Article category
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Article category
Original Articles
- Thyroid
- Phospholipase C-γ as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Graves’ Orbitopathy
- Tae Hoon Roh, Min Kyung Chae, Jae Sang Ko, Don O. Kikkawa, Sun Young Jang, Jin Sook Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):739-749. Published online November 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1780
- 1,503 View
- 93 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
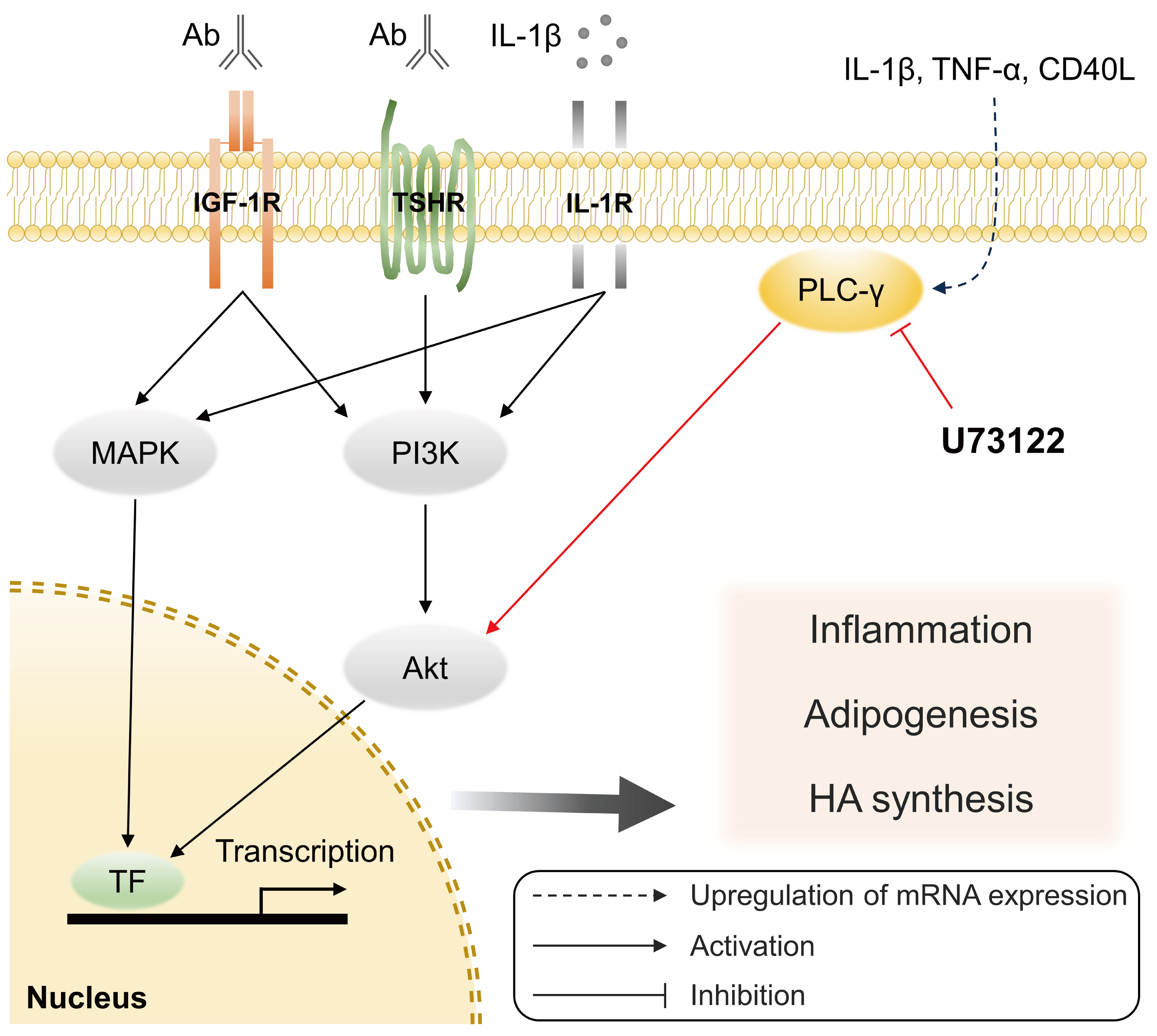
Phospholipase C-γ (PLC-γ) plays a crucial role in immune responses and is related to the pathogenesis of various inflammatory disorders. In this study, we investigated the role of PLC-γ and the therapeutic effect of the PLC-specific inhibitor U73122 using orbital fibroblasts from patients with Graves’ orbitopathy (GO).
Methods
The expression of phospholipase C gamma 1 (PLCG1) and phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLCG2) was evaluated using polymerase chain reaction in GO and normal orbital tissues/fibroblasts. The primary cultures of orbital fibroblasts were treated with non-toxic concentrations of U73122 with or without interleukin (IL)-1β to determine its therapeutic efficacy. The proinflammatory cytokine levels and activation of downstream signaling molecules were determined using Western blotting.
Results
PLCG1 and PLCG2 mRNA expression was significantly higher in GO orbital tissues than in controls (P<0.05). PLCG1 and PLCG2 mRNA expression was significantly increased (P<0.05) in IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and a cluster of differentiation 40 ligand-stimulated GO fibroblasts. U73122 significantly inhibited the IL-1β-induced expression of proinflammatory molecules, including IL-6, IL-8, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, cyclooxygenase-2, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and phosphorylated protein kinase B (p-Akt) and p38 (p-p38) kinase in GO fibroblasts, whereas it inhibited IL-6, IL-8, and ICAM-1, and p-Akt and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) in normal fibroblasts (P<0.05).
Conclusion
PLC-γ-inhibiting U73122 suppressed the production of proinflammatory cytokines and the phosphorylation of Akt and p38 kinase in GO fibroblasts. This study indicates the implications of PLC-γ in GO pathogenesis and its potential as a therapeutic target for GO.

- Thyroid
- Exploring the Association between Thyroid Function and Frailty: Insights from Representative Korean Data
- Youn-Ju Lee, Min-Hee Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung-Min Lee, Sang Ah Chang, Jeongmin Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):729-738. Published online November 2, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1769
- 1,053 View
- 71 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigates the association between thyroid function and frailty in the old patients using representative data.
Methods
The study was conducted using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2013 to 2015. The study population included 2,416 participants aged 50 years and older with available thyroid function test data. Frailty assessment was performed using the Fried frailty phenotype. The prevalence of frailty was analyzed across different thyroid diseases and thyroid function parameters.
Results
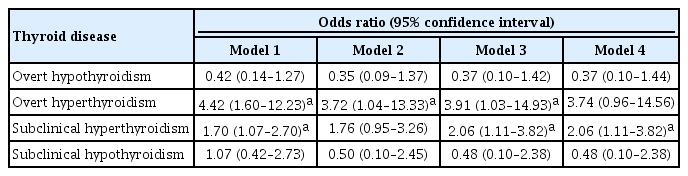
The significant association between thyroid dysfunction and frailty was observed in overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism. After adjusting for various factors, the association between thyroid dysfunction and frailty remained significant. On the other hand, overt hypothyroidism did not show a significant association with frailty in the adjusted analysis. For individuals with overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism, higher levels of free thyroxine (FT4) were significantly associated with an increased risk of frailty (aOR >999; 95% CI, >999 to 999). Among individuals with overt hypothyroidism, lower level of FT4 levels and high thyrotropin (TSH) levels showed a significant association with frailty risk (FT4: aOR, <0.01; TSH: aOR, 999). In participants with subclinical hypothyroidism, there were no significant associations between parameters for thyroid and frailty risk.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that thyroid dysfunction, particularly overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism, may be associated with an increased risk of frailty in the old patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of thyroid feedback quantile-based index with diabetes in euthyroid adults in the United States and China
Heng Wan, Genfeng Yu, Yajun He, Siyang Liu, Xingying Chen, Yuqi Jiang, Hualin Duan, Xu Lin, Lan Liu, Jie Shen
Annals of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Associations of thyroid feedback quantile-based index with diabetes in euthyroid adults in the United States and China

- Thyroid
- Comparative Analysis of Driver Mutations and Transcriptomes in Papillary Thyroid Cancer by Region of Residence in South Korea
- Jandee Lee, Seonhyang Jeong, Hwa Young Lee, Sunmi Park, Meesson Jeong, Young Suk Jo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):720-729. Published online November 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1758

- 946 View
- 42 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Radiation exposure is a well-known risk factor for papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). South Korea has 24 nuclear reactors in operation; however, no molecular biological analysis has been performed on patients with PTC living near nuclear power plants.
Methods
We retrospectively included patients with PTC (n=512) divided into three groups according to their place of residence at the time of operation: inland areas (n=300), coastal areas far from nuclear power plants (n=134), and nuclear power plant areas (n=78). After propensity score matching (1:1:1) by age, sex, and surgical procedure, the frequency of representative driver mutations and gene expression profiles were compared (n=50 per group). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), BRAF, thyroid differentiation, and radiation scores were calculated and compared.
Results
No significant difference was observed in clinicopathological characteristics, including radiation exposure history and the frequency of incidentally discovered thyroid cancer, among the three groups. BRAFV600E mutation was most frequently detected in the groups, with no difference among the three groups. Furthermore, gene expression profiles showed no statistically significant difference. EMT and BRAF scores were higher in our cohort than in cohorts from Chernobyl tissue bank and The Cancer Genome Atlas Thyroid Cancer; however, there was no difference according to the place of residence. Radiation scores were highest in the Chernobyl tissue bank but exhibited no difference according to the place of residence.
Conclusion
Differences in clinicopathological characteristics, frequency of representative driver mutations, and gene expression profiles were not observed according to patients’ region of residence in South Korea.

- Thyroid
- Long-Term Changes in the Mortality Rates of Thyroid Cancer in Korea: Analysis of Korean National Data from 1985 to 2020
- Yun Mi Choi, Min-Ju Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Mi Kyung Kwak, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Won Bae Kim, Won Gu Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):588-595. Published online September 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1723
- 1,412 View
- 85 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Thyroid cancer mortality has been largely overlooked as relatively stable given the large gap between thyroid cancer incidence and mortality. This study evaluated long-term trends in age-standardized mortality rates (ASMRs) throughout Korea and compared them with mortality data reported by the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER).
Methods
Cancer-specific mortality data from 1985 to 2020 were obtained from Statistics Korea. ASMRs from thyroid cancer were calculated based on the Korean mid-year resident registration population of 2005. We assessed SEER*Explorer and downloaded the mortality data.
Results
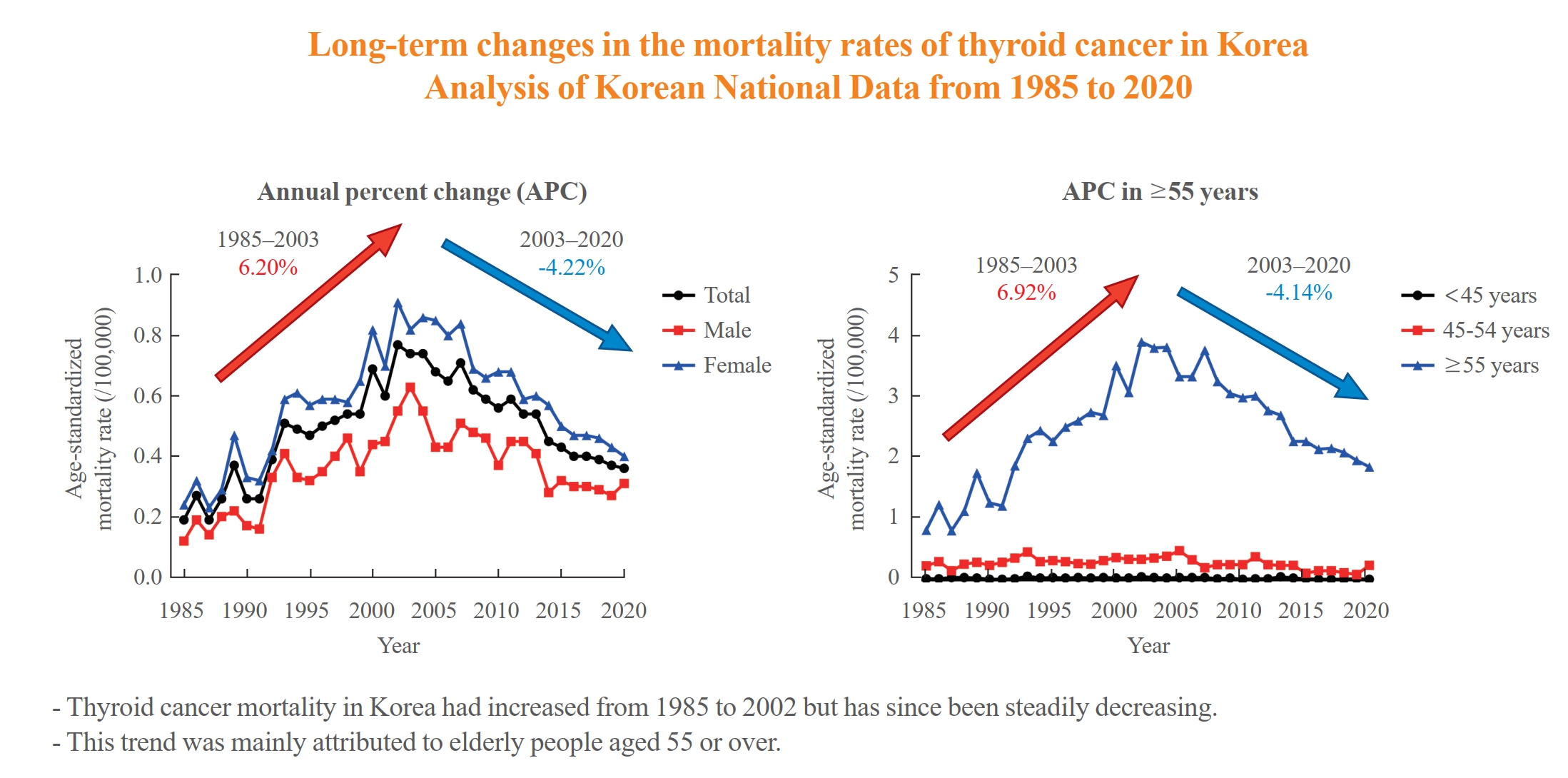
The ASMR increased from 0.19 to 0.77/100,000 between 1985 and 2002 but decreased continuously to 0.36/100,000 in 2020. The annual percent change (APC) in the ASMR between 1985 and 2003 and between 2003 and 2020 was 6.204 and −4.218, respectively, with similar patterns observed in both men and women. The ASMR of the SEER showed a modest increase from 1988 to 2016 and then stabilized. In subgroup analysis, the ASMR of the old age group (≥55 years) increased significantly from 0.82 in 1985 to 3.92/100,000 in 2002 (APC 6.917) but then decreased again to 1.86/100,000 in 2020 (APC −4.136). ASMRs according to the age group in the SEER showed a relatively stable trend even in the elderly group.
Conclusion
The ASMR of thyroid cancer in Korea had increased from 1985 to 2002 but has since been steadily decreasing. This trend was mainly attributed to elderly people aged 55 or over. The absolute APC value of Korea was much higher than that of the SEER. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- It Is Time to Understand the Additional Benefits of Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Kyeong Jin Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 95. CrossRef - A Clinical Audit of Thyroid Hormonal Replacement After Total Thyroidectomy
Islam Mansy, Abdelfatah M Elsenosy, Eslam M Hassan, Mujtaba Zakria
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- It Is Time to Understand the Additional Benefits of Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma

- Thyroid
- Beyond Acute COVID-19: Investigating the Incidence of Subacute Thyroiditis in Long COVID-19 in Korea
- Jeongmin Lee, Gi Hyeon Seo, Keeho Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):455-461. Published online August 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1711
- 2,572 View
- 179 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The correlation between acute coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and subacute thyroiditis (SAT) has not been clearly investigated in “long COVID” patients. We aimed to investigate the incidence of SAT during convalescence and after the acute phase of COVID-19, comparing with that of the general population.
Methods
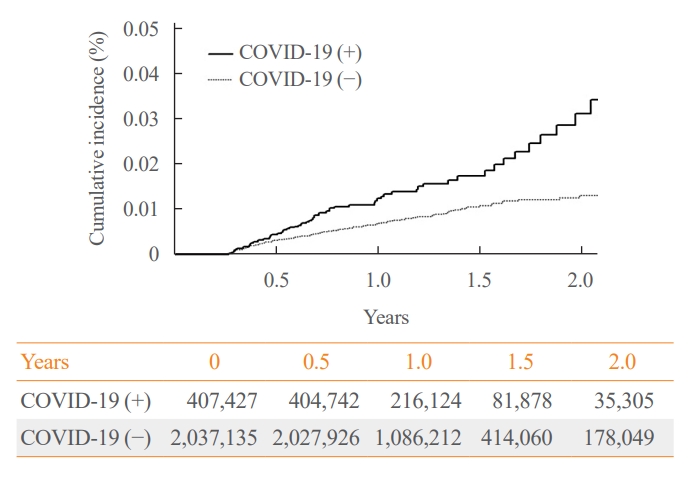
Data from a total of 422,779 COVID-19 patients and a control group of 2,113,895 individuals were analyzed. The index date was defined as the date 3 months after confirmation of COVID-19. The incidence rate (IR) of SAT and hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated per 100,000 persons. Subgroup analysis included analysis of HRs 90–179 and 180 days post-COVID-19 diagnosis; and additional analysis was conducted according to hospitalization status, sex, and age group.
Results
The IR of SAT was 17.28 per 100,000 persons (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.56 to 23.20) in the COVID-19 group and 8.63 (95% CI, 6.37 to 11.45) in the control group. The HR of COVID-19 patients was 1.76 (95% CI, 1.01 to 3.06; P=0.045). The HR of SAT was 1.39 (95% CI, 0.82 to 2.34; P=0.220) up to 6 months after the index date and 2.30 (95% CI, 1.60 to 3.30; P<0.001) beyond 6 months. The HR for SAT among COVID-19 patients was 2.00 (95% CI, 1.41 to 2.83) in hospitalized patients and 1.76 (95% CI, 1.01 to 3.06) in non-hospitalized patients compared to the control group. The IR of SAT was 27.09 (95% CI, 20.04 to 35.82) for females and 6.47 (95% CI, 3.34 to 11.30) for males. In the 19 to 64 age group, the IR of SAT was 18.19 (95% CI, 13.70 to 23.67), while the IR was 9.18 (95% CI, 7.72 to 10.84) in the 65 to 69 age group.
Conclusion
SAT could be a potential long-term complication of COVID-19. Long-term surveillance for thyroid dysfunction is needed especially in hospitalized, female and young-aged subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thyroid dysfunction in COVID-19
David Tak Wai Lui, Chi Ho Lee, Yu Cho Woo, Ivan Fan Ngai Hung, Karen Siu Ling Lam
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Subacute Thyroiditis in the Time of COVID-19
Hwa Young Ahn
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 186. CrossRef - Occult endocrine disorders newly diagnosed in patients with post-COVID-19 symptoms
Yasuhiro Nakano, Naruhiko Sunada, Kazuki Tokumasu, Hiroyuki Honda, Yuki Otsuka, Yasue Sakurada, Yui Matsuda, Toru Hasegawa, Daisuke Omura, Kanako Ochi, Miho Yasuda, Hideharu Hagiya, Keigo Ueda, Fumio Otsuka
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - rRisk of incident thyroid dysfunction in the post-acute phase of COVID-19: a population-based cohort study in Hong Kong
David Tak Wai Lui, Xi Xiong, Ching‐Lung Cheung, Francisco Tsz Tsun Lai, Xue Li, Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Celine Sze Ling Chui, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Franco Wing Tak Cheng, Lanlan Li, Matthew Shing Hin Chung, Chi Ho Lee, Yu Cho Woo, Kathryn Choon Beng Tan, Carlos
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Thyroid dysfunction in COVID-19

- Thyroid
- Different Molecular Phenotypes of Progression in BRAF- and RAS-Like Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Jinsun Lim, Han Sai Lee, Jiyun Park, Kyung-Soo Kim, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Young Shin Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):445-454. Published online July 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1702
- 1,587 View
- 99 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) can be classified into two distinct molecular subtypes, BRAF-like (BL) and RASlike (RL). However, the molecular characteristics of each subtype according to clinicopathological factors have not yet been determined. We aimed to investigate the gene signatures and tumor microenvironment according to clinicopathological factors, and to identify the mechanism of progression in BL-PTCs and RL-PTCs.
Methods
We analyzed RNA sequencing data and corresponding clinicopathological information of 503 patients with PTC from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. We performed differentially expressed gene (DEG), Gene Ontology, and molecular pathway enrichment analyses according to clinicopathological factors in each molecular subtype. EcoTyper and CIBERSORTx were used to deconvolve the tumor cell types and their surrounding microenvironment.
Results
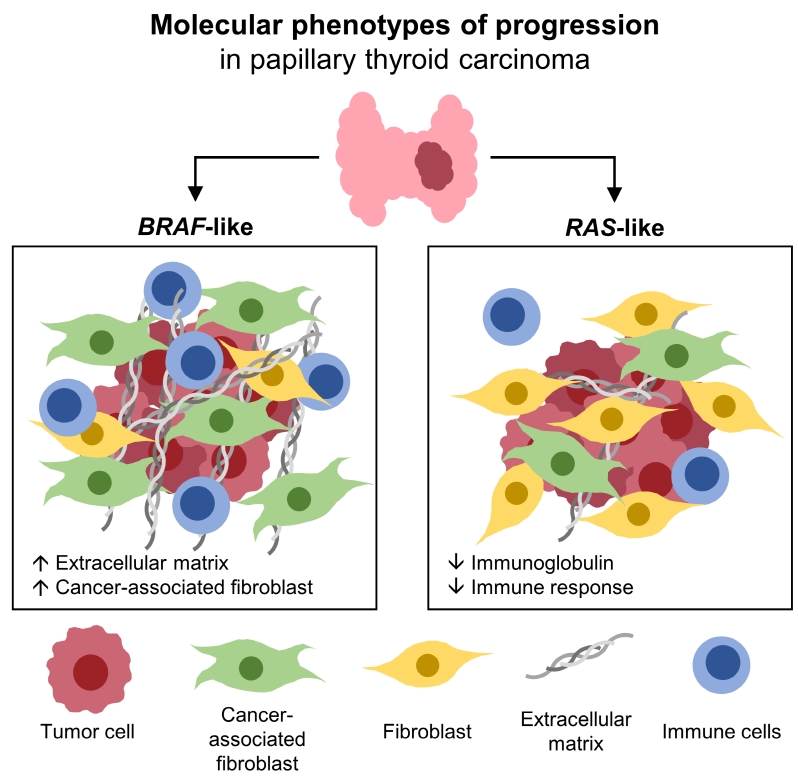
Even for the same clinicopathological factors, overlapping DEGs between the two molecular subtypes were uncommon, indicating that BL-PTCs and RL-PTCs have different progression mechanisms. Genes related to the extracellular matrix were commonly upregulated in BL-PTCs with aggressive clinicopathological factors, such as old age (≥55 years), presence of extrathyroidal extension, lymph node metastasis, advanced tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage, and high metastasis-age-completeness of resection- invasion-size (MACIS) scores (≥6). Furthermore, in the deconvolution analysis of tumor microenvironment, cancer-associated fibroblasts were significantly enriched. In contrast, in RL-PTCs, downregulation of immune response and immunoglobulin-related genes was significantly associated with aggressive characteristics, even after adjusting for thyroiditis status.
Conclusion
The molecular phenotypes of cancer progression differed between BL-PTC and RL-PTC. In particular, extracellular matrix and cancer-associated fibroblasts, which constitute the tumor microenvironment, would play an important role in the progression of BL-PTC that accounts for the majority of advanced PTCs.

- Thyroid
- Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
- Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):436-444. Published online July 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1684
- 1,767 View
- 124 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the changes of incidence and treatment of choice for hyperthyroidism from 2003 to 2018 and explore the treatment-related complications and concomitant comorbidities in South Korea using data from the National Health Insurance Service.
Methods
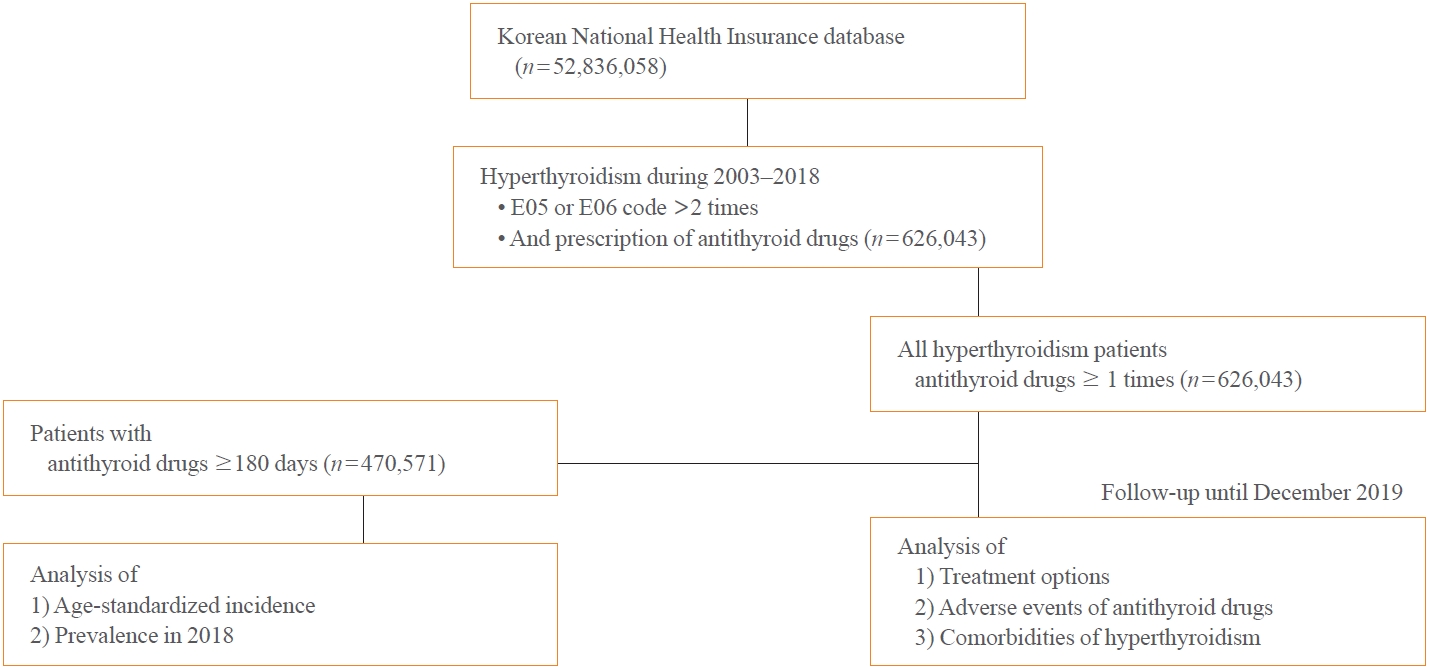
This is a retrospective observational study. Hyperthyroidism was defined as a case having two or more diagnostic codes of thyrotoxicosis, with antithyroid drug intake for more than 6 months.
Results
The average age-standardized incidence of hyperthyroidism from 2003 to 2018 was 42.23 and 105.13 per 100,000 men and women, respectively. In 2003 to 2004, hyperthyroidism was most often diagnosed in patients in their 50s, but in 2017 to 2018, people were most often diagnosed in their 60s. During the entire period, about 93.7% of hyperthyroidism patients were prescribed with antithyroid drugs, and meanwhile, the annual rates of ablation therapy decrease from 7.68% in 2008 to 4.56% in 2018. Antithyroid drug-related adverse events, mainly agranulocytosis and acute hepatitis, as well as complications of hyperthyroidism such as atrial fibrillation or flutter, osteoporosis, and fractures, occurred more often in younger patients.
Conclusion
In Korea, hyperthyroidism occurred about 2.5 times more in women than in men, and antithyroid drugs were most preferred as the first-line treatment. Compared to the general population, hyperthyroid patients may have a higher risk of atrial fibrillation or flutter, osteoporosis, and fractures at a younger age. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients
Jung-Chi Hsu, Kang-Chih Fan, Ting-Chuan Wang, Shu-Lin Chuang, Ying-Ting Chao, Ting-Tse Lin, Kuan-Chih Huang, Lian-Yu Lin, Lung-Chun Lin
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
Hyemi Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 392. CrossRef - Is Thyroid Dysfunction Associated with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms? A Population-Based, Nested Case–Control Study from Korea
Hyeree Park, Sun Wook Cho, Sung Ho Lee, Kangmin Kim, Hyun-Seung Kang, Jeong Eun Kim, Aesun Shin, Won-Sang Cho
Thyroid®.2023; 33(12): 1483. CrossRef
- Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients

Editorial
- Thyroid
- The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
- Hyemi Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):392-394. Published online August 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.401
- 1,193 View
- 86 Download

Review Article
- Thyroid
- Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Focus on Proven Health Effects in the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines
- Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):381-391. Published online August 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1778

- 2,975 View
- 457 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is characterized by elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and normal free thyroxine levels. The Korean Thyroid Association recently issued a guideline for managing SCH, which emphasizes Korean-specific TSH diagnostic criteria and highlights the health benefits of levothyroxine (LT4) treatment. A serum TSH level of 6.8 mIU/L is presented as the reference value for diagnosing SCH. SCH can be classified as mild (TSH 6.8 to 10.0 mIU/L) or severe (TSH >10.0 mIU/L), and patients can be categorized as adults (age <70 years) or elderly (age ≥70 years), depending on the health effects of LT4 treatment. An initial increase in serum TSH levels should be reassessed with a subsequent measurement, including a thyroid peroxidase antibody test, preferably 2 to 3 months after the initial assessment. While LT4 treatment is not generally recommended for mild SCH in adults, it is necessary for severe SCH in patients with underlying coronary artery disease or heart failure and it may be considered for those with concurrent dyslipidemia. Conversely, LT4 treatment is generally not recommended for elderly patients, regardless of SCH severity. For those SCH patients who are prescribed LT4 treatment, the dosage should be personalized, and serum TSH levels should be regularly monitored to maintain the optimal LT4 regimen.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Implications of Different Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Reference Intervals between TSH Kits for the Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Won Sang Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 188. CrossRef
- Clinical Implications of Different Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Reference Intervals between TSH Kits for the Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism

Corrigendum
- Thyroid
- Corrigendum: Abstract and Text Correction. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Reference Range and Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2015
- Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Gyeongji Woo, Hyejin Kim, Yumi Cho, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Myung-Hee Shin, Jin Woo Park, Hai-Lin Park, Kyungwon Oh, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):357. Published online May 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.301
- Corrects: Endocrinol Metab 2017;32(1):106
- 1,242 View
- 60 Download

Original Articles
- Thyroid
- Thyroid Hormone Reference Intervals among Healthy Individuals In Lanzhou, China
- Yan Lu, Wen-Xia Zhang, De-Hong Li, Lian-Hua Wei, Yu-Jun Zhang, Fu-Na Shi, Shen Zhou
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):347-356. Published online June 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1638
- 1,945 View
- 115 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The common reference intervals (RIs) for thyroid hormones currently used in China are provided by equipment manufacturers. This study aimed to establish thyroid hormone RIs in the population of Lanzhou, a city in the subplateau region of northwest China, and compare them with previous reports and manufacturer-provided values.
Methods
In total, 3,123 individuals (1,680 men, 1,443 women) from Lanzhou, an iodine-adequate area of China, perceived as healthy were selected. The Abbott Architect analyzer was used to determine the serum concentration of thyroid hormones. The 95% RI was estimated using the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles as the lower and upper reference limits, respectively.
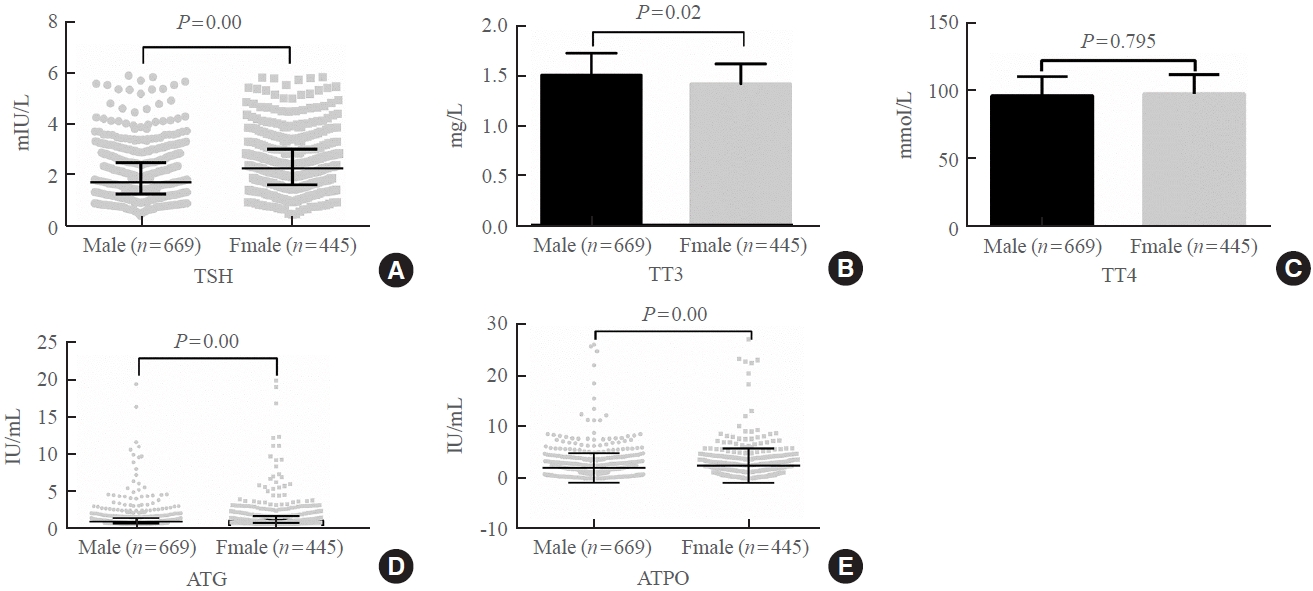
Results
The serum levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), total triiodothyronine (TT3), antithyroglobulin (ATG) antibody, and antithyroid peroxidase (ATPO) antibody levels were significantly correlated with sex (P<0.05). TSH, total thyroxine (TT4), and ATPO levels were significantly correlated with age (P<0.05). The serum levels of TSH, ATG, and ATPO in men were significantly lower than in women; in contrast, the serum TT3 level was significantly higher in men than in women (P<0.05). Serum TSH, TT3, TT4, and ATG levels differed across age groups (P<0.05), but no such variation was observed for ATG levels (P>0.05). The established RIs of TSH, ATG, and ATPO in this study differed between sexes (P<0.05). The thyroid hormone RIs established herein were inconsistent with the manufacturer-provided values.
Conclusion
The RIs of thyroid hormones in the healthy population of Lanzhou were inconsistent with those in the manufacturer’s manual. Validated sex-specific values are required for diagnosing thyroid diseases.

- Thyroid
- The Early Changes in Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulin Bioassay over Anti-Thyroid Drug Treatment Could Predict Prognosis of Graves’ Disease
- Jin Yu, Han-Sang Baek, Chaiho Jeong, Kwanhoon Jo, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Min Hee Kim, Jungmin Lee, Dong-Jun Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):338-346. Published online June 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1664

- 1,682 View
- 100 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To determine whether baseline thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) bioassay or its early response upon treatment with an anti-thyroid drug (ATD) can predict prognosis of Graves’ disease (GD) in real-world practice.
Methods
This retrospective study enrolled GD patients who had previous ATD treatment with TSI bioassay checked at baseline and at follow-up from April 2010 to November 2019 in one referral hospital. The study population were divided into two groups: patients who experienced relapse or continued ATD (relapse/persistence), and patients who experienced no relapse after ATD discontinuation (remission). The slope and area under the curve at 1st year (AUC1yr) of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibodies including TSI bioassay and thyrotropin-binding inhibitory immunoglobulin (TBII) were calculated as differences between baseline and second values divided by time duration (year).
Results
Among enrolled 156 study subjects, 74 (47.4%) had relapse/persistence. Baseline TSI bioassay values did not show significant differences between the two groups. However, the relapse/persistence group showed less decremental TSI bioassay in response to ATD than the remission group (–84.7 [TSI slope, –198.2 to 8.2] vs. –120.1 [TSI slope, –204.4 to –45.9], P=0.026), whereas the TBII slope was not significantly different between the two groups. The relapse/persistence group showed higher AUC1yr of TSI bioassay and TBII in the 1st year during ATD treatment than the remission group (AUC1yr for TSI bioassay, P=0.0125; AUC1yr for TBII,P =0.001).
Conclusion
Early changes in TSI bioassay can better predict prognosis of GD than TBII. Measurement of TSI bioassay at beginning and follow-up could help predict GD prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced predictive validity of integrative models for refractory hyperthyroidism considering baseline and early therapy characteristics: a prospective cohort study
Xinpan Wang, Tiantian Li, Yue Li, Qiuyi Wang, Yun Cai, Zhixiao Wang, Yun Shi, Tao Yang, Xuqin Zheng
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients
Jung-Chi Hsu, Kang-Chih Fan, Ting-Chuan Wang, Shu-Lin Chuang, Ying-Ting Chao, Ting-Tse Lin, Kuan-Chih Huang, Lian-Yu Lin, Lung-Chun Lin
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Enhanced predictive validity of integrative models for refractory hyperthyroidism considering baseline and early therapy characteristics: a prospective cohort study

Review Article
- Thyroid
- Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease during Pregnancy and Postpartum: 2023 Revised Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines
- Hwa Young Ahn, Ka Hee Yi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):289-294. Published online June 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1696
- 6,353 View
- 697 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Thyroid hormone plays a critical role in fetal growth and development, and thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy is associated with several adverse outcomes, such as miscarriage and preterm birth. In this review, we introduce and explain three major changes in the revised Korean Thyroid Association (KTA) guidelines for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy: first, the normal range of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) during pregnancy; second, the treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism; and third, the management of euthyroid pregnant women with positive thyroid autoantibodies. The revised KTA guidelines adopt 4.0 mIU/L as the upper limit of TSH in the first trimester. A TSH level between 4.0 and 10.0 mIU/L, combined with free thyroxine (T4) within the normal range, is defined as subclinical hypothyroidism, and a TSH level over 10 mIU/L is defined as overt hypothyroidism regardless of the free T4 level. Levothyroxine treatment is recommended when the TSH level is higher than 4 mIU/L in subclinical hypothyroidism, regardless of thyroid peroxidase antibody positivity. However, thyroid hormone therapy to prevent miscarriage is not recommended in thyroid autoantibody-positive women with normal thyroid function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Use of thyroid hormones in hypothyroid and euthyroid patients: A survey of members of the Endocrine Society of Australia
Nicole Lafontaine, Suzanne J. Brown, Petros Perros, Enrico Papini, Endre V. Nagy, Roberto Attanasio, Laszlo Hegedüs, John P. Walsh
Clinical Endocrinology.2024; 100(5): 477. CrossRef - Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Focus on Proven Health Effects in the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines
Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 381. CrossRef - Maternal isolated hypothyroxinemia in the first trimester is not associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, except for macrosomia: a prospective cohort study in China
Jing Du, Linong Ji, Xiaomei Zhang, Ning Yuan, Jianbin Sun, Dan Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Use of thyroid hormones in hypothyroid and euthyroid patients: A survey of members of the Endocrine Society of Australia

Letter
- Thyroid
- Thyroid Disorder: A Possible Forgotten Clinical Feature of Monkeypox
- Beuy Joob, Viroj Wiwanitkit
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):285-286. Published online September 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1566
- 21,581 View
- 109 Download
- 1 Web of Science

Image of Interest
- Thyroid
- Propylthiouracil-Induced Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Positive Vasculitis and Agranulocytosis: A Rare Case with Life-Threatening Multiple Systemic Manifestations
- Da Hyun Kang, Mi-Kyung Song, Sang-Hyeon Ju, Song-I Lee, Yea Eun Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):282-284. Published online March 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1643
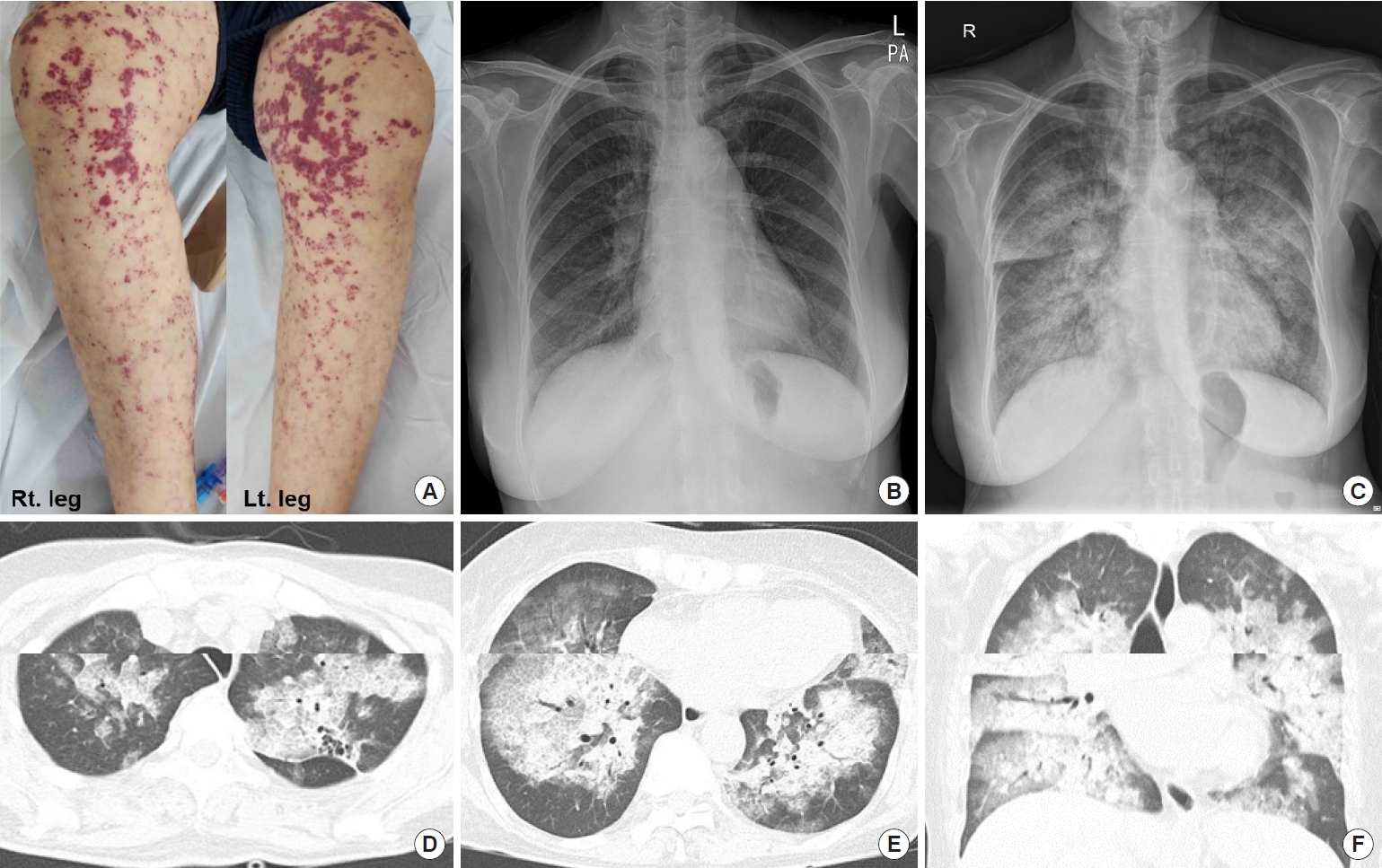
- 1,185 View
- 91 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



