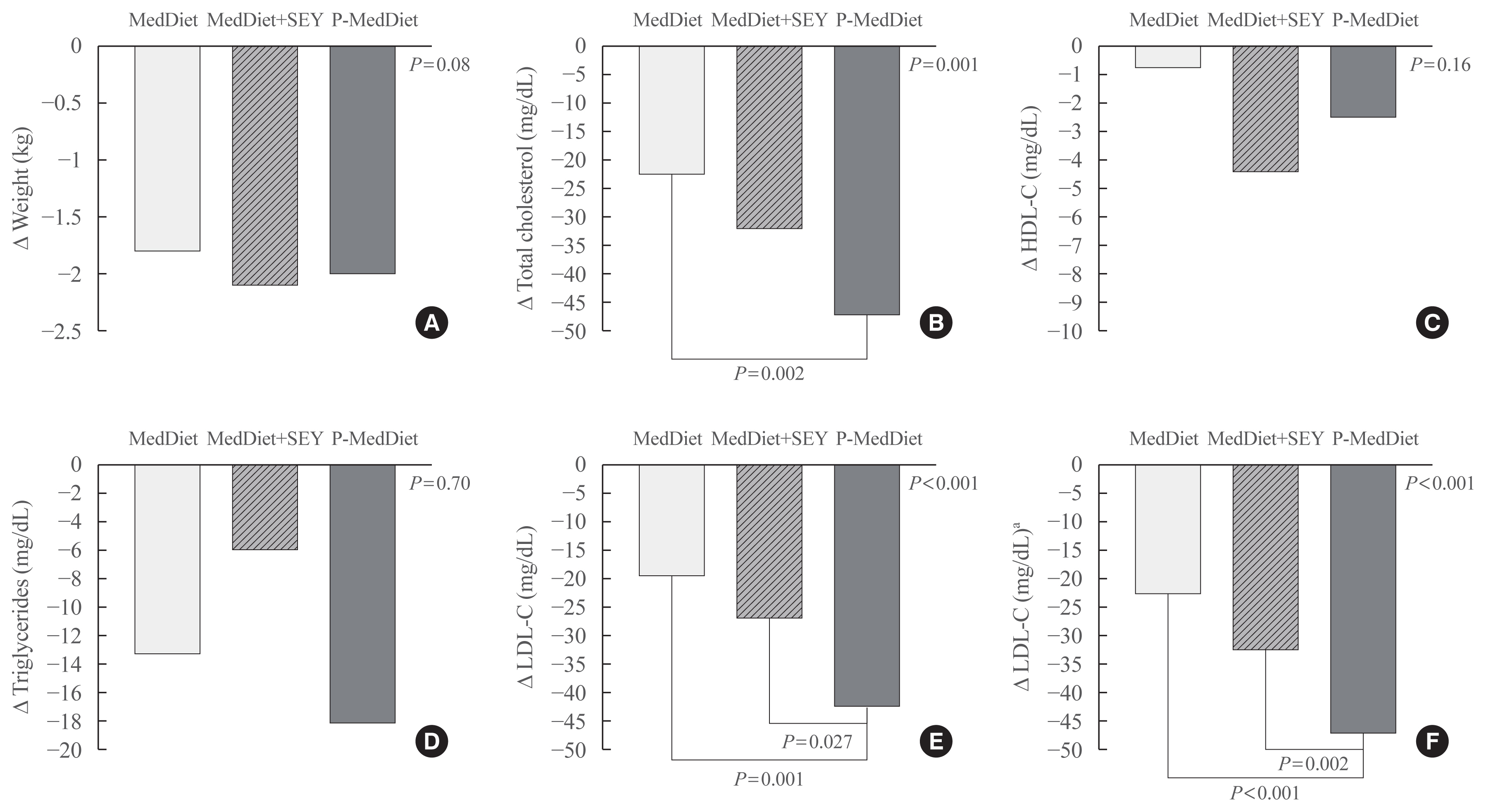
- Effects of a Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet and a Mediterranean Diet with or without a Sterol-Enriched Yogurt in Individuals with Hypercholesterolemia
- Yvelise Ferro, Elisa Mazza, Mariantonietta Salvati, Emma Santariga, Salvatore Giampà, Rocco Spagnuolo, Patrizia Doldo, Roberta Pujia, Adriana Coppola, Carmine Gazzaruso, Arturo Pujia, Tiziana Montalcini
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):298-307. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.298
- 6,733 View
- 140 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
A growing number of functional foods have been proposed to reduce cholesterol levels and the Portfolio Diet, which includes a combination of plant sterols, fibres, nuts, and soy protein, reduces low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) from 20% to 30% in individuals with hyperlipidaemia. In this pilot study, the aim was to investigate whether a Mediterranean Diet incorporating a new and simple combination of cholesterol-lowering foods, excluding soy and nuts (namely the Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet), would reduce LDL-C levels, in the short-term, better than a Mediterranean Diet plus a sterol-enriched yogurt or a Mediterranean Diet alone.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated 24 individuals on a Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet and 48 matched individuals on a Mediterranean Diet with or without a sterol-enriched yogurt (24 each groups) as controls.
Results
At follow-up (after 48±12 days), we observed an LDL reduction of 21±4, 23±4, and 44±4 mg/dL in the Mediterranean Diet alone, Mediterranean Diet plus yogurt and Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet respectively (P<0.001).
Conclusion
A Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet, incorporating a new combination of functional foods such as oats or barley, plant sterols, chitosan, and green tea but not soy and nuts, may reduce LDL of 25% in the short term in individuals with hypercholesterolemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intrinsic and environmental basis of aging: A narrative review
Carla Navarro, Juan Salazar, María P. Díaz, Maricarmen Chacin, Raquel Santeliz, Ivana Vera, Luis D′Marco, Heliana Parra, Mary Carlota Bernal, Ana Castro, Daniel Escalona, Henry García-Pacheco, Valmore Bermúdez
Heliyon.2023; 9(8): e18239. CrossRef - Application of small angle X‐ray scattering in exploring the effect of edible oils with different unsaturation FAs on bioaccessibility of stigmasterol oleate
Ying Wang, Tao Wang, Zhangtie Wang, Yiwen Guo, Ruijie Liu, Ming Chang
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.2023; 103(15): 7764. CrossRef - Phyto-Enrichment of Yogurt to Control Hypercholesterolemia: A Functional Approach
Harsh Kumar, Kanchan Bhardwaj, Natália Cruz-Martins, Ruchi Sharma, Shahida Anusha Siddiqui, Daljeet Singh Dhanjal, Reena Singh, Chirag Chopra, Adriana Dantas, Rachna Verma, Noura S. Dosoky, Dinesh Kumar
Molecules.2022; 27(11): 3479. CrossRef - Familial Hypercholesterolemia and Its Current Diagnostics and Treatment Possibilities: A Literature Analysis
Kristina Zubielienė, Gintarė Valterytė, Neda Jonaitienė, Diana Žaliaduonytė, Vytautas Zabiela
Medicina.2022; 58(11): 1665. CrossRef - Mediterranean Diet a Potential Strategy against SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Narrative Review
Yvelise Ferro, Roberta Pujia, Samantha Maurotti, Giada Boragina, Angela Mirarchi, Patrizia Gnagnarella, Elisa Mazza
Medicina.2021; 57(12): 1389. CrossRef
- Intrinsic and environmental basis of aging: A narrative review

- Clinical Study
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism Affects the Long-Term Outcomes of Patients Who Undergo Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery but Not Heart Valve Surgery
- Hana Kim, Sung Hye Kong, Jae Hoon Moon, Sang Yoon Kim, Kay-Hyun Park, Jun Sung Kim, Joong Haeng Choh, Young Joo Park, Cheong Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):308-318. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.308

- 6,467 View
- 151 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The aim of this study was to determine the associations between subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) and long-term cardiovascular outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or heart valve surgery (HVS).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed and compared all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and cardiovascular events in 461 patients who underwent CABG and 104 patients who underwent HVS.
Results
During a mean±standard deviation follow-up duration of 7.6±3.8 years, there were 187 all-cause deaths, 97 cardiovascular deaths, 127 major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), 11 myocardial infarctions, one unstable angina, 70 strokes, 30 hospitalizations due to heart failure, 101 atrial fibrillation, and 33 coronary revascularizations. The incidence of all-cause mortality after CABG was significantly higher in patients with SCH (n=36, 55.4%) than in euthyroid patients (n=120, 30.3%), with a hazard ratio of 1.70 (95% confidence interval, 1.10 to 2.63; P=0.018) after adjustment for age, sex, current smoking status, body mass index, underlying diseases, left ventricular dysfunction, and emergency operation. Interestingly, low total triiodothyronine (T3) levels in euthyroid patients who underwent CABG were significantly associated with increased risks of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and MACE, but those associations were not observed in HVS patients. Both free thyroxine and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels in euthyroid patients were not related with any cardiovascular outcomes in either the CABG or HVS group.
Conclusion
SCH or low total T3 might be associated with a poor prognosis after CABG, but not after HVS, implying that preoperative thyroid hormonal status may be important in ischemic heart disease patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Subclinical hypothyroidism and clinical outcomes after cardiac surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Michele Dell’Aquila, Camilla S. Rossi, Tulio Caldonazo, Gianmarco Cancelli, Lamia Harik, Giovanni J. Soletti, Kevin R. An, Jordan Leith, Hristo Kirov, Mudathir Ibrahim, Michelle Demetres, Arnaldo Dimagli, Mohamed Rahouma, Mario Gaudino
JTCVS Open.2024; 18: 64. CrossRef - The Association Between Hypothyroidism Treatment and Mortality in Patients Hospitalized in Surgical Wards
Hiba Masri-Iraqi, Yaron Rudman, Carmel Friedrich Dubinchik, Idit Dotan, Talia Diker-Cohen, Liat Sasson, Tzipora Shochat, Ilan Shimon, Eyal Robenshtok, Amit Akirov
Endocrine Research.2023; 48(2-3): 68. CrossRef - Mid-term outcomes of patients with subclinical hypothyroidism after coronary bypass surgery
Dong Zhao, Wei Zhao, Chuangshi Wang, Fei Xu, Wei Zhao, Xieraili Tiemuerniyazi, Hao Ma, Wei Feng
Interdisciplinary CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thyroid Pathology in High-Risk Cardiac Surgery Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Olena K. Gogayeva, Anatoliy V. Rudenko, Vasyl V. Lazoryshynets, Serhii A. Rudenko, Tetiana A. Andrushchenko
Ukrainian Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery.2022; 30(1 (46)): 9. CrossRef - High-TSH Subclinical Hypothyroidism Is Associated With Postoperative Mortality in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection
Shi-Pan Wang, Yuan Xue, Hai-Yang Li, Wen-Jian Jiang, Hong-Jia Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triiodothyronine improves contractile recovery of human atrial trabeculae after hypoxia/reoxygenation
Petra Kleinbongard, Philipp Kuthan, Chantal Eickelmann, Philipp Jakobs, Joachim Altschmied, Judith Haendeler, Arjang Ruhparwar, Matthias Thielmann, Gerd Heusch
International Journal of Cardiology.2022; 363: 159. CrossRef - Hypothyroidism Is Correlated with Ventilator Complications and Longer Hospital Days after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery in a Relatively Young Population: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study
Jiun-Yu Lin, Pei-Chi Kao, Yi-Ting Tsai, Chi-Hsiang Chung, Wu-Chien Chien, Chih-Yuan Lin, Chieh-Hua Lu, Chien-Sung Tsai
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(13): 3881. CrossRef - Minor perturbations of thyroid homeostasis and major cardiovascular endpoints—Physiological mechanisms and clinical evidence
Patrick Müller, Melvin Khee-Shing Leow, Johannes W. Dietrich
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism: Prevalence, Health Impact, and Treatment Landscape
Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 500. CrossRef
- Subclinical hypothyroidism and clinical outcomes after cardiac surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis

- Clinical Study
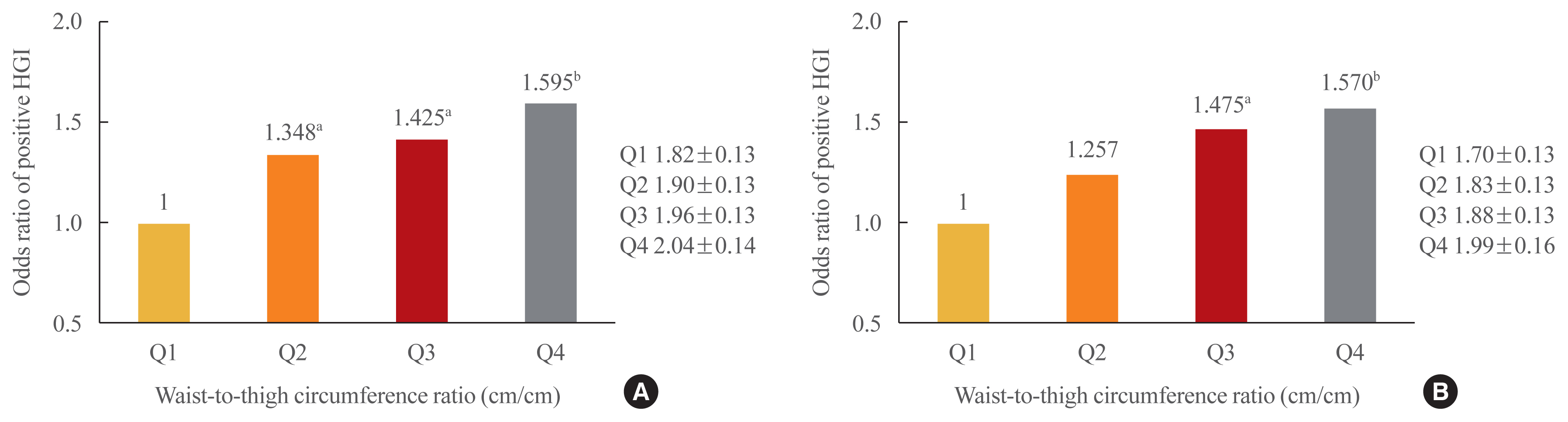
- Relationships between Thigh and Waist Circumference, Hemoglobin Glycation Index, and Carotid Plaque in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Myung Ki Yoon, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Kap Bum Huh, Chul Sik Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):319-328. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.319
- 8,294 View
- 145 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the relationships of thigh and waist circumference with the hemoglobin glycation index (HGI) and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
This observational study included 3,075 Korean patients with type 2 diabetes, in whom anthropometric measurements and carotid ultrasonography were conducted. HGI was defined as the measured hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level minus the predicted HbA1c level, which was calculated using the linear relationship between HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose levels. Carotid atherosclerosis was defined as a clearly isolated focal plaque or focal wall thickening >50% of the surrounding intima-media thickness.
Results
The frequency of a positive HGI decreased with increasing thigh circumference in men and increased with increasing waist circumference in women after adjusting for potential confounding variables. Thigh and waist circumference had a combined augmentative effect on the likelihood of positive HGI, which was dramatically higher in patients in higher waist-to-thigh ratio quartiles (adjusted odds ratios for the highest compared to the lowest quartile: 1.595 in men and 1.570 in women). Additionally, the larger the thigh circumference, the lower the risk of carotid atherosclerosis, although in women, this relationship lacked significance after adjustment for potential confounders.
Conclusion
HGI was associated with thigh circumference in men and waist circumference in women. In addition, the combination of low thigh circumference and high waist circumference was strongly associated with a higher HGI in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. In particular, thigh circumference was associated with carotid atherosclerosis in men. However, further longitudinal studies are warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between hemoglobin glycation index and subclinical myocardial injury in the general population free from cardiovascular disease
Zhenwei Wang, Yihai Liu, Jing Xie, Nai-Feng Liu
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(2): 469. CrossRef - Association of Hemoglobin Glycation Index With Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography: A Retrospective Study
Zhezhe Chen, Duanbin Li, Maoning Lin, Hangpan Jiang, Tian Xu, Yu Shan, Guosheng Fu, Min Wang, Wenbin Zhang
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of continuous glucose monitoring-assessed glucose variability with intima-media thickness and ultrasonic tissue characteristics of the carotid arteries: a cross-sectional analysis in patients with type 2 diabetes
Naohiro Taya, Naoto Katakami, Tomoya Mita, Yosuke Okada, Satomi Wakasugi, Hidenori Yoshii, Toshihiko Shiraiwa, Akihito Otsuka, Yutaka Umayahara, Kayoko Ryomoto, Masahiro Hatazaki, Tetsuyuki Yasuda, Tsunehiko Yamamoto, Masahiko Gosho, Iichiro Shimomura, Hi
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between hemoglobin glycation index and subclinical myocardial injury in the general population free from cardiovascular disease

- Clinical Study
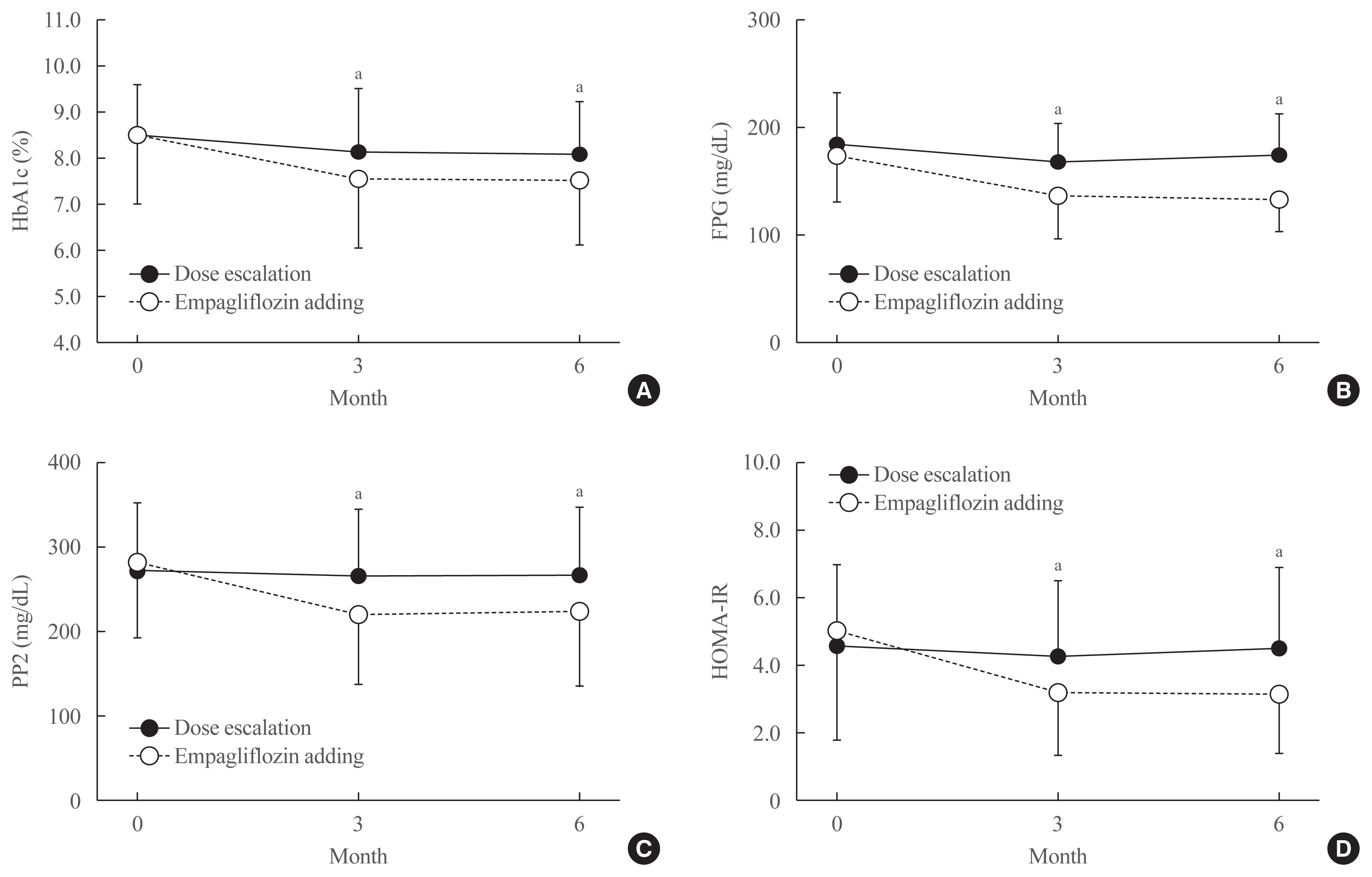
- Glycemic Efficacy and Metabolic Consequences of an Empagliflozin Add-on versus Conventional Dose-Increasing Strategy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled by Metformin and Sulfonylurea
- Yujin Shin, Ji Hye Moon, Ho Jun Chin, Ele Ferrannini, Soo Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):329-338. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.329
- 6,486 View
- 213 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We assessed the glucose-lowering efficacy of adding empagliflozin versus dose escalating existing medications in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods
This was a 6-month retrospective case-control study in subjects with uncontrolled T2D (glycated hemoglobin [HbA1c] >7%) on conventional treatment. The study group started add-on therapy with empagliflozin (10 mg once a day) while the control group was up-titrated with existing medication, using either monotherapy or a combination of metformin, sulfonylurea, and a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor. The primary endpoints included changes in HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and 2-hour postprandial glucose (PP2) levels. Secondary outcomes included changes in body composition, body mass index (BMI), and serum ketone bodies, and urinary excretion of sodium, potassium, chlorine, calcium, phosphorus, and glucose.
Results
After treatment, the reduction in HbA1c was significantly greater in the empagliflozin group than in controls (from 8.6%±1.6% to 7.6%±1.5% vs. 8.5%±1.1% to 8.1%±1.1%; P<0.01). Similar patterns were found in FPG and PP2 levels. Empagliflozin decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure, triglycerides, and alanine and aspartate aminotransferase levels. Body weight, BMI, waist circumference, fat mass, and abdominal visceral fat area decreased significantly while lean body mass was maintained. Total ketones, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate levels increased significantly after empagliflozin.
Conclusion
In addition to glucose lowering, an empagliflozin add-on regimen decreased blood pressure and body fat, and improved metabolic profiles significantly. Empagliflozin add-on is superior to dose escalation in patients with T2D who have inadequate glycemic control on standard medications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Independent association of thigh muscle fat density with vascular events in Korean adults
Hun Jee Choe, Won Chang, Matthias Blüher, Steven B. Heymsfield, Soo Lim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, Empagliflozin, is associated with significant reduction in weight, body mass index, fasting glucose, and A1c levels in Type 2 diabetic patients with established coronary heart disease: the SUPER GATE study
Satilmis Bilgin, Ozge Kurtkulagi, Tuba Taslamacioglu Duman, Burcin Meryem Atak Tel, Gizem Kahveci, Murat Kiran, Eray Erge, Gulali Aktas
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2022; 191(4): 1647. CrossRef - A randomized clinical trial evaluating the effect of empagliflozin on triglycerides in obese adults: Role of visceral fat
Min Hee Lee, Ian J. Neeland, Natalia de Albuquerque Rocha, Connor Hughes, Craig R. Malloy, Eunsook S. Jin
Metabolism Open.2022; 13: 100161. CrossRef - Initial combination of metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin in drug‐naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: Safety and metabolic effects
Soo Lim, Minji Sohn, Yujin Shin, Ele Ferrannini
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(4): 757. CrossRef - Correlation of dynamic membrane fluctuations in red blood cells with diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risks
Minji Sohn, Ji Eun Lee, MinGeun Ahn, YongKeun Park, Soo Lim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison betweeen dapagliflozin add-on therapy and insulin dose escalation in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes treated with insulin: DVI study
Yujin Shin, Haeri Choi, Soo Lim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 175: 108843. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 and Associated Preventive Measures on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in South Korea
Minji Sohn, Bo Kyung Koo, Ho Il Yoon, Kyoung-Ho Song, Eu Suk Kim, Hong Bin Kim, Soo Lim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2021; 30(3): 248. CrossRef
- Independent association of thigh muscle fat density with vascular events in Korean adults

- Clinical Study
- Long-Term Results of Thermal Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Se Jin Cho, Jung Hwan Baek, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):339-350. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.339
- 10,762 View
- 306 Download
- 37 Web of Science
- 44 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Ultrasound-guided thermal ablations have become one of the main options for treating benign thyroid nodules. To determine efficacy of thermal ablation of benign thyroid nodules, we performed a meta-analysis of studies with long-term follow-up of more than 3 years.
Methods
Databases were searched for studies published up to August 25, 2019, reporting patients with benign thyroid nodules treated with thermal ablation and with follow-up data of more than 3 years. Data extraction and quality assessment were performed according to PRISMA guidelines. The analysis yielded serial volume reduction rates (VRRs) of ablated nodules for up to 3 years or more, and adverse effect of ablation during follow-up. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and laser ablation (LA) were compared in a subgroup analysis.
Results
The pooled VRRs for ablated nodules showed rapid volume reduction before 12 months, a plateau from 12 to 36 months, and more volume reduction appearing after 36 months, demonstrating long-term maintenance of treatment efficacy. Thermal ablation had an acceptable complication rate of 3.8%. Moreover, patients undergoing nodule ablation showed no unexpected delayed complications during the follow-up period. In the subgroup analysis, RFA was shown to be superior to LA in terms of the pooled VRR and the number of patients who underwent delayed surgery.
Conclusion
Thermal ablations are safe and effective methods for treating benign thyroid nodules, as shown by a long follow-up analysis of more than 3 years. In addition, RFA showed superior VRRs compared with LA for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules, with less regrowth and less delayed surgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Five-year follow-up results of thermal ablation for benign thyroid nodules: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Xidong Xu, Ying Peng, Guoxin Han
American Journal of Otolaryngology.2024; 45(1): 104025. CrossRef - Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Nodules and for Cancer, Too?
Jonathon O. Russell, Kaitlyn M. Frazier
Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America.2024; 57(1): 83. CrossRef - An anthropomorphic thyroid phantom for ultrasound‐guided radiofrequency ablation of nodules
Tim Boers, Wyger Brink, Leonardo Bianchi, Paola Saccomandi, Johan van Hespen, Germen Wennemars, Sicco Braak, Michel Versluis, Srirang Manohar
Medical Physics.2024; 51(2): 826. CrossRef - The safety and efficacy of radiofrequency ablation in benign pediatric thyroid disease in the US: An initial case series
Grace S. Kim, Hilary Seeley, Julia Noel, Iram Ahmad, Kara Meister
Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Radioiodine versus radiofrequency ablation to treat autonomously functioning thyroid nodules: a systematic review and comparative meta-analysis
Luca Giovanella, Maria Luisa Garo, Alfredo Campenní, Petra Petranović Ovčariček
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel and Advanced Ultrasound Techniques for Thyroid Thermal Ablation
Wai-Kin Chan, Jui-Hung Sun, Miaw-Jene Liou, Chia-Jung Hsu, Yu-Ling Lu, Wei-Yu Chou, Yan-Rong Li, Feng-Hsuan Liu
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 40. CrossRef - Sublethal thermal stress promotes migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells
Chi-Yu Kuo, Chung-Hsin Tsai, Jun Kui Wu, Shih-Ping Cheng, Yi-Hsien Hsieh
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0298903. CrossRef - The Role of Radiofrequency Ablation in Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules
Meghal Shah, Catherine McManus
Surgical Clinics of North America.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasound imaging in thyroid nodule diagnosis, therapy, and follow‐up: Current status and future trends
Tim Boers, Sicco J. Braak, Nicole E. T. Rikken, Michel Versluis, Srirang Manohar
Journal of Clinical Ultrasound.2023; 51(6): 1087. CrossRef - Ultrasound (US)-Guided Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
Byung Seup Kim
Journal of Surgical Ultrasound.2023; 10(1): 14. CrossRef - Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation versus Thyroidectomy for the Treatment of Benign Thyroid Nodules in Elderly Patients: A Propensity-Matched Cohort Study
L. Yan, X.Y. Li, Y. Li, Y. Luo
American Journal of Neuroradiology.2023; 44(6): 693. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Ablative Treatments for Benign Thyroid Nodules: Current Evidence and Future Directions
Enrico Papini, Laszlo Hegedüs
Thyroid®.2023; 33(8): 890. CrossRef - Influence factors and nomogram for volume reduction rate in benign thyroid nodule after thermal ablation
Shiliang Cao, Lijia Wang, Ying Wei, Zhenlong Zhao, Jie Wu, Mingan Yu
International Journal of Hyperthermia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Choice in Ablative Therapies for Thyroid Nodules
Q Lina Hu, Jennifer H Kuo
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - 2022 Taiwan clinical multicenter expert consensus and recommendations for thyroid radiofrequency ablation
Wei-Che Lin, Wen-Chieh Chen, Pei-Wen Wang, Yi-Chia Chan, Yen-Hsiang Chang, Harn-Shen Chen, Szu-Tah Chen, Wei-Chih Chen, Kai-Lun Cheng, Shun-Yu Chi, Pi-Ling Chiang, Chen-Kai Chou, Feng-Fu Chou, Shun-Chen Huang, Feng-Hsuan Liu, Sheng-Dean Luo, Fen-Yu Tseng,
Ultrasonography.2023; 42(3): 357. CrossRef - Comparison of the Efficiency of Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation Methods in the Treatment of Benign Thyroid Nodules
Mahi N. Cerit, Cem Yücel, Ethem T. Cerit, Mehmet M. Yalçın, Halit N. Şendur, Suna Ö. Oktar
Academic Radiology.2023; 30(10): 2172. CrossRef - Radiofrequency ablation for autonomously functioning nodules as treatment for hyperthyroidism: subgroup analysis of toxic adenoma and multinodular goitre and predictors for treatment success
M. M. D. van der Meeren, F. B. M. Joosten, S. H. P. P. Roerink, L. N. Deden, W. J. G. Oyen
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2023; 50(12): 3675. CrossRef - Massive Hemorrhage and Mortality Following Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation
Seulki Song, Jin Pyeong Kim
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Approach for Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation
Jung Suk Sim
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2023; 84(5): 1017. CrossRef - General Principles for the Safe Performance, Training, and Adoption of Ablation Techniques for Benign Thyroid Nodules: An American Thyroid Association Statement
Catherine F. Sinclair, Jung Hwan Baek, Kathleen E. Hands, Steven P. Hodak, Timothy C. Huber, Iram Hussain, Brian Hung-Hin Lang, Julia E. Noel, Maria Papaleontiou, Kepal N. Patel, Gilles Russ, Jonathon Russell, Stefano Spiezia, Jennifer H. Kuo
Thyroid®.2023; 33(10): 1150. CrossRef - A comprehensive review of interventional ablation techniques for the management of thyroid nodules and metastatic lymph nodes
Jennifer H. Kuo, Catherine F. Sinclair, Brian Lang, Stefano Spiezia, Mingan Yu, Eun Ju Ha, Dong Gyu Na, Chiara Offi, Kepal N. Patel, Jung Hwan Baek
Surgery.2022; 171(4): 920. CrossRef - Radiofrequency ablation and related ultrasound‐guided ablation technologies for treatment of benign and malignant thyroid disease: An international multidisciplinary consensus statement of the American Head and Neck Society Endocrine Surgery Section with
Lisa A. Orloff, Julia E. Noel, Brendan C. Stack, Marika D. Russell, Peter Angelos, Jung Hwan Baek, Kevin T. Brumund, Feng‐Yu Chiang, Mary Beth Cunnane, Louise Davies, Andrea Frasoldati, Anne Y. Feng, Laszlo Hegedüs, Ayaka J. Iwata, Emad Kandil, Jennifer K
Head & Neck.2022; 44(3): 633. CrossRef - Assessment of thyroid-specific quality of life in patients with benign symptomatic thyroid nodules treated with radiofrequency or ethanol ablation: a prospective multicenter study
So Yeong Jeong, Eun Ju Ha, Jung Hwan Baek, Tae Yong Kim, Yu-Mi Lee, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jeonghun Lee
Ultrasonography.2022; 41(1): 204. CrossRef - Thyroid Nodule Radiofrequency Ablation: Complications and Clinical Follow Up
James Y. Lim, Jennifer H. Kuo
Techniques in Vascular and Interventional Radiology.2022; 25(2): 100824. CrossRef - Radiofrequency Ablation of Solid, Non-Functional Thyroid Nodules
Michael Douek
Techniques in Vascular and Interventional Radiology.2022; 25(2): 100821. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Thermal Ablation for Treating Lymph Node Metastasis From Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Zheng Ding, Juan Chen, Zhiguang Chen, Xiaoke Zeng, Pengchao Zheng, Xuemei Wang, Xinwu Cui, Liang Sang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraoperative Neuromonitoring: Evaluating the Role of Continuous IONM and IONM Techniques for Emerging Surgical and Percutaneous Procedures
Catherine McManus, Jennifer Hong Kuo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Ablation for the Management of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma in the Era of Active Surveillance and Hemithyroidectomy
Sae Rom Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
Current Oncology Reports.2022; 24(8): 1045. CrossRef - enhanced anarchic society optimization technique for the classification of ultrasound thyroid images using ILBP
D. Anitha, S. Sathya Priya
International journal of health sciences.2022; : 4713. CrossRef - Image-Guided Percutaneous Ablation for Primary and Metastatic Tumors
Arian Mansur, Tushar Garg, Apurva Shrigiriwar, Vahid Etezadi, Christos Georgiades, Peiman Habibollahi, Timothy C. Huber, Juan C. Camacho, Sherif G. Nour, Alan Alper Sag, John David Prologo, Nariman Nezami
Diagnostics.2022; 12(6): 1300. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided microwave ablation versus surgical resection for Bethesda category IV thyroid nodules: A retrospective comparative study
Jingjing Yang, Ya Zhang, Xingjia Li, Yueting Zhao, Xue Han, Guofang Chen, Xiaoqiu Chu, Ruiping Li, Jianhua Wang, Fei Huang, Chao Liu, Shuhang Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term follow-up of the radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: the value of additional treatment
Hyun Jin Kim, Jung Hwan Baek, Woojin Cho, Jung Suk Sim
Ultrasonography.2022; 41(4): 661. CrossRef - Das „heiße“ Schilddrüsenkarzinom mit einem kritischen Blick auf die Thermoablation
Joachim Jähne, Andreas Niesen, Joachim Bernhardts, Marija Hillemans
Der Chirurg.2021; 92(1): 34. CrossRef - Current Practice of Percutaneous Ablation Technologies for Thyroid Nodules 2020
Haris Muhammad, Jonathon O. Russell, Prasanna Santhanam, Aniqa Tehreem, Ralph P. Tufano
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports.2021; 9(1): 52. CrossRef - RFA and benign thyroid nodules: Review of the current literature
Haris Muhammad, Prasanna Santhanam, Jonathon O. Russell, Jennifer H. Kuo
Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology.2021; 6(1): 155. CrossRef - Thermal Treatment Options for Benign Thyroid Nodules—The Role of Radio-Frequency Ablation and Laser Therapy
Erivelto Volpi
Clinical Thyroidology.2021; 33(1): 17. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy of different ultrasound-guided ablation for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Linye He, Wanjun Zhao, Zijing Xia, Anping Su, Zhihui Li, Jingqiang Zhu, Ivan D. Florez
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(1): e0243864. CrossRef - Unresolved Clinical Issues in Thermal Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules: Regrowth at Long-Term Follow-Up
Jung Suk Sim, Jung Hwan Baek
Korean Journal of Radiology.2021; 22(8): 1436. CrossRef - Current Status and Challenges of US-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Thyroid Nodules in the Long Term: A Systematic Review
Stella Bernardi, Andrea Palermo, Rosario Francesco Grasso, Bruno Fabris, Fulvio Stacul, Roberto Cesareo
Cancers.2021; 13(11): 2746. CrossRef - Update of Radiofrequency Ablation for Treating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules. The Future Is Now
Ralph P. Tufano, Pia Pace-Asciak, Jonathon O. Russell, Carlos Suárez, Gregory W. Randolph, Fernando López, Ashok R. Shaha, Antti Mäkitie, Juan P. Rodrigo, Luiz Paulo Kowalski, Mark Zafereo, Peter Angelos, Alfio Ferlito
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Benign Thyroid Nodules
Huynh Q Khanh, Nguyen L Vuong, Tran Q Tien
World Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2021; 12(3): 117. CrossRef - Long-Term Outcomes of Thermal Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: The Issue of Regrowth
Jung Suk Sim, Jung Hwan Baek, Rosaria Meccariello
International Journal of Endocrinology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Matrix 3D ultrasound-assisted thyroid nodule volume estimation and radiofrequency ablation: a phantom study
T. Boers, S. J. Braak, M. Versluis, S. Manohar
European Radiology Experimental.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Learning curve analysis of radiofrequency ablation for benign thyroid nodules
Chi-Yu Kuo, Chien-Liang Liu, Chung-Hsin Tsai, Shih-Ping Cheng
International Journal of Hyperthermia.2021; 38(1): 1536. CrossRef
- Five-year follow-up results of thermal ablation for benign thyroid nodules: Systematic review and meta-analysis


 KES
KES



 First
First Prev
Prev



