Article category
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Article category
Brief Report
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
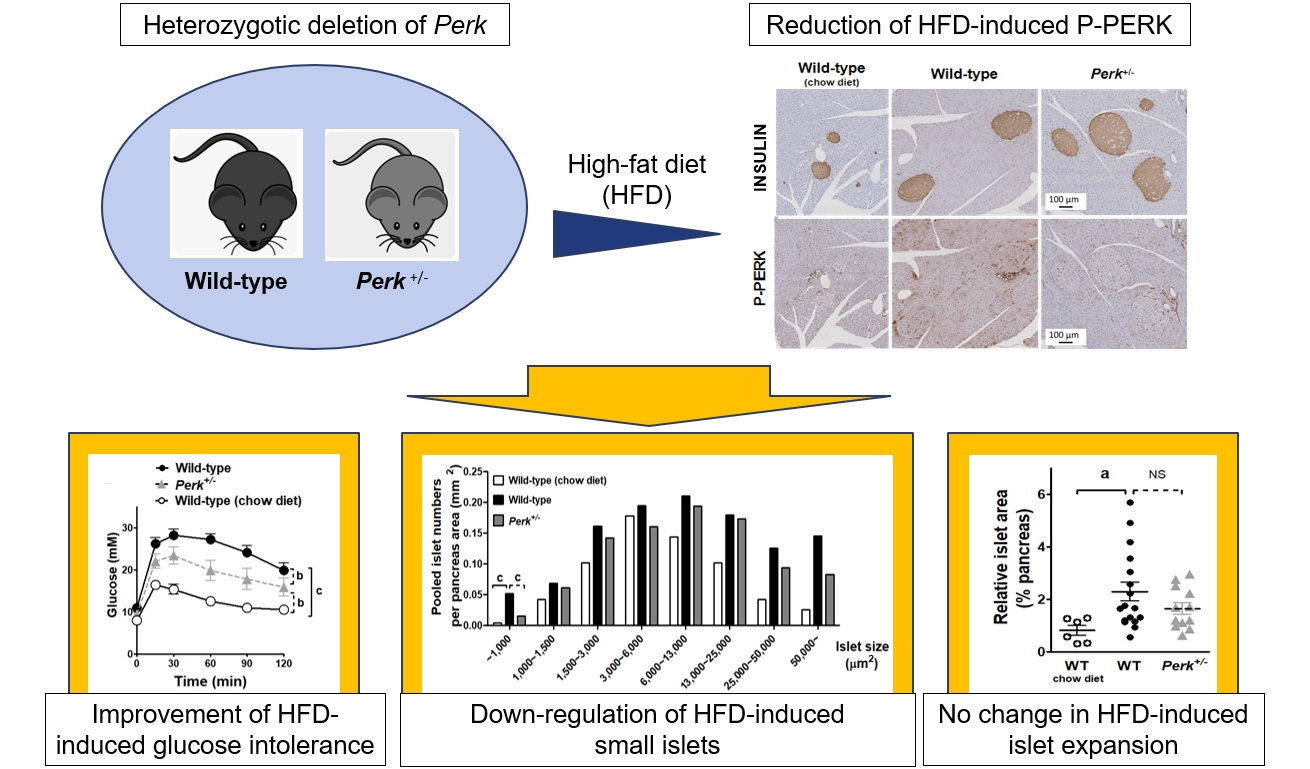
- Partial Deletion of Perk Improved High-Fat Diet-Induced Glucose Intolerance in Mice
- Jooyeop Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seoil Moon, Ji Yoon Lim, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):782-787. Published online November 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1738
- 683 View
- 41 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Although pancreatic endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) is indispensable to beta cells, low-dose PERK inhibitor improved glucose- stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Current study examined if partial deletion of Perk (Perk+/-) recapitulated the effects of PERK inhibitor, on the contrary to the complete deletion. Perk+/- mice and wild-type controls were fed with a high-fat diet (HFD) for 23 weeks. Glucose tolerance was evaluated along with serum insulin levels and islet morphology. Perk+/- mice on normal chow were comparable to wild-type mice in various metabolic features. HFD-induced obesity was not influenced by Perk reduction; however, HFD-induced glucose intolerance was significantly improved since 15-week HFD. HFD-induced compromises in GSIS were relieved by Perk reduction, accompanied by reductions in phosphorylated PERK and activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) in the islets. Meanwhile, HFD-induced islet expansion was not significantly affected. In summary, partial deletion of Perk improved glucose tolerance and GSIS impaired by diet-induced obesity, without changes in body weights or islet mass.

Original Article
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):770-781. Published online November 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1726

- 1,051 View
- 45 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Elevated γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GTP) levels are associated with metabolic syndrome. We investigated the association of cumulative exposure to high γ-GTP with the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in a large-scale population.
Methods
Using nationally representative data from the Korean National Health Insurance system, 1,640,127 people with 4 years of consecutive γ-GTP measurements from 2009 to 2012 were included and followed up until the end of 2019. For each year of the study period, participants were grouped by the number of exposures to the highest γ-GTP quartile (0–4), and the sum of quartiles (0–12) was defined as cumulative γ-GTP exposure. The hazard ratio for CVD was evaluated using the Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
During the 6.4 years of follow-up, there were 15,980 cases (0.97%) of myocardial infarction (MI), 14,563 (0.89%) of stroke, 29,717 (1.81%) of CVD, and 25,916 (1.58%) of death. Persistent exposure to high γ-GTP levels was associated with higher risks of MI, stroke, CVD, and death than those without such exposure. The risks of MI, stroke, CVD, and mortality increased in a dose-dependent manner according to total cumulative γ-GTP (all P for trend <0.0001). Subjects younger than 65 years, with a body mass index <25 kg/m2, and without hypertension or fatty liver showed a stronger relationship between cumulative γ-GTP and the incidence of MI, CVD, and death.
Conclusion
Cumulative γ-GTP elevation is associated with CVD. γ-GTP could be more widely used as an early marker of CVD risk, especially in individuals without traditional CVD risk factors.

Editorial
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Potential of γ-Glutamyl Transferase as a Novel Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease
- Sang Youl Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):667-668. Published online December 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.602
- 784 View
- 36 Download

Original Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
- Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):568-577. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1770

- 1,449 View
- 109 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) has become an important tool for evaluating cardiovascular disease (CVD). This study evaluated the significance of CACS for future CVD through more than 10 years of follow-up in asymptomatic Korean populations with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) known to have a relatively low CACS burden.
Methods
We enrolled 981 asymptomatic T2DM patients without CVD at baseline who underwent CACS evaluation using multidetector computed tomography between January 2008 and December 2014. They were grouped into five predefined CACS categories based on Agatston scores and followed up by August 2020. The primary endpoint was incident CVD events, including coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial disease.
Results
The relative risk of CVD was significantly higher in patients with CACS ≥10, and the significance persisted after adjustment for known confounders. A higher CACS category indicated a higher incidence of future CVD: hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) 4.09 (1.79 to 9.36), 12.00 (5.61 to 25.69), and 38.79 (16.43 to 91.59) for 10≤ CACS <100, 100≤ CACS <400, and CACS ≥400, respectively. During the 12-year follow-up period, the difference in event-free survival more than doubled as the category increased. Patients with CACS below 10 had very low CVD incidence throughout the follow-up. The receiver operating characteristic analysis showed better area under curve when the CACS cutoff was 10 than 100.
Conclusion
CACS can be a sensitive marker of CVD risk. Specifically, CACS above 10 is an indicator of CVD high-risk requiring more intensive medical treatment in Koreans with T2DM.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
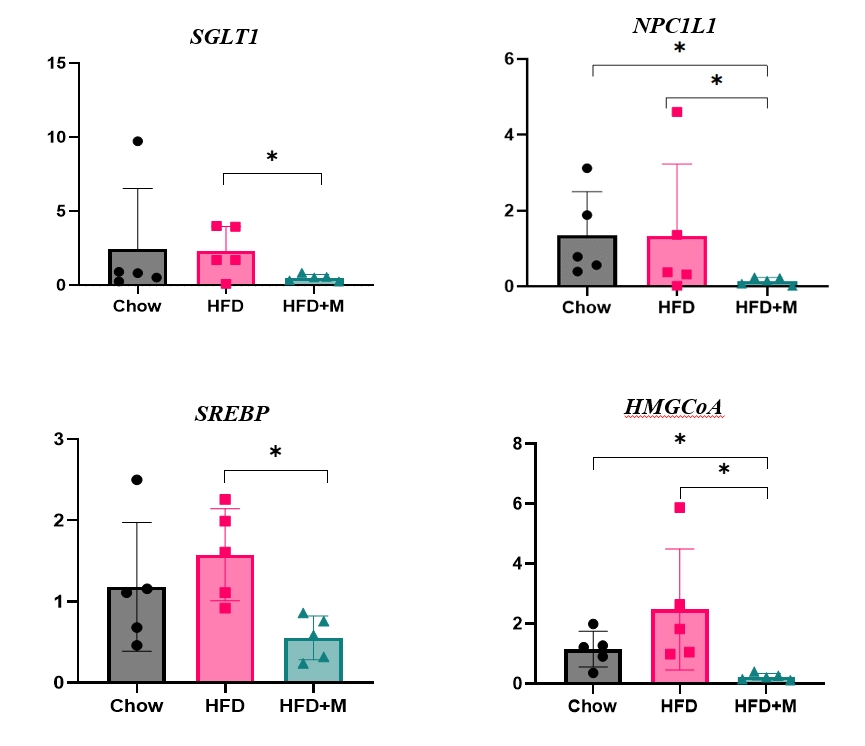
- Protective Effects of Melatonin in High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis via Decreased Intestinal Lipid Absorption and Hepatic Cholesterol Synthesis
- Hyungjune Ku, Yeonji Kim, Alvin Lyle Kim, Garam Lee, Youngsik Choi, Bukyung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):557-567. Published online September 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1672
- 1,875 View
- 91 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The preventative effect of melatonin on the development of obesity and the progression of fatty liver under a high-fat diet (HFD) has been well elucidated through previous studies. We investigated the mechanism behind this effect regarding cholesterol biosynthesis and regulation of cholesterol levels.
Methods
Mice were divided into three groups: normal chow diet (NCD); HFD; and HFD and melatonin administration group (HFD+M). We assessed the serum lipid profile, mRNA expression levels of proteins involved in cholesterol synthesis and reabsorption in the liver and nutrient transporters in the intestines, and cytokine levels. Additionally, an in vitro experiment using HepG2 cells was performed.
Results
Expression of hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP-2), 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR), and low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) demonstrated that melatonin administration significantly reduces hepatic cholesterol synthesis in mice fed an HFD. Expression of intestinal sodium-glucose transporter 1 (SGLT1), glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2), GLUT5, and Niemann-pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) demonstrated that melatonin administration significantly reduces intestinal carbohydrate and lipid absorption in mice fed an HFD. There were no differences in local and circulatory inflammatory cytokine levels among the NCD, HFD, and HFD+M group. HepG2 cells stimulated with palmitate showed reduced levels of SREBP, LDLR, and HMGCR indicating these results are due to the direct mechanistic effect of melatonin on hepatocytes.
Conclusion
Collectively, these data indicate the mechanism behind the protective effects of melatonin from weight gain and liver steatosis under HFD is through a reduction in intestinal caloric absorption and hepatic cholesterol synthesis highlighting its potential in the treatment of obesity and fatty liver disease.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
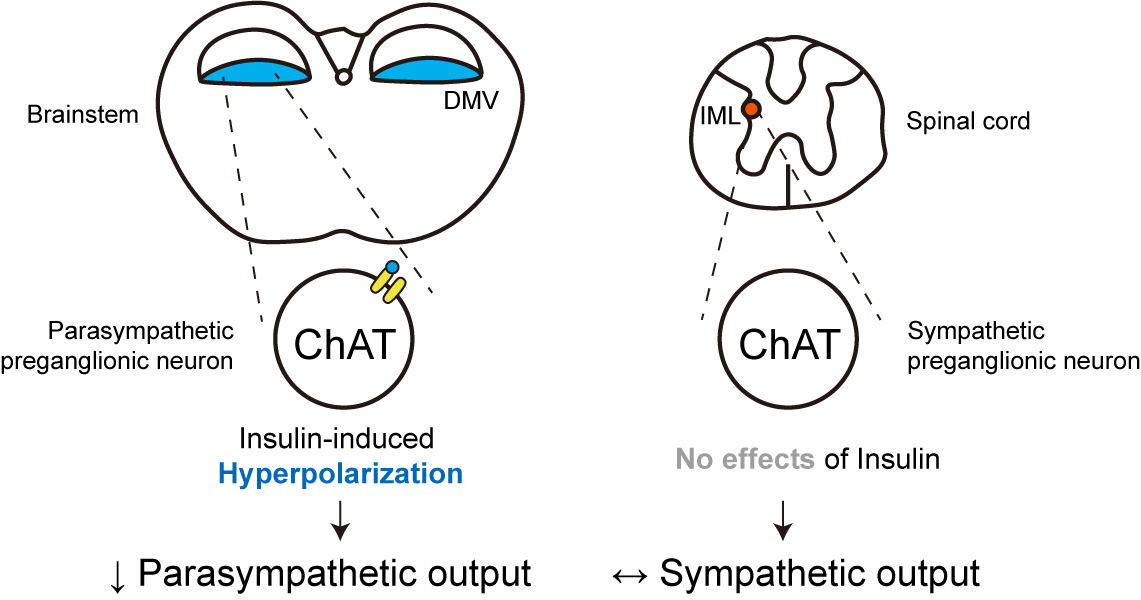
- Insulin Preferentially Regulates the Activity of Parasympathetic Preganglionic Neurons over Sympathetic Preganglionic Neurons
- Uisu Hyun, Yoon Young Kweon, Jong-Woo Sohn
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):545-556. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1725
- 1,324 View
- 74 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Insulin is a peptide hormone that regulates post-prandial physiology, and it is well known that insulin controls homeostasis at least in part via the central nervous system. In particular, insulin alters the activity of neurons within the autonomic nervous system. However, currently available data are mostly from unidentified brainstem neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (DMV).
Methods
In this study, we used several genetically engineered mouse models to label distinct populations of neurons within the brainstem and the spinal cord for whole-cell patch clamp recordings and to assess several in vivo metabolic functions.
Results
We first confirmed that insulin directly inhibited cholinergic (parasympathetic preganglionic) neurons in the DMV. We also found inhibitory effects of insulin on both the excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic currents recorded in DMV cholinergic neurons. In addition, GABAergic neurons of the DMV and nucleus tractus solitarius were inhibited by insulin. However, insulin had no effects on the cholinergic sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the spinal cord. Finally, we obtained results suggesting that the insulininduced inhibition of parasympathetic preganglionic neurons may not play a critical role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis and gastrointestinal motility.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that insulin inhibits parasympathetic neuronal circuitry in the brainstem, while not affecting sympathetic neuronal activity in the spinal cord.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
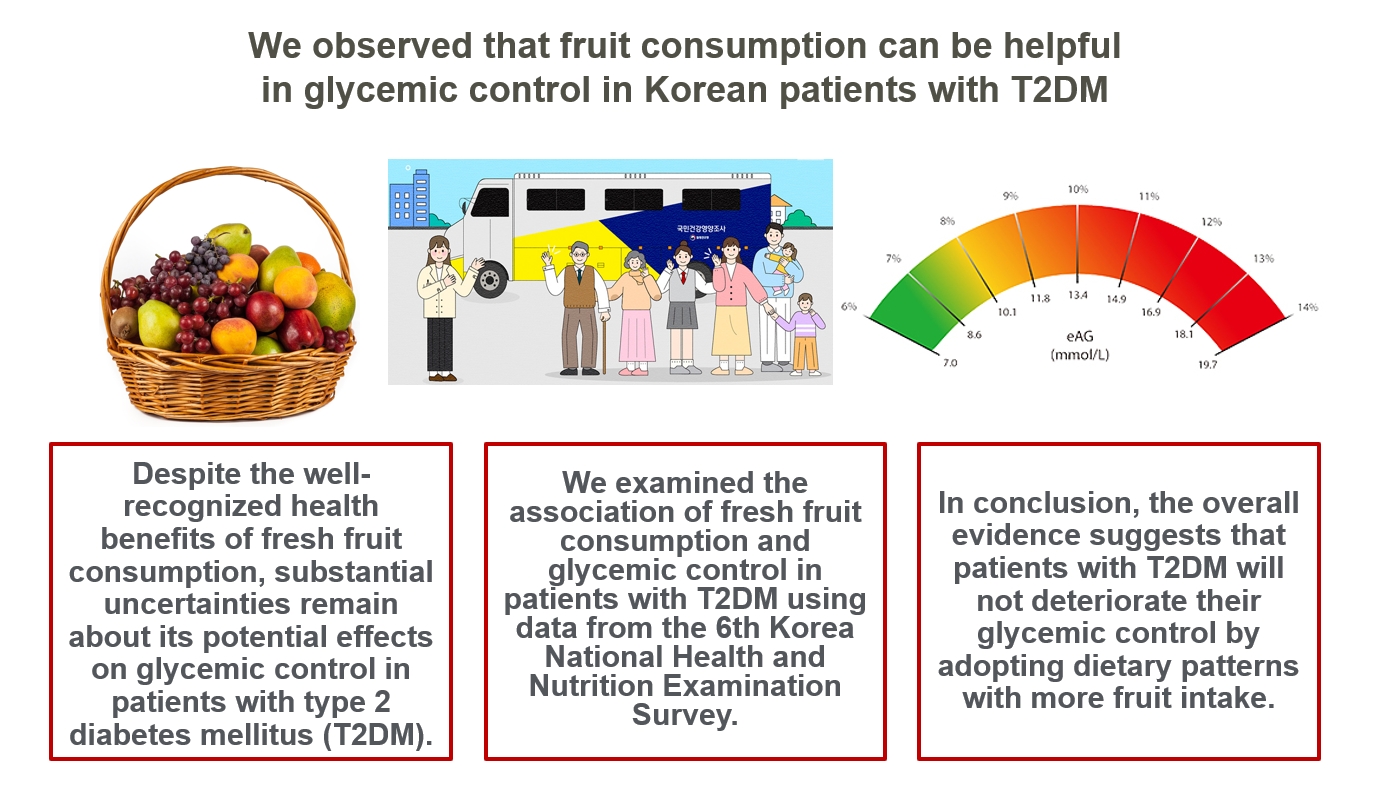
- Intake of Fruit and Glycemic Control in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Eunju Yoon, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):538-544. Published online August 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1730
- 1,850 View
- 108 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Despite the well-recognized health benefits of fresh fruit consumption, there is still substantial uncertainty about its potential effects on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We examined the association of fresh fruit consumption and glycemic control in patients with T2DM using data from the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The study sample was divided into three groups based on weekly fruit consumption frequency for the analysis.
Results
Patients with the highest fruit intake were older than those in the other two groups, and women were more likely to consume fruits in general. Being a current smoker and weekly alcohol intake also showed negative correlations according to the fruit intake tertiles. Fruit consumption was positively correlated with better hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels. Moreover, patients in the highest tertile of fruit intake were 3.48 times more likely to be in good glycemic control defined as HbA1c <7%.
Conclusion
We observed that fruit consumption can be helpful in glycemic control in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship between Alcohol Consumption and Diabetes in Korean Adults
Gi Tae Kim, Jae Woong Sull
Biomedical Science Letters.2023; 29(3): 159. CrossRef
- The Relationship between Alcohol Consumption and Diabetes in Korean Adults

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
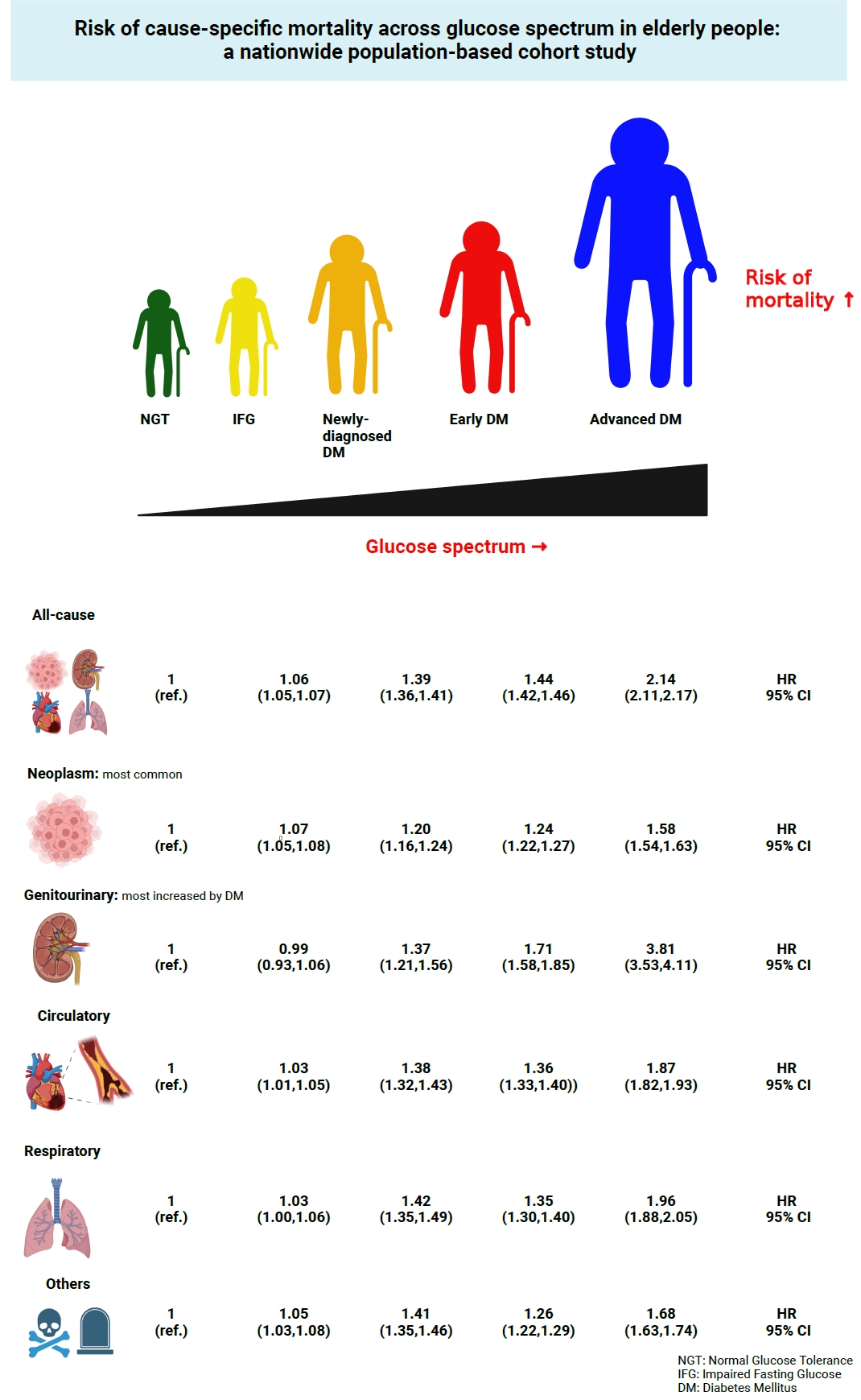
- Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Committee of Big Data, Korean Endocrine Society
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):525-537. Published online September 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1765
- 1,526 View
- 88 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the risk of cause-specific mortality according to glucose tolerance status in elderly South Koreans.
Methods
A total of 1,292,264 individuals aged ≥65 years who received health examinations in 2009 were identified from the National Health Information Database. Participants were classified as normal glucose tolerance, impaired fasting glucose, newly-diagnosed diabetes, early diabetes (oral hypoglycemic agents ≤2), or advanced diabetes (oral hypoglycemic agents ≥3 or insulin). The risk of system-specific and disease-specific deaths was estimated using multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis.
Results
During a median follow-up of 8.41 years, 257,356 deaths were recorded. Diabetes was associated with significantly higher risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 1.58; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.57 to 1.60); death due to circulatory (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.46 to 1.52), respiratory (HR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.47 to 1.55), and genitourinary systems (HR, 2.22; 95% CI, 2.10 to 2.35); and neoplasms (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.28 to 1.32). Diabetes was also associated with a significantly higher risk of death due to ischemic heart disease (HR, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.63 to 1.76), cerebrovascular disease (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.41 to 1.50), pneumonia (HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.63 to 1.76), and acute or chronic kidney disease (HR, 2.23; 95% CI, 2.09 to 2.38). There was a stepwise increase in the risk of death across the glucose spectrum (P for trend <0.0001). Stroke, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease increased the risk of all-cause mortality at every stage of glucose intolerance.
Conclusion
A dose-dependent association between the risk of mortality from various causes and severity of glucose tolerance was noted in the elderly population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef
- The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population

Editorial
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
- Sunghwan Suh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):522-524. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.502
- 789 View
- 47 Download

Review Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
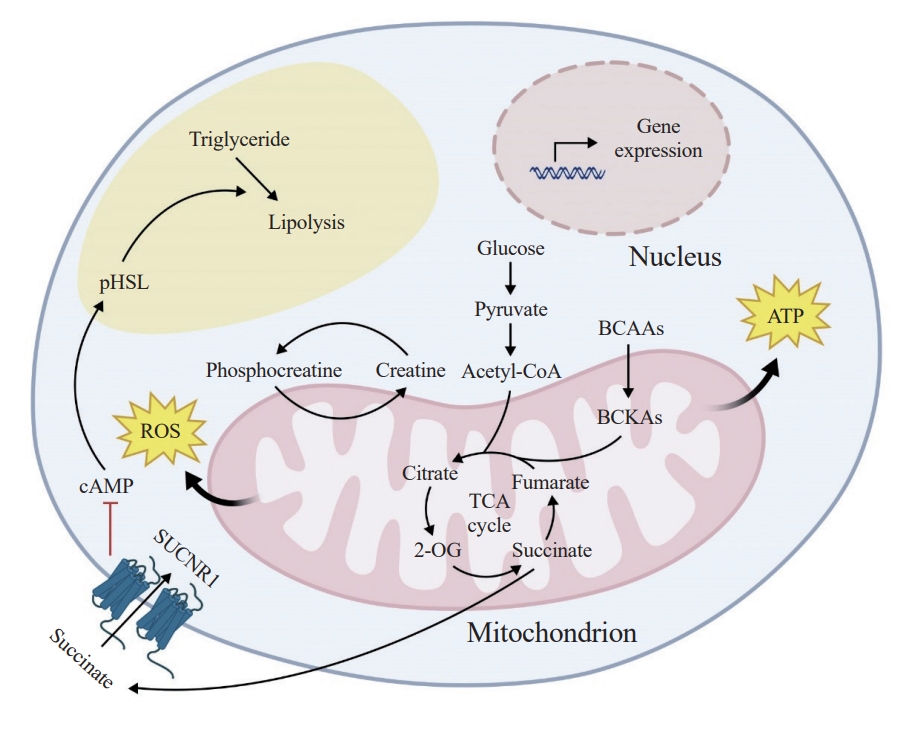
- The Emerging Importance of Mitochondria in White Adipocytes: Neither Last nor Least
- Juan Cai, Fenfen Wang, Mengle Shao
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):493-503. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1813
- 1,826 View
- 89 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The growing recognition of mitochondria’s crucial role in the regulation of white adipose tissue remodeling and energy balance underscores its significance. The marked metabolic diversity of mitochondria provides the molecular and cellular foundation for enabling adipose tissue plasticity in response to various metabolic cues. Effective control of mitochondrial function at the cellular level, not only in thermogenic brown and beige adipocytes but also in energy-storing white adipocytes, exerts a profound influence on adipose homeostasis. Furthermore, mitochondria play a pivotal role in intercellular communication within adipose tissue via production of metabolites with signaling properties. A more comprehensive understanding of mitochondrial regulation within white adipocytes will empower the development of targeted and efficacious strategies to enhance adipose function, leading to advancements in overall metabolic health.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
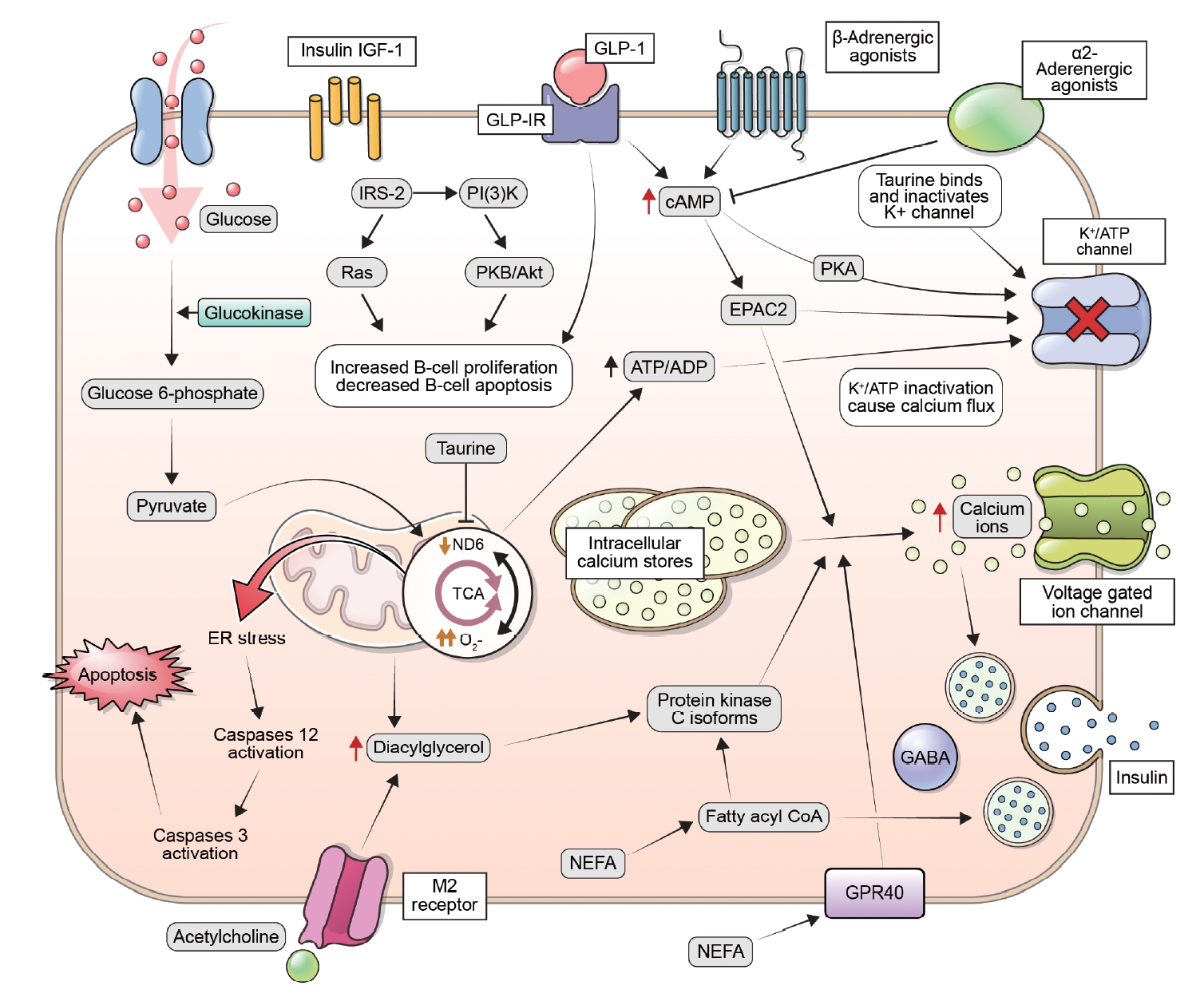
- The Impact of Taurine on Obesity-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms Underlying Its Effect
- Kainat Ahmed, Ha-Neul Choi, Jung-Eun Yim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):482-492. Published online October 17, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1776
- 2,416 View
- 148 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This review explores the potential benefits of taurine in ameliorating the metabolic disorders of obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D), highlighting the factors that bridge these associations. Relevant articles and studies were reviewed to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between obesity and the development of T2D and the effect of taurine on those conditions. The loss of normal β-cell function and development of T2D are associated with obesity-derived insulin resistance. The occurrence of diabetes has been linked to the low bioavailability of taurine, which plays critical roles in normal β-cell function, anti-oxidation, and anti-inflammation. The relationships among obesity, insulin resistance, β-cell dysfunction, and T2D are complex and intertwined. Taurine may play a role in ameliorating these metabolic disorders through different pathways, but further research is needed to fully understand its effects and potential as a therapeutic intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of a Very Low-Calorie Diet on Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory and Metabolomic Profile in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Subjects
Neus Bosch-Sierra, Carmen Grau-del Valle, Christian Salom, Begoña Zaragoza-Villena, Laura Perea-Galera, Rosa Falcón-Tapiador, Susana Rovira-Llopis, Carlos Morillas, Daniel Monleón, Celia Bañuls
Antioxidants.2024; 13(3): 302. CrossRef
- Effect of a Very Low-Calorie Diet on Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory and Metabolomic Profile in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Subjects

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):472-481. Published online October 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1805

- 2,477 View
- 206 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Previous studies have consistently demonstrated the positive effects of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) on glycemic outcomes and complications of diabetes in people with type 1 diabetes. Guidelines now consider CGM to be an essential and cost-effective device for managing type 1 diabetes. As a result, insurance coverage for it is available. Evidence supporting CGM continues to grow and expand to broader populations, such as pregnant people with type 1 diabetes, people with type 2 diabetes treated only with basal insulin therapy, and even type 2 diabetes that does not require insulin treatment. However, despite the significant risk of hyperglycemia in pregnancy, which leads to complications in more than half of affected newborns, CGM indications and insurance coverage for those patients are unresolved. In this review article, we discuss the latest evidence for using CGM to offer glycemic control and reduce perinatal complications, along with its cost-effectiveness in pregestational type 1 and type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus. In addition, we discuss future prospects for CGM coverage and indications based on this evidence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
Mohammad Mansour, M. Saeed Darweesh, Ahmed Soltan
Alexandria Engineering Journal.2024; 89: 224. CrossRef
- Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends

Original Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
- Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):426-435. Published online July 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1737

- 2,041 View
- 131 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The effects of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors over the course of long-term treatment remain unclear, and concerns have been raised regarding the role of DPP-4 inhibitors in carcinogenesis in the pancreas. Earlier studies of pancreatic adverse events have reported conflicting results.
Methods
This study analyzed Korean National Health Insurance Service data from January 2009 to December 2012. Patients who had type 2 diabetes mellitus and took two or more oral glucose-lowering drugs (GLDs) were included. Patients prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors (n=51,482) or other GLDs (n=51,482) were matched at a 1:1 ratio using propensity score matching. The risk of pancreatic cancer was calculated using Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional-hazards regression analysis.
Results
During a median follow-up period of 7.95 years, 1,051 new cases of pancreatic cancer were identified. The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for DPP-4 inhibitor use was 0.99 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.88 to 1.12) compared with the other GLD group. In an analysis limited to cases diagnosed with pancreatic cancer during hospitalization, the adjusted HR for the use of DPP-4 inhibitors was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.86 to 1.17) compared with patients who took other GLDs. Using the other GLD group as the reference group, no trend was observed for elevated pancreatic cancer risk with increased DPP-4 inhibitor exposure.
Conclusion
In this population-based cohort study, DPP-4 inhibitor use over the course of relatively long-term follow-up showed no significant association with an elevated risk of pancreatic cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
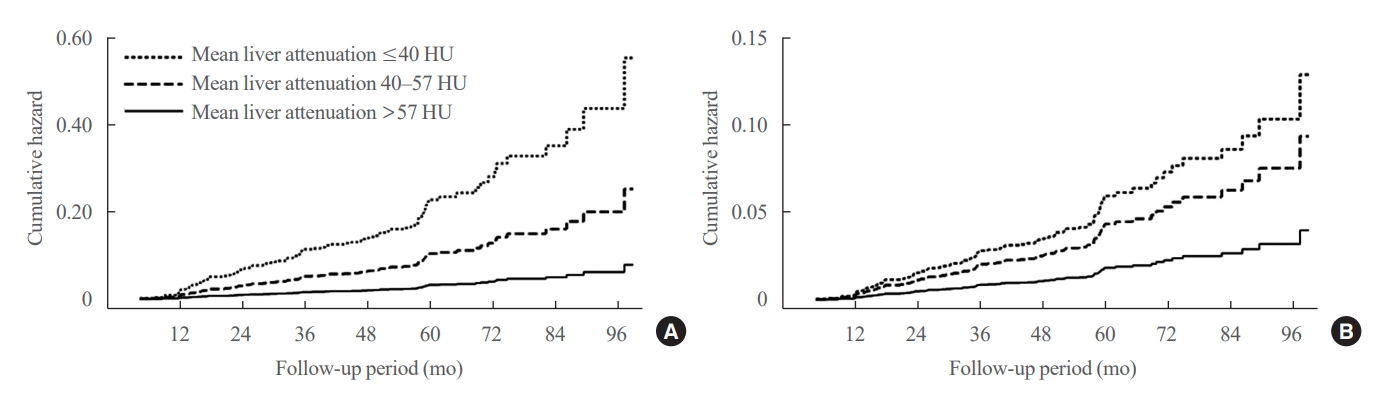
- Greater Severity of Steatosis Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Incident Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study
- Ji Min Han, Jung Hwan Cho, Hye In Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Yu-Ji Lee, Jung Won Lee, Kwang Min Kim, Ji Cheol Bae
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):418-425. Published online July 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1729
- 1,025 View
- 74 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Fatty liver is associated with increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. We aimed to evaluate whether the severity of hepatic steatosis is associated with incident diabetes.
Methods
We conducted a longitudinal analysis using data from 1,798 participants who underwent a comprehensive health checkup and abdominal computed tomography (CT). We assessed the association between baseline liver attenuation value on non-contrast CT images and risk of incident diabetes. All the participants were categorized into three groups based on the baseline liver attenuation value on non-contrast CT images: without hepatic steatosis (>57 Hounsfield unit [HU]), mild hepatic steatosis (41–57 HU), and moderate to severe hepatic steatosis (≤40 HU).
Results
During a median follow-up period of 5 years, 6.0% of the study participants progressed to diabetes. The incidence of diabetes was 17.3% in the moderate to severe hepatic steatosis group, 9.0% in the mild steatosis group, and 2.9% in those without hepatic steatosis. In a multivariate adjustment model, as compared with participants without hepatic steatosis, those with moderate to severe steatosis had a hazard ratio (HR) of 3.24 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.64 to 4.2) for the development of diabetes, and those in the mild steatosis group had a HR of 2.33 (95% CI, 1.42 to 3.80). One standard deviation decrease in mean CT attenuation values of the liver was associated with a 40% increase in the development of diabetes (multivariate adjusted HR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.2 to 1.63).
Conclusion
We found a positive association between severity of hepatic steatosis and risk of incident diabetes. Greater severity of steatosis was associated with a higher risk of incident diabetes.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Future Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A 16-Year Follow-up in a Prospective, Community-Dwelling Cohort Study
- Joon Ho Moon, Yongkang Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H. Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):406-417. Published online August 3, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1703

- 2,554 View
- 160 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
While the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is a measure of insulin resistance, its association with cardiovascular disease (CVD) has not been well elucidated. We evaluated the TyG index for prediction of CVDs in a prospective large communitybased cohort.
Methods
Individuals 40 to 70 years old were prospectively followed for a median 15.6 years. The TyG index was calculated as the Ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL)×fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2]. CVDs included any acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular disease. We used a Cox proportional hazards model to estimate CVD risks according to quartiles of the TyG index and plotted the receiver operating characteristics curve for the incident CVD.
Results
Among 8,511 subjects (age 51.9±8.8 years; 47.5% males), 931 (10.9%) had incident CVDs during the follow-up. After adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, total cholesterol, smoking, alcohol, exercise, and C-reactive protein, subjects in the highest TyG quartile had 36% increased risk of incident CVD compared with the lowest TyG quartile (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% confidence interval, 1.10 to 1.68). Carotid plaque, assessed by ultrasonography was more frequent in subjects in the higher quartile of TyG index (P for trend=0.049 in men and P for trend <0.001 in women). The TyG index had a higher predictive power for CVDs than the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (area under the curve, 0.578 for TyG and 0.543 for HOMA-IR). Adding TyG index on diabetes or hypertension alone gave sounder predictability for CVDs.
Conclusion
The TyG index is independently associated with future CVDs in 16 years of follow-up in large, prospective Korean cohort. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kaisheng Yuan, Bing Wu, Ruiqi Zeng, Fuqing Zhou, Ruixiang Hu, Cunchuan Wang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 169. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride glucose index and chronic total coronary occlusion: A cross-sectional study from southwest China
Kaiyong Xiao, Huili Cao, Bin Yang, Zhe Xv, Lian Xiao, Jianping Wang, Shuiqing Ni, Hui Feng, Zhongwei He, Lei Xv, Juan Li, Dongmei Xv
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(4): 850. CrossRef - The association between TyG and all-cause/non-cardiovascular mortality in general patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is modified by age: results from the cohort study of NHANES 1999–2018
Younan Yao, Bo Wang, Tian Geng, Jiyan Chen, Wan Chen, Liwen Li
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Evaluation of the novel three lipid indices for predicting five- and ten-year incidence of cardiovascular disease: findings from Kerman coronary artery disease risk factors study (KERCADRS)
Alireza Jafari, Hamid Najafipour, Mitra Shadkam, Sina Aminizadeh
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



